Three Types of Muscle Tissue (Skeletal, Smooth, Cardiac) Anatomy Compilation Review
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Ben from registerednessrn.com explores the three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscles are voluntary, attach to bones, and facilitate movement. Cardiac muscle, found only in the heart, is involuntary and characterized by striations and intercalated discs for synchronized contraction. Smooth muscle, found throughout the body, is involuntary, lacks striations, and varies in structure and function depending on its location, such as in the digestive system or blood vessels.
Takeaways
- 💪 Skeletal muscle tissue attaches to bones and is responsible for voluntary movement, posture support, and heat production.
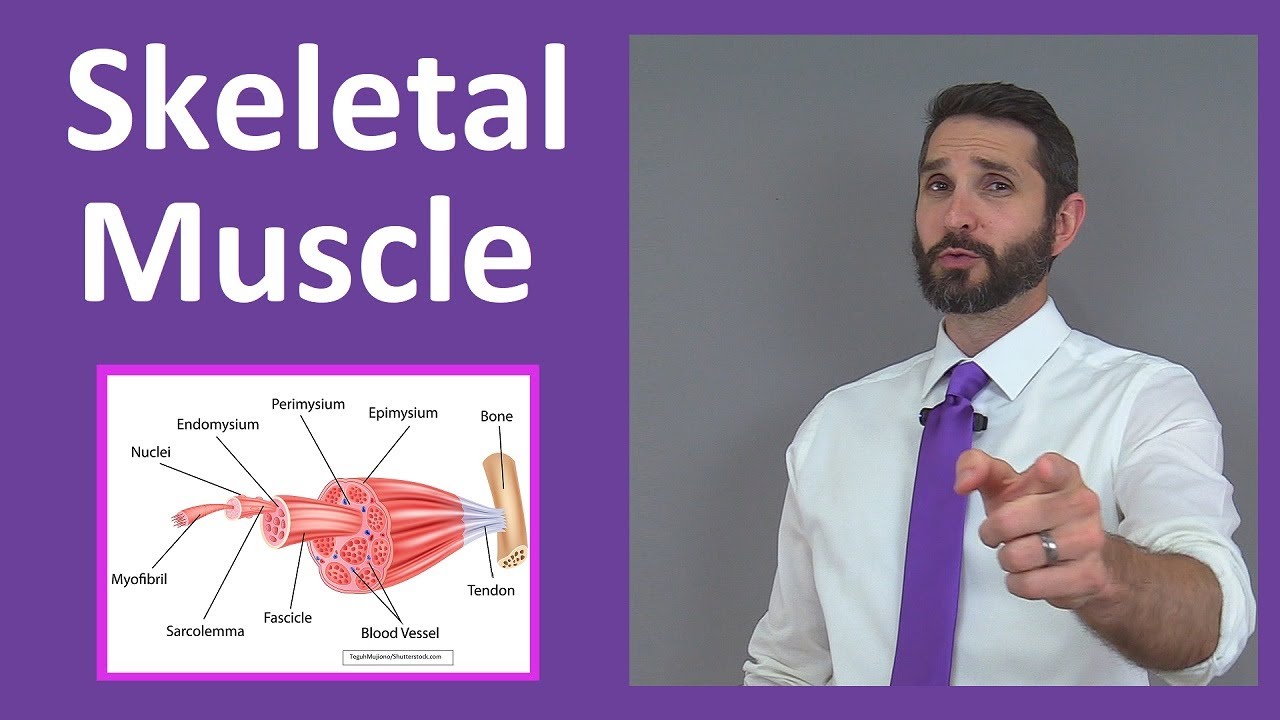
- 🦴 Skeletal muscles are composed of connective tissue layers, muscle fibers, blood vessels, and nerves, and they attach to bones via tendons.
- 🔬 The structure of skeletal muscle includes the epimysium, perimysium, endomysium, and muscle fibers with myofibrils and sarcomeres.
- 🏋️♂️ Skeletal muscle contraction occurs through the sliding of actin and myosin filaments within sarcomeres, causing the muscle to shorten.
- ❤️ Cardiac muscle tissue is found only in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
- 🔴 Cardiac muscle cells, or cardiomyocytes, are interconnected by intercalated discs, which allow for synchronized contractions.
- 🌀 Cardiac muscle tissue is involuntary, controlled by the autonomic nervous system, unlike skeletal muscle which is voluntary.
- 🔄 Smooth muscle tissue is located throughout the body, including the skin, reproductive, respiratory, and urinary systems, and in hollow organs and blood vessels.
- 🟦 Smooth muscle has a fusiform shape, lacks sarcomeres and striations, and is controlled involuntarily by the autonomic nervous system.
- 🔗 Smooth muscle contraction is initiated by calcium ions and involves the interaction of actin and myosin filaments, similar to other muscle types but without organized sarcomeres.
- 🔑 There are two subtypes of smooth muscle: single-unit (unitary) and multi-unit, which differ in their innervation and activation by nerve fibers.
Q & A
What are the three types of muscle tissue discussed in the video?
-The three types of muscle tissue discussed in the video are skeletal muscle tissue, cardiac muscle tissue, and smooth muscle tissue.
How do skeletal muscles differ from the other two types of muscle tissue?
-Skeletal muscles differ from the other two types of muscle tissue in that they attach to bones, contract on a voluntary basis via the somatic nervous system, and serve functions such as supporting posture, protecting organs, and producing heat.
What is the primary function of skeletal muscle tissue?
-The primary function of skeletal muscle tissue is to facilitate movement by contracting and relaxing, allowing voluntary body movement.
What is the structure of a sarcomere, and what is its role in muscle contraction?
-A sarcomere is the repeating unit within a myofibril that is responsible for muscle contraction. It contains thin actin filaments and thick myosin filaments that slide past each other during contraction, causing the sarcomere to shorten.
What is unique about the location and function of cardiac muscle tissue?
-Cardiac muscle tissue is unique in that it is only found in the heart. Its function is to contract in a rhythmic motion to pump blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients.
How do cardiac muscle cells differ structurally from skeletal muscle cells?
-Cardiac muscle cells, or cardiomyocytes, are irregularly shaped and branched, contain one or two centrally located nuclei, and are connected by intercalated discs, which are absent in skeletal muscle tissue.
What is the significance of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle tissue?
-Intercalated discs are significant in cardiac muscle tissue as they form an interlocking connection between individual cardiac cells, allowing for the rapid passage of electrical signals, which results in synchronized contraction of the heart.
Where is smooth muscle tissue typically located in the body?
-Smooth muscle tissue is found throughout the body, including in the skin, reproductive, respiratory, and urinary systems, as well as in hollow organs like the intestines, bladder, uterus, and stomach.
How does the structure of smooth muscle tissue differ from that of skeletal and cardiac muscle tissue?
-Smooth muscle tissue lacks organized sarcomeres and myofibrils, which are present in both skeletal and cardiac muscle tissue. It also does not have the striated appearance due to the absence of these structures.
What is the difference between single-unit and multi-unit smooth muscle?
-Single-unit smooth muscle is innervated by few nerve fibers and can contract an entire sheet of muscle cells simultaneously due to gap junctions, while multi-unit smooth muscle requires multiple nerve fibers as it has fewer gap junctions, and each cell needs its own electrical impulse to contract.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)