Harmonic Sequence
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the concept of harmonic sequences is explored through definition, illustration, and problem-solving. A harmonic sequence is defined as one where the reciprocals of its terms form an arithmetic sequence. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to identify harmonic sequences and calculate specific terms, such as finding the 21st term of a given sequence. The video also explains how to determine the harmonic mean between two numbers by creating an arithmetic sequence from their reciprocals. The key takeaway is that a sequence is harmonic only if the sequence of its reciprocals is arithmetic.
Takeaways
- 🔢 A harmonic sequence is defined by the property that the reciprocals of its terms form an arithmetic sequence.
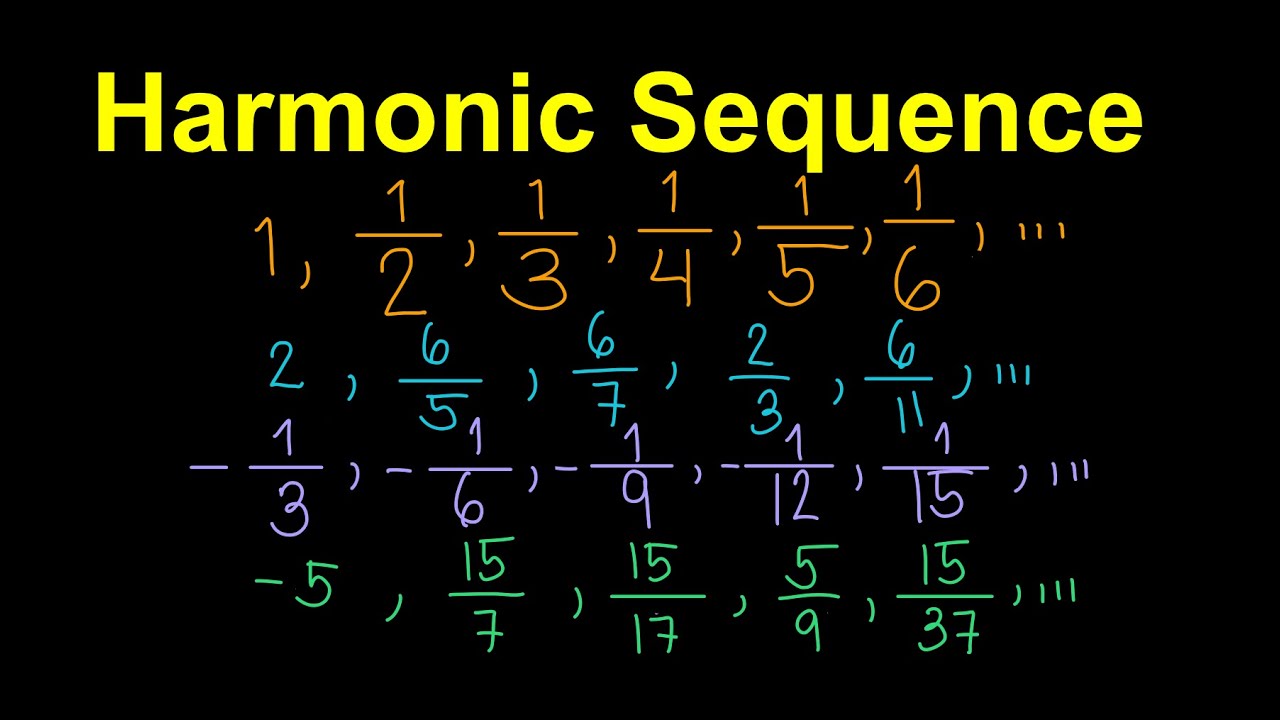
- 🌐 The example given for a harmonic sequence includes terms like 1/4, 1/7, 1/10, 1/13, 1/16, where the reciprocals (4, 7, 10, 13, 16) form an arithmetic sequence with a common difference of 3.
- 🔄 To determine if a sequence is harmonic, check if the sequence of reciprocals is arithmetic.
- 📝 Another example sequence, 3/5, 3/7, 1/3, 3/11, 3/13, is confirmed harmonic because the sequence of reciprocals (5/3, 7/3, 3, 11/3, 13/3) is arithmetic with a common difference of 2/3.
- 🧮 The formula to find the nth term of an arithmetic sequence is used to determine the terms of the harmonic sequence: \( a_n = a_1 + (n - 1) \times d \).
- 📉 The third example sequence, 1/3, 1/10, 1/17, 1/24, 1/31, is shown to be harmonic, and the formula is applied to find the 21st term, which is 1/143.
- 🔍 The harmonic mean between two numbers is found by creating an arithmetic sequence from the reciprocals of the numbers and then finding the reciprocal of the middle term.
- 🤔 The script emphasizes that if the sequence of reciprocals is not arithmetic, then the original sequence is not harmonic.
- 📚 The video concludes with a reminder of the importance of the arithmetic nature of reciprocal sequences in defining harmonic sequences.
- 👋 The video ends with a thank you note, inviting viewers to engage with the content and signaling the end of the educational session.
Q & A
What is a harmonic sequence?
-A harmonic sequence is a sequence where the reciprocals of the terms form an arithmetic sequence.
How is the arithmetic sequence related to a harmonic sequence?
-The arithmetic sequence is related to a harmonic sequence by the property that the differences between the reciprocals of consecutive terms in the harmonic sequence are constant, which is characteristic of an arithmetic sequence.
What is an example of a harmonic sequence given in the script?
-An example of a harmonic sequence given in the script is 1/4, 1/7, 1/10, 1/13, 1/16, and so on, where the reciprocals 4, 7, 10, 13, 16 form an arithmetic sequence with a common difference of 3.
How can you determine if a sequence is harmonic by checking its reciprocals?
-To determine if a sequence is harmonic, you check if the sequence formed by the reciprocals of its terms is an arithmetic sequence, meaning there is a constant difference between consecutive terms.
What is the formula used to find the nth term of an arithmetic sequence?
-The formula used to find the nth term of an arithmetic sequence is 'a_n = a_1 + (n - 1) × d', where 'a_n' is the nth term, 'a_1' is the first term, and 'd' is the common difference.
How do you find the 21st term of a harmonic sequence when given the first term of its corresponding arithmetic sequence?
-To find the 21st term of a harmonic sequence, first determine the 21st term of the corresponding arithmetic sequence using the formula 'a_{21} = a_1 + (21 - 1) × d', then take the reciprocal of that term to get the harmonic sequence term.
What is the harmonic mean between two numbers?
-The harmonic mean between two numbers is the reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of their reciprocals. It is calculated by taking the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the two numbers, divided by 2.
How do you calculate the common difference of an arithmetic sequence if you know the first and third terms?
-To calculate the common difference of an arithmetic sequence when you know the first and third terms, subtract the first term from the third term and divide by the difference in their positions (which is 2 in this case).
What is the significance of the common difference in determining if a sequence is harmonic?
-The common difference in the arithmetic sequence formed by the reciprocals of a harmonic sequence is significant because it confirms the constant rate of change between consecutive terms, which is a defining characteristic of both arithmetic and harmonic sequences.
Why is it important to ensure the sequence formed by the reciprocals is arithmetic before declaring a sequence harmonic?
-It is important to ensure the sequence formed by the reciprocals is arithmetic before declaring a sequence harmonic because the definition of a harmonic sequence relies on this property. If the reciprocals do not form an arithmetic sequence, the original sequence cannot be harmonic.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Harmonic Sequence (Tagalog/Filipino Math)

Curso completo de Raciocínio Lógico para Concursos Públicos 2019 Aula 14

Matematika SMA - Barisan dan Deret (1) - Barisan Aritmatika, Rumus Barisan Aritmatika (A)

HARMONIC SEQUENCE | GRADE 10 MATHEMATICS Q1
Tali Busur Lingkaran - Matematika SMA Kelas XI Kurikulum Merdeka

Berpikir Komputasional - Informatika Kelas XI
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
