Layers of the Earth—What are they? How were they found? (Educational)
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the discovery and understanding of Earth's layered structure, from the crust to the core, using seismic wave data from earthquakes. It explains how scientists determined the Earth's composition and boundaries, comparing the layers to an egg for scale. The script also touches on the role of plate tectonics, the mantle's ductility, and the core's density and magnetic field generation, highlighting the importance of Earth's internal heat in driving geological phenomena.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Our understanding of Earth's interior comes from studying earthquakes.
- 📏 Five centuries ago, Earth was thought to be a uniform sphere, but Newton later proposed a denser interior.
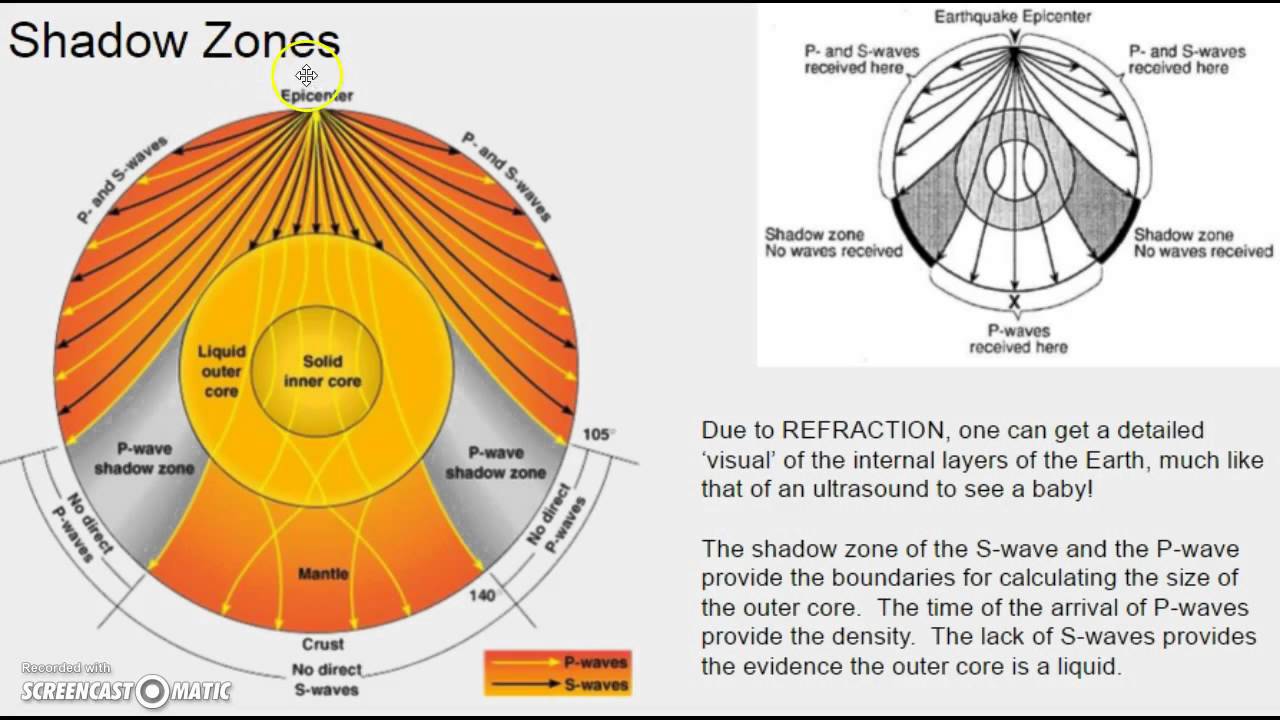
- 🔍 Seismic waves from earthquakes allow scientists to 'see' deep into Earth's layers.
- 🥚 Earth is composed of three main layers: crust, mantle, and core, analogous to an egg's shell, white, and yolk.
- 🌋 Seismic waves reflect and refract at boundaries due to changes in composition, density, and temperature.
- 💻 Advances in computer technology aid in refining our knowledge of Earth's interior structure.
- 🧪 The crust is made of eight major elements and varies in thickness from 5-10 km to 75 km.
- 🌐 The mantle is composed of the same elements as the crust but in different proportions, with a thickness of about 2,900 km.
- 🔥 The core is nearly twice as dense as the mantle and consists of a liquid outer core and a solid inner core.
- 🌏 Plate tectonics is driven by convection currents in the mantle, which cause earthquakes and volcanic activity.
Q & A
How have scientists gained knowledge about Earth's interior?
-Scientists have gained knowledge about Earth's interior by monitoring earthquakes and analyzing the travel times of seismic waves to worldwide stations, which helps them understand the boundaries and composition of Earth's layers.
What was the historical belief about Earth's structure before the scientific method was applied?
-Five centuries ago, the world believed that Earth was a sphere made of uniform rock throughout.
What contribution did Sir Isaac Newton make to our understanding of Earth's interior?
-Sir Isaac Newton calculated that the interior of the Earth must be made of far denser material than the surface rock, and his estimate of the Earth's overall density remains essentially unchanged today.
How did the discovery of using earthquake data impact the study of Earth's layers?
-The discovery allowed scientists to use seismic waves from earthquakes as a method for looking deep beneath the surface, leading to the determination of Earth's three-layer structure based on chemical composition.
What are the three main layers of Earth, and how are they analogous to an egg?
-The three main layers of Earth are the crust, mantle, and core. They can be compared to an egg, with the shell representing the crust, the white the mantle, and the yolk the core.
How do seismic waves help in determining the location of Earth's layers?
-Seismic waves travel in all directions from an earthquake's hypocenter. The changes in composition, density, and temperature cause these waves to reflect and refract along boundaries, revealing the locations of different layers.
What are the main elements that make up the Earth's crust, and how does its thickness vary?
-The crust is made chiefly of oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium. Its thickness ranges from 5–10 kilometers in the oceanic crust to up to 75 kilometers in the continental crust.
What is the difference between the crust and tectonic plates?
-The crust is the outermost layer of Earth and is part of the tectonic plates. Tectonic plates include both the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle, forming a rigid layer known as the lithosphere.
What is the composition and structure of the mantle?
-The mantle is composed of the same elements as the crust but in different proportions, with heavier elements increasing with depth. It is 2,900 km thick with little chemical variation but distinct physical variations due to temperature and pressure differences.
How is the Earth's core different from the egg yolk analogy?
-Unlike the egg yolk analogy, Earth's core is made up of two distinct parts: the liquid outer core and a solid inner core. The inner core is hotter but under greater pressure, which changes the material from liquid to solid.
What is the role of the asthenosphere in relation to the lithosphere?
-The asthenosphere is a ductile zone in the upper mantle where the right combination of heat and pressure allows the material to be more plastic and malleable. It lies beneath the brittle uppermost mantle and the overlying crust, which together form the lithosphere.
How do convection currents contribute to plate tectonics?
-Convection currents, driven by temperature, pressure, and gravity, provide the mechanism for plate tectonics. They cause the lithospheric plates to move, leading to geological phenomena such as earthquakes and volcanoes.
Why are earthquakes important for understanding Earth's interior?
-Earthquakes are important because they allow scientists to 'see' deep into the Earth by studying the behavior of seismic waves. This helps in understanding the structure and composition of Earth's interior layers.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)