6 - 2 Seismic Waves - Interior/Exterior Earth
Summary
TLDRThis screencast explores how seismic waves reveal the Earth's internal structure. By understanding wave properties like velocity, reflection, and refraction, we learn about the different layers inside the Earth. P-waves travel through both solids and liquids, while S-waves only pass through solids, providing key insights into the Earth's core. Using wave behavior, scientists can map boundaries between the Earth’s layers, such as the mantle and outer core. The script emphasizes how seismic waves are essential for studying earthquakes and plate boundaries, helping us visualize the Earth's structure much like an ultrasound reveals a baby’s development.
Takeaways
- 😀 Seismic waves are energy that travel through the Earth, helping us study its internal structure.
- 😀 Waves move at constant velocity through a homogeneous medium, but change velocity when entering a different material.
- 😀 Reflection and refraction are key properties of waves when they encounter boundaries between different media.
- 😀 Amplitude of a wave is directly related to its energy; higher energy waves have larger amplitudes.
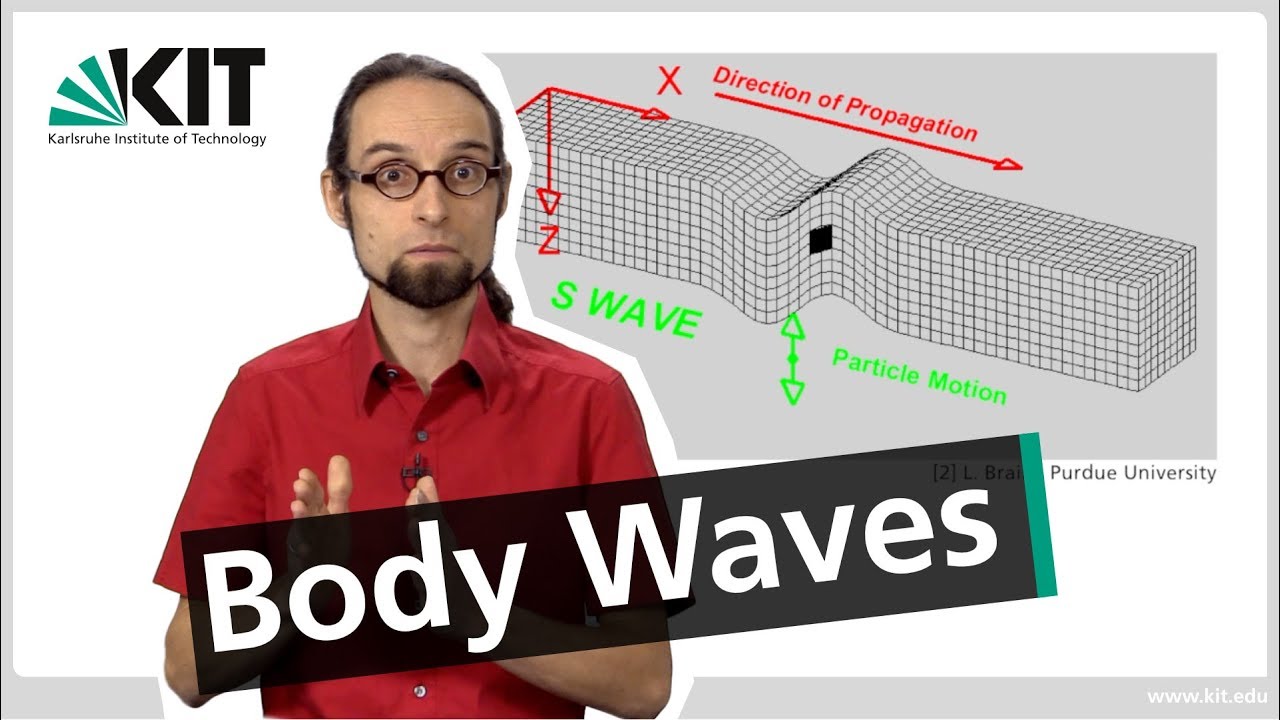
- 😀 Primary (P) waves are longitudinal and can travel through both solids and liquids, whereas Secondary (S) waves are transverse and can only travel through solids.
- 😀 Shadow zones are areas where certain seismic waves do not reach due to refraction and reflection at boundaries inside the Earth.
- 😀 The outer core of the Earth is liquid, as indicated by the lack of S-waves passing through it.
- 😀 By studying wave velocities and shadow zones, we can determine the size and state (solid or liquid) of the Earth's layers.
- 😀 The boundary between the mantle and outer core causes a dramatic change in wave velocity due to the transition from solid to liquid.
- 😀 Understanding the behavior of seismic waves allows us to map Earth's internal layers and learn about phenomena like earthquakes and volcanism at plate boundaries.
Q & A
What is the significance of wave properties in understanding the Earth's interior?
-Wave properties such as reflection, refraction, and velocity changes are crucial for understanding Earth's layers. By studying how waves behave when they travel through different materials, scientists can infer the composition and state (solid or liquid) of Earth's interior.
How do seismic waves change as they travel through different media?
-Seismic waves change speed and direction when they encounter different media. For example, waves travel at a different velocity in continental crust compared to oceanic crust, and they refract or reflect at boundaries between materials with different properties.
What are the differences between P-waves and S-waves?
-P-waves (primary waves) are longitudinal waves that can travel through both solids and liquids, while S-waves (secondary waves) are transverse waves that only travel through solids. This difference helps explain why S-waves do not pass through Earth's liquid outer core.
What is the concept of a 'shadow zone' in seismic studies?
-A shadow zone is an area where seismic waves, particularly S-waves, do not reach due to their inability to travel through liquids. This zone helps scientists infer the properties of Earth's interior, such as the liquid state of the outer core.
How does the refraction of seismic waves help us understand Earth's internal layers?
-When seismic waves refract as they pass through different materials, it indicates a change in the material's density or composition. By studying these refracted waves, scientists can map out the layers of the Earth, such as the solid mantle and the liquid outer core.
What is the relationship between wave amplitude and energy?
-Wave amplitude is directly proportional to the amount of energy in the wave. A larger amplitude indicates higher energy, which is typically observed closer to the epicenter of an earthquake, where the waves have not traveled as far and have more energy.
What does the change in seismic wave velocity indicate about Earth's layers?
-A change in seismic wave velocity indicates a transition between different layers of the Earth, such as from solid to liquid. For example, when P-waves slow down as they enter the liquid outer core, it suggests a shift from solid mantle to liquid outer core.
How does the index of refraction affect wave behavior?
-The index of refraction determines how much a wave bends when passing from one medium to another. A higher refractive index means the wave will bend more toward the normal line. For example, light bends toward the normal when entering a denser material, like glass.
What role do plate boundaries play in earthquake distribution?
-Earthquakes are most commonly found along plate boundaries, where tectonic plates interact. These boundaries are sites of active geological processes such as subduction, rifting, or transform motion, which generate stress and lead to earthquakes.
How do seismic waves help determine the size and composition of Earth's outer core?
-Seismic waves, particularly the lack of S-waves in the outer core, provide evidence that the outer core is liquid. The velocity changes of P-waves as they move through the core allow scientists to calculate the size and density of the Earth's layers, including the outer core.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Earth’s Interior, Seismic Waves and Tsunami | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 2 Module 2

Earthquakes and Seismology in Earth’s Interior
Basic Geophysics: Body Waves
GCSE Physics - Seismic Waves #75

Seismic Waves: On Exploring Earth's Interior

ข้อมูลในการศึกษาและแบ่งชั้นโครงสร้างโลก (โลกและอวกาศ ม.6 บทที่ 5)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)