Perfect Square Trinomial
Summary
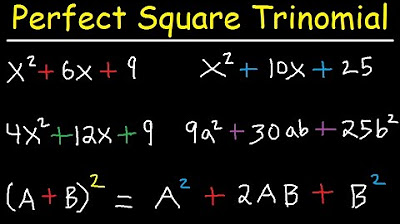
TLDRThe video script provides a comprehensive guide on identifying and factoring perfect square trinomials. It emphasizes the criteria for a trinomial to be a perfect square: a positive first and last term that are perfect squares, and a middle term that is twice the product of the square roots of the first and last terms. The script includes examples to illustrate the process, demonstrating how to factor expressions like \(x^2 + 2xy + y^2\) and \(4x^2 + 20x + 25\) into the square of a binomial, and explains why certain expressions, such as \(x^2 + 5x + 6\), do not qualify as perfect squares.
Takeaways
- 📚 A perfect square trinomial is a quadratic expression that can be factored into the square of a binomial.
- 🔑 The first and last terms of a perfect square trinomial must be perfect squares and have the same sign.
- 🤔 The middle term should be twice the product of the square roots of the first and last terms.
- ✅ Examples given include \( X^2 + 2xy + Y^2 \) and \( 4x^2 + 20x + 25 \), which are perfect square trinomials.
- ❌ The expression \( x^2 + 5x + 6 \) is not a perfect square trinomial because the last term is not a perfect square.
- 🔍 To determine if an expression is a perfect square, check if the first and last terms are perfect squares and the middle term is twice their product.
- 📐 The process of factoring a perfect square trinomial involves taking the square root of the first and last terms and squaring them.
- 📝 The factored form of a perfect square trinomial is either \( (x + y)^2 \) or \( (x - y)^2 \), depending on the sign of the middle term.
- 👉 For negative middle terms, the factored form is the square of the difference, such as \( (x - y)^2 \).
- 📌 The script provides a step-by-step method to identify and factor perfect square trinomials, including examples with various signs and terms.
- 📝 The script also explains how to correctly write the factored form of a perfect square trinomial, emphasizing the importance of the signs and the square roots of the first and last terms.
Q & A
What is a perfect square trinomial?
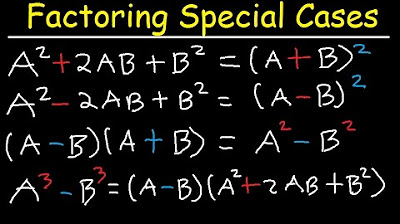
-A perfect square trinomial is a type of quadratic expression that can be factored into the square of a binomial. It has the form \(a^2 + 2ab + b^2\) or \(a^2 - 2ab + b^2\), where \(a\) and \(b\) are terms, and the middle term is either the sum or the difference of twice the product of \(a\) and \(b\).
How can you determine if a given expression is a perfect square trinomial?
-To determine if an expression is a perfect square trinomial, check if the first and last terms are perfect squares and if the middle term is twice the product of the square roots of the first and last terms, with the same sign as the middle term in the original expression.
What is the significance of the sign of the middle term in a perfect square trinomial?
-The sign of the middle term in a perfect square trinomial indicates whether the binomial in the factored form will be added or subtracted. A positive middle term results in an addition in the binomial, while a negative middle term results in subtraction.
Why is the first term of a perfect square trinomial always positive?
-The first term of a perfect square trinomial is always positive because a perfect square is the result of squaring a real number, which cannot be negative.
Can the last term of a perfect square trinomial be negative?
-No, the last term of a perfect square trinomial cannot be negative, as it must also be a perfect square, and the square of any real number is non-negative.
What is the process of factoring a perfect square trinomial?
-To factor a perfect square trinomial, identify the square roots of the first and last terms and write the expression as the square of the sum or difference of these terms, depending on the sign of the middle term.
How do you factor the expression \(x^2 + 10x + 25\)?
-The expression \(x^2 + 10x + 25\) can be factored as \((x + 5)^2\) because \(x^2\) and \(25\) are perfect squares, and \(10x\) is twice the product of \(x\) and \(5\).
What is the factored form of the expression \(16x^2 + 72x + 81\)?
-The factored form of \(16x^2 + 72x + 81\) is \((4x + 9)^2\), as \(16x^2\) and \(81\) are perfect squares, and \(72x\) is twice the product of \(4x\) and \(9\).
Why is the expression \(x^2 + 5x + 6\) not a perfect square trinomial?
-The expression \(x^2 + 5x + 6\) is not a perfect square trinomial because the last term, \(6\), is not a perfect square, and \(5x\) is not twice the product of the square roots of the first and last terms.
What is the factored form of a perfect square trinomial with a negative middle term?
-If a perfect square trinomial has a negative middle term, its factored form will be the square of the difference of the terms, for example, \(x^2 - 2xy + y^2\) factors to \((x - y)^2\).
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)