Horizontal Gene Transfer (Transformation, Conjugation, Transduction)
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses gene transfer, distinguishing between vertical (parent to offspring) and horizontal (between organisms) types. It highlights the benefits of horizontal gene transfer, such as antibiotic resistance, and explains three main methods: transformation, conjugation, and transduction. The script also mentions the use of viral vectors in lab settings for gene integration.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Gene transfer is the process of DNA moving between organisms.
- 🌱 Vertical gene transfer occurs from parent to offspring, passing traits down generations.
- 🔄 Horizontal gene transfer involves gene exchange between existing organisms, often benefiting the recipient.
- 💊 Horizontal gene transfer can provide a selective advantage, such as antibiotic resistance.
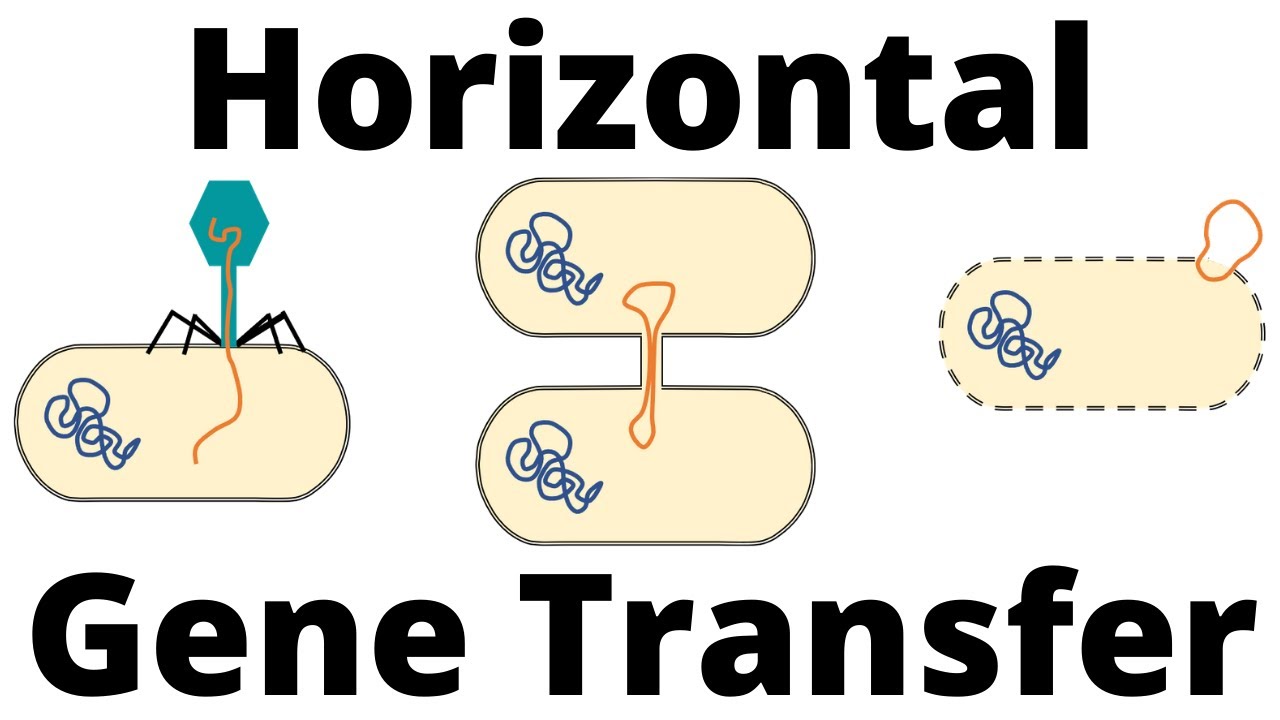
- 🔬 There are three main types of horizontal gene transfer: transformation, conjugation, and transduction.
- 🌐 Transformation is when bacteria take in free genetic material from the environment, often in the form of plasmids.
- 🤝 Conjugation involves direct contact between bacteria to transfer genetic material, facilitated by pili.
- 🔗 In conjugation, a mobile plasmid is transferred from the donor to the recipient, which then synthesizes a complementary strand.
- 🦠 Transduction uses a viral agent to transfer DNA between bacteria, sometimes incorporating bacterial DNA into the viral genome.
- 🧪 Viral vectors can be utilized in labs to integrate specific genes into the genome of eukaryotic cells.
- 📚 Further details on these concepts can be explored through corresponding educational videos.
Q & A
What is gene transfer?
-Gene transfer is the process by which DNA is passed between organisms, either from parent to offspring (vertical gene transfer) or between existing organisms (horizontal gene transfer).
What is the significance of horizontal gene transfer for bacteria?
-Horizontal gene transfer is significant for bacteria as it allows them to acquire new genes, which can enable the production of new proteins and grant new functionalities, such as antibiotic resistance, providing a selective advantage.
What are the three main types of horizontal gene transfer?
-The three main types of horizontal gene transfer are transformation, conjugation, and transduction.
How does transformation work in the context of gene transfer?
-Transformation involves a bacterium taking in free genetic material from the environment, often in the form of a plasmid, which can then either be integrated into the bacterial chromosome or exist as a separate plasmid.
What is meant by bacterial competence in the context of gene transfer?
-Bacterial competence refers to the ability of a bacterium to take in foreign DNA from its environment, which is a key aspect of the transformation process.
Can you describe the process of conjugation in gene transfer?
-Conjugation involves the transfer of genetic material between two bacteria through direct contact. It involves the production of a pilus by the donor, attachment of the recipient, nicking of the mobile plasmid, transfer of a single-stranded plasmid to the recipient, and synthesis of a complementary strand in both cells to form a double-stranded circular plasmid.
What is the role of a pilus in conjugation?
-The pilus is a structure produced by the donor bacterium in conjugation that helps attach to and draw the recipient bacterium closer, facilitating the transfer of genetic material.
How does transduction differ from the other types of gene transfer?
-Transduction involves the use of a viral agent to transfer DNA between bacteria. It can occur when a virus infects a bacterial cell and integrates its DNA into the bacterial genome, potentially incorporating some of the bacterial DNA into new viral particles that infect other bacteria.
Can viral vectors be used in laboratory settings for gene transfer?
-Yes, viral vectors can be used in laboratories to integrate genes of interest into the genome of eukaryotic cells, leveraging the natural process of transduction.
What is the potential advantage of using viral vectors in gene therapy?
-The advantage of using viral vectors in gene therapy is their ability to efficiently deliver genetic material into target cells, which can be crucial for treating genetic disorders or introducing therapeutic genes.
How might the script suggest further exploration of gene transfer concepts?
-The script suggests that viewers can choose to explore any of the three concepts of gene transfer in more detail by selecting the corresponding video displayed on the screen.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
Transformation, Transduction and Conjugation (Horizontal Gene Transfer in Bacteria)

Regression estimates of heritability

Supplier Relationship Management Process: System, Tools and Types of Collaboration - AIMS UK

ELS- LESSON 2- REPRODUCTION

MACAM-MACAM TUMPUAN (ROL, SENDI DAN JEPIT) MEKANIKA TEKNIK KELAS X SMK BANGUNAN

Keberagaman Antargolongan Masyarakat Indonesia|Part 1|Pendidikan Pancasila Kelas 7
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
