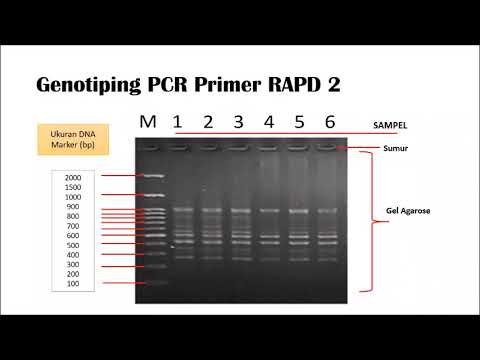
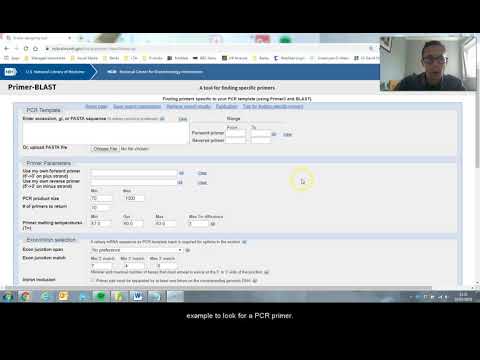
DESAIN PRIMER DAN PROBE
Summary
TLDRIn this tutorial, the speaker walks viewers through the process of designing PCR primers using NCBI and Primer3 Plus. The video demonstrates how to search for gene sequences on NCBI, refine search results for human genes, and select suitable sequences for PCR. The speaker then explains how to use Primer3 Plus to design primer pairs, ensuring they meet specific requirements such as optimal size, melting temperature, and GC content. Finally, the primers are validated using the BLAST tool to confirm specificity, and users are shown how to order the designed primers for experimentation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Search for genes on NCBI using the appropriate database, and filter results to focus on Homo sapiens for human-specific research.
- 😀 Use RefSeq (Reference Sequence) as it is curated and recommended for reliable research results.
- 😀 Select a gene sequence of appropriate length (avoid sequences that are too long for ease of handling).
- 😀 Use Primer3Plus to design primers and probes, pasting the gene sequence into the tool for analysis.
- 😀 Set primer design parameters such as length (18–27 bp), Tm (57–63°C), and GC content (40–60%) for optimal results.
- 😀 Avoid primer design issues like self-dimer formation, cross-dimers, hairpins, or improper hybridization.
- 😀 For probes, ensure Tm is higher than primers, and avoid self-complementarity and dimer formation to maintain specificity.
- 😀 Use BLAST (nucleotide BLAST) to verify the specificity of your designed primers and probes, ensuring they match the target gene (100% identity and high query cover).
- 😀 Ensure that all primers and probes are specific to the gene of interest (e.g., FMO5 in Homo sapiens).
- 😀 Once primers and probes are validated, order them through a trusted distributor for synthesis.
- 😀 The whole process includes refining primer conditions, testing probe specificity, and ordering the final product for PCR experiments.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the tutorial in the video?
-The main purpose of the tutorial is to demonstrate how to design PCR primers using NCBI and Primer 3 Plus for research, including how to ensure primer specificity and quality.
Why does the speaker use NCBI for searching gene sequences?
-The speaker uses NCBI because it provides a reliable source of gene sequences, including RefSeq, which is commonly used in research for primer design and sequencing.
What is RefSeq and why is it important in primer design?
-RefSeq (Reference Sequence) is a curated collection of sequences representing reference genes, and it is important because it ensures that the primer design is based on a validated and reliable sequence for human genes, reducing errors in research.
What role does Primer 3 Plus play in this tutorial?
-Primer 3 Plus is used to design primers by taking the sequence from NCBI and generating primer pairs based on specific settings such as size, melting temperature, and GC content to ensure efficient PCR amplification.
What are the key settings that need to be adjusted when designing primers in Primer 3 Plus?
-Key settings include primer size, melting temperature (TM), GC content, and ensuring the primers have minimal self-complementarity, hairpin structures, and dimer formations.
Why is it important to minimize hairpin and dimer formations when designing primers?
-Minimizing hairpin and dimer formations is crucial because these structures can interfere with primer binding and reduce the efficiency of PCR amplification, leading to inaccurate or incomplete results.
What does the 'thermal melting' (TM) value represent in primer design?
-The 'thermal melting' (TM) value represents the temperature at which half of the DNA strands in a primer duplex will denature. It is important to ensure that the TM of the forward and reverse primers is similar for optimal binding during PCR.
How does the speaker confirm the specificity of the primers?
-The specificity of the primers is confirmed by submitting them to NCBI BLAST, which checks if the primers match only the target gene sequence in Homo sapiens with 100% identity and good query cover.
Why is a 100% identity and high query cover in BLAST results important?
-A 100% identity and high query cover indicate that the primers are highly specific to the target gene, ensuring they will amplify the correct DNA sequence without cross-reactivity with other sequences.
What is the significance of using the FMO5 gene in the example of the tutorial?
-The FMO5 gene is used as an example to show how to design primers for a specific gene in Homo sapiens. The speaker checks that the primers are highly specific for this gene to ensure accuracy in subsequent PCR experiments.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)