The Entire History of the Middle East
Summary
TLDRThe script traces the history of the Middle East from the rise of early civilizations in Mesopotamia and Egypt through successive empires, religious transformations, and imperial rivalries. It covers the spread of Islam, the golden age and fragmentation of the Islamic caliphates, the Crusades, Mongol invasions, and the long dominance of the Ottoman Empire. Moving into the modern era, it examines European colonialism, the creation of new states, Arab nationalism, the Arab-Israeli conflict, oil politics, revolutions, wars, and foreign intervention. The narrative concludes with contemporary upheavals, regional power struggles, and ongoing geopolitical tensions shaping today’s Middle East.
Takeaways
- 😀 Ancient Mesopotamia is considered the birthplace of human civilization, where agriculture, urbanization, and writing were first developed.
- 😀 The Sumerians pioneered foundational technologies such as the first cities, writing, bureaucracies, and legal codes, influencing the development of later civilizations.
- 😀 The region known as the 'Fertile Crescent'—spanning from Mesopotamia to Egypt—was home to multiple advanced cultures that laid the groundwork for modern civilization.
- 😀 Over time, empires like the Akkadian, Babylonian, Assyrian, and Persian dominated the Middle East, each contributing to the region's military, cultural, and administrative legacy.
- 😀 The conquest of Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC spread Hellenistic culture across the Middle East, blending Greek and local traditions and fostering a cosmopolitan environment.
- 😀 The rise of the Roman Empire led to the spread of Christianity in the region, which became the official religion by the early 4th century AD, shaping the cultural and spiritual landscape.
- 😀 The Byzantine Empire, centered in Constantinople, and the Sassanian Empire dominated the Middle East from the 3rd to 7th centuries, setting the stage for the emergence of Islam.
- 😀 Islam, founded by the Prophet Muhammad in the 7th century, rapidly united the Arab tribes and established a new imperial order that spread across the Middle East and beyond.
- 😀 The rise of the Islamic Caliphates, particularly the Umayyad and Abbasid dynasties, fostered a golden age of cultural, scientific, and intellectual advancements.
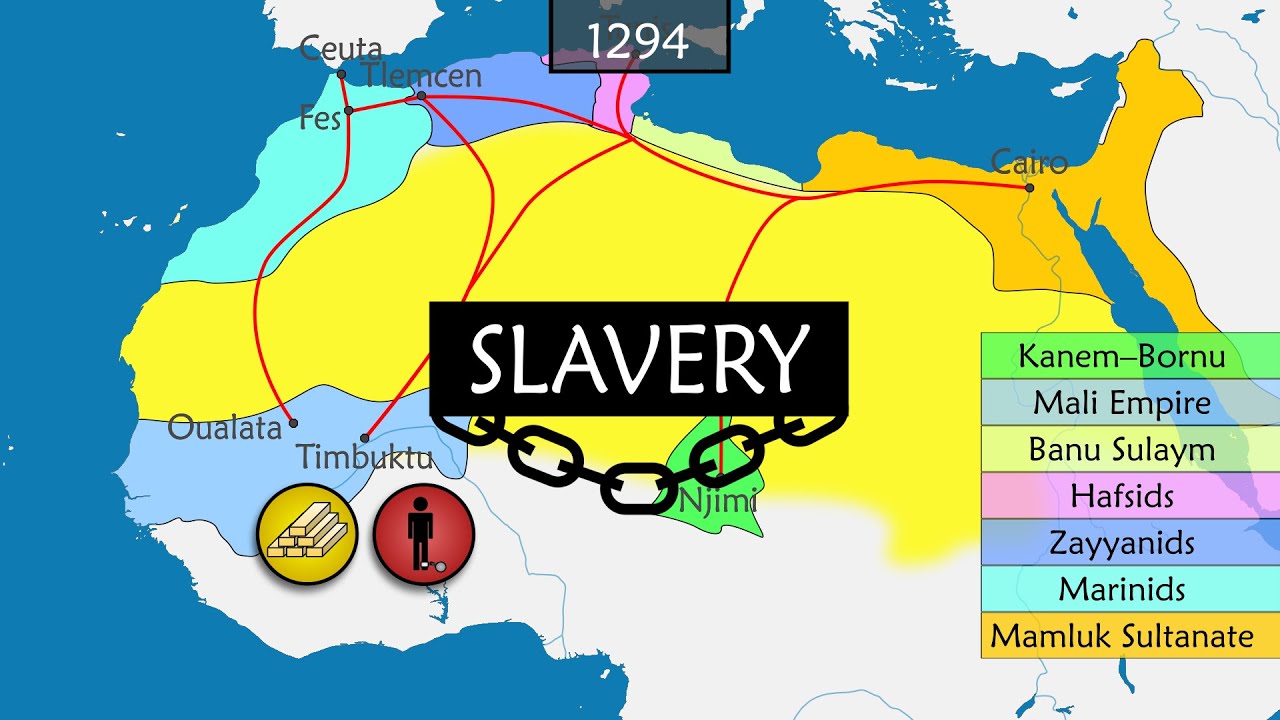
- 😀 The Ottoman Empire, which emerged in the 14th century, dominated the Middle East for centuries, but its decline in the 19th century due to internal and external pressures marked a turning point for the region's modern history.
Q & A
What was the significance of ancient Mesopotamia in the history of human civilization?
-Ancient Mesopotamia, particularly the Sumerians, is considered the birthplace of urban civilization. It was here that human societies transitioned from a nomadic lifestyle to settled agricultural communities. The Sumerians pioneered foundational technologies such as writing, law codes, and bureaucracy, which laid the groundwork for future civilizations.
How did the Phoenicians contribute to the development of writing systems?
-The Phoenicians developed one of the earliest alphabets, which was a significant advancement in writing. This alphabet later influenced the Greek and Latin scripts and became the foundation of the modern alphabet used today across much of the world.
What was the impact of Alexander the Great's conquests on the Middle East?
-Alexander the Great's conquests in the 4th century BC brought Hellenistic culture to the Middle East. Despite the fragmentation of his empire after his death, his influence led to the fusion of Greek and local traditions, creating a cosmopolitan environment that facilitated the exchange of ideas, arts, and sciences.
What was the Pax Romana, and how did it affect the Middle East?
-The Pax Romana was a period of relative peace and stability in the Roman Empire lasting approximately two centuries. It brought economic integration, infrastructure development, and administrative cohesion to the Middle East, helping to consolidate Roman control over regions like the Levant and Egypt.
How did the rise of Islam in the 7th century transform the Middle East?
-Islam emerged as a revolutionary religious and political force in the Arabian Peninsula. The rapid conquests by the first Caliphs established Islam as both a unifying religious identity and the foundation of a new imperial order, significantly altering the region's political, cultural, and religious landscape.
What was the significance of the Abbasid Caliphate's golden age?
-The Abbasid Caliphate's golden age, particularly in Baghdad, became a center for learning, trade, and culture. The House of Wisdom was pivotal in translating and preserving classical knowledge, and the Abbasids made significant advances in mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy, influencing both the Islamic world and Europe.
What factors contributed to the decline of the Ottoman Empire in the 17th and 18th centuries?
-The Ottoman Empire began to decline due to internal struggles such as corruption, economic stagnation, and bureaucratic inefficiency. Externally, European powers like Austria, Russia, and later Britain and France eroded Ottoman territory and influence. The empire's inability to modernize in comparison to European powers earned it the title 'the sick man of Europe.'
What was the role of the Sykes-Picot Agreement in shaping the modern Middle East?
-The Sykes-Picot Agreement of 1916, a secret deal between Britain and France, divided Ottoman Arab territories into spheres of influence after World War I. The artificial borders drawn without consideration for ethnic and sectarian realities sowed the seeds for future conflicts and instability in the region.
How did the Camp David Accords in 1979 alter the Middle Eastern geopolitical landscape?
-The Camp David Accords in 1979 marked the first peace agreement between an Arab country, Egypt, and Israel. Egypt regained the Sinai Peninsula in exchange for recognizing Israel diplomatically. This event shifted the balance of power in the region, with Egypt's alignment changing toward the West and a growing ideological rivalry with Iran.
What were the main consequences of the 2003 Iraq War for the Middle East?
-The 2003 Iraq War, initiated by the United States, led to the rapid collapse of Saddam Hussein's regime but sparked widespread sectarian violence between Sunni and Shia factions. This instability created a fertile ground for extremist movements like ISIS and contributed to a decade of chaos, regional instability, and increased U.S. military presence in the region.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)