11 Most Important Circle Theorems You Need To Know!
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fundamental properties and theorems of circles, explaining key concepts such as radius, diameter, chord, arc, and sector. It covers essential circle theorems like equal angles subtended by the same arc, the relationship between angles at the center and circumference, and the properties of tangents and secants. The video also explores cyclic quadrilaterals, alternate segment theorems, and the tangent-secant theorem, providing a comprehensive understanding of circle geometry with real-world applications and problem-solving.
Takeaways
- 😀 The center of a circle is equidistant from all points on the circle, and a line drawn from the center to any point on the circle is called the radius.
- 😀 The diameter of a circle is a straight line passing through the center, and it is always twice the length of the radius.
- 😀 A chord is a line segment connecting any two points on the circle, while an arc is a curved part of the circle between two points.
- 😀 A sector is the region between two radii and an arc, and a segment is the region between a chord and the arc.
- 😀 The circumference of a circle is the perimeter, or total length of its boundary.
- 😀 A tangent to a circle touches the circle at exactly one point without crossing it, and a secant intersects the circle at two points.
- 😀 Angles subtended by the same arc are equal, meaning that if an arc subtends angles at multiple points on the circle, all such angles will be equal.
- 😀 The angle at the center of the circle is always twice the angle at the circumference formed by the same arc.
- 😀 The angle subtended by a semicircle at the circumference is always 90°, which is explained by dividing the circle's total 180° angle into two equal parts.
- 😀 In a cyclic quadrilateral, opposite angles are supplementary, meaning they always add up to 180°.
- 😀 The tangent to a circle is always perpendicular to the radius at the point where it touches the circle.
- 😀 If two tangents are drawn from a single external point, they will be equal in length, and the line joining the external point to the center bisects the angle between the two tangents.
- 😀 The alternate segment theorem states that the angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle the same chord subtends in the opposite segment of the circle.
- 😀 The chord bisector theorem states that a line perpendicular to a chord and dividing it into two equal parts must pass through the center of the circle.
- 😀 The equal chords, equal angles theorem states that if two chords are of equal length, the angles subtended by them at the center of the circle are also equal.
- 😀 The secant-tangent theorem relates to the product of distances when a tangent and secant meet at an external point outside the circle.
- 😀 The chord-chord power theorem states that if two chords intersect inside the circle, the product of the lengths of the segments of one chord equals the product of the lengths of the segments of the other chord.
Q & A
What is the center of a circle and how is it related to the points on the circle?
-The center of a circle is the point equidistant from all points on the circle. All points on the circle are at the same distance from this center.
What is the difference between a radius and a diameter?
-A radius is the line segment that connects the center of the circle to any point on the circle. A diameter is a line segment passing through the center and connecting two points on the circle, and it is always twice the length of the radius.
What is a chord, and what is the longest chord in a circle?
-A chord is a line segment that connects any two points on the circle, not necessarily passing through the center. The longest possible chord in a circle is the diameter.
What is the definition of an arc in a circle?
-An arc is a curved part of the circle between two points on the circle.
What does the term 'sector' refer to in a circle?
-A sector is the region or area between two radii and an arc of a circle.
How is a tangent different from a secant in relation to a circle?
-A tangent is a straight line that touches the circle at exactly one point without crossing it, while a secant is a straight line that intersects the circle at two distinct points.
What does the term 'subtended' mean in the context of a circle?
-In the context of a circle, 'subtended' refers to the angle formed at a point (either at the center or on the circumference) by an arc or chord.
State Theorem 1: Angles subtended by the same arc are equal.
-This theorem states that if an arc subtends an angle at multiple points on the circle, all such angles will be equal. For example, if an angle is 65° at one point, it will be 65° at all other points subtended by the same arc.
What is Theorem 2: The angle at the center is twice the angle at the circumference?
-This theorem states that the angle subtended by an arc at the center of the circle is always twice the angle subtended by the same arc at the circumference.
What is the significance of Theorem 3: The angle in a semicircle is always 90°?
-This theorem states that if an arc is a semicircle (its endpoints lie on the diameter), then the angle subtended by that arc at the circumference is always 90°.
What does Theorem 4: The cyclic quadrilateral theorem say?
-A cyclic quadrilateral is one where all four vertices lie on the circumference of a circle. The opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are always supplementary, meaning they add up to 180°.
What does Theorem 5: Theorem of tangent and radius state?
-This theorem states that a tangent to a circle is always perpendicular to the radius at the point where it touches the circle.
Explain Theorem 6: The two tangents theorem.
-If two tangents are drawn from a single external point to a circle, then these tangents will always be equal in length. The line joining the external point to the center of the circle bisects the angle formed between the two tangents.
What does Theorem 7: The alternate segment theorem state?
-The alternate segment theorem states that the angle between a tangent and a chord drawn from the point of contact is always equal to the angle subtended by the same chord in the opposite segment of the circle.
What is the Chord Bisector Theorem (Theorem 8)?
-The Chord Bisector Theorem states that if a line is both perpendicular to a chord and divides it into two equal parts, then the line must pass through the center of the circle.
Explain Theorem 9: Equal chords equal angles.
-This theorem states that if two chords in a circle are of equal length, then the angles subtended by these chords at the center of the circle will also be equal.
What is the significance of Theorem 10: The secant and tangent theorem?
-This theorem states that if a secant and a tangent are drawn from an external point to a circle, the product of the distances from the external point to the two points of intersection of the secant will be equal to the square of the distance from the external point to the point of contact of the tangent.
What is Theorem 11: The chord-chord power theorem?
-The Chord-Chord Power Theorem states that if two chords intersect inside a circle, the products of the lengths of the segments of the chords will be equal. In other words, if the segments of the chords are labeled as 'a', 'b', 'c', and 'd', then a * b = c * d.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Materi Matematika Kelas 8: Lingkaran
Lingkaran (Bagian 1) - Unsur-unsur, Hubungan Sudut Pusat dan Sudut Keliling | SMP MTs Kelas VIII

Circles: radius, diameter, circumference and Pi | Geometry | Khan Academy
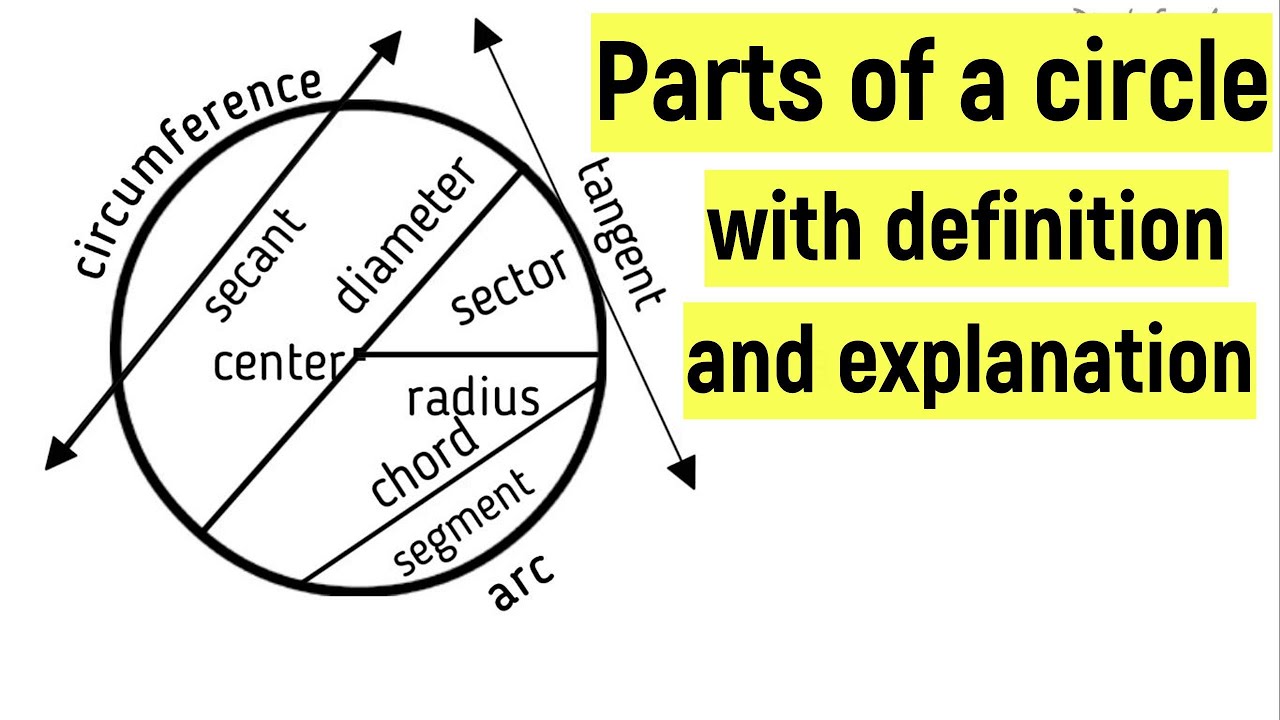
Parts of a circle with explanation | Learn the parts of a circle | Circle parts |

Unsur-unsur Lingkaran | Matematika Kelas XI

Matematika kelas 8 | Unsur-unsur Lingkaran, titik pusat, Jari, Diameter, Busur, Juring, tembereng
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
