Levelized Cost of Electricity - Energy Consulting #energy #infrastructure #ehicorp
Summary
TLDRThis script explains how power plant costs are structured, focusing on four main components: capital, fixed, variable, and fuel costs. It highlights the complexity of calculating the Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE), which is used to compare the cost efficiency of different power plants. The process involves amortizing capital costs, factoring in fixed and variable operating expenses, and adjusting for fuel costs, particularly for natural gas plants. By breaking down these costs per megawatt hour, the LCOE provides a useful metric for comparing power plants of varying types, capacities, and fuel sources.
Takeaways
- 😀 Power plant costs include capital costs, fixed operation costs, variable operation costs, and fuel costs.
- 😀 Capital costs represent the cost to build or buy a power plant, and these are spread over the plant's lifetime.
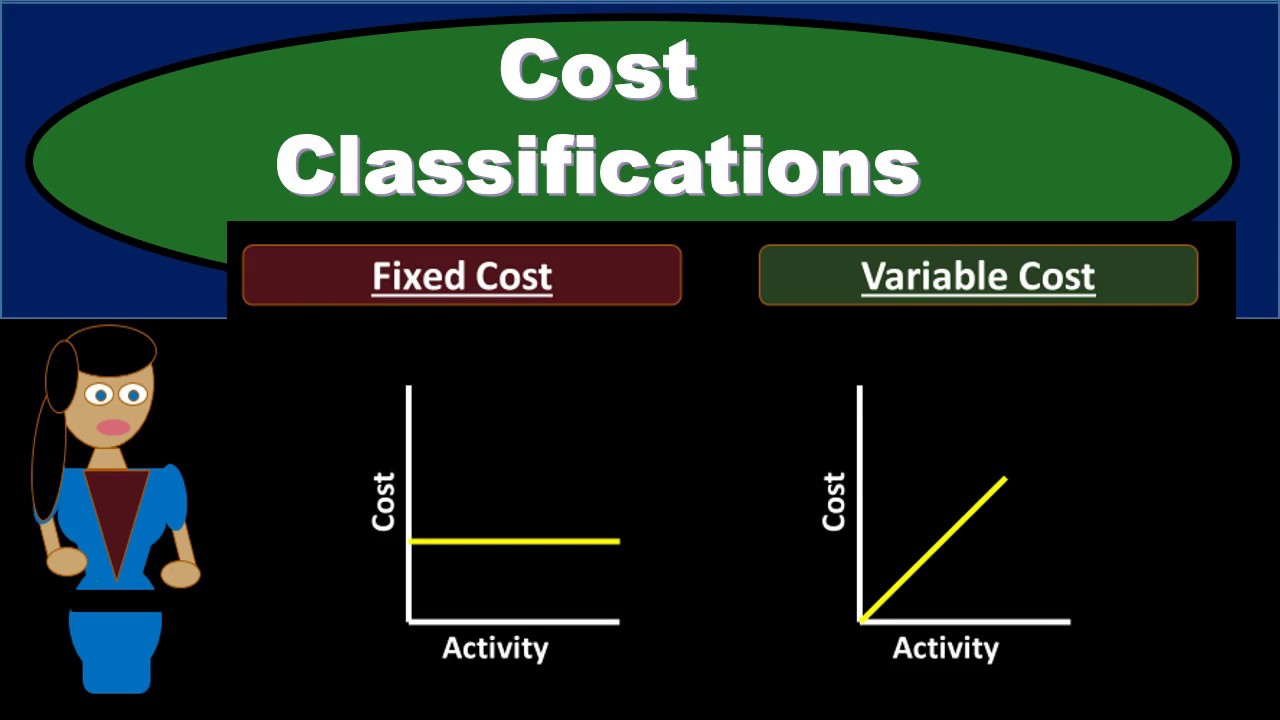
- 😀 Fixed operation costs are the expenses to maintain a power plant in operation, regardless of its power output.
- 😀 Variable operation costs change with the plant's electricity output, increasing when the plant runs at capacity.
- 😀 Fuel costs, for plants using fuels like coal, natural gas, or nuclear, are often separated as a specific category due to their magnitude.
- 😀 Renewable plants like wind and solar have zero fuel costs since they generate energy from free natural sources.
- 😀 The Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) is a metric that allows comparison of the overall cost of energy production across different plants.
- 😀 LCOE is calculated by dividing the total cost of energy production over the plant's lifetime by the total energy output, usually measured in dollars per megawatt-hour or cents per kilowatt-hour.
- 😀 The first component of LCOE is the capital cost amortized over the plant's lifetime, including interest rates and payment structure.
- 😀 Fixed costs are also considered in the LCOE calculation and are divided by the plant's capacity factor and hours per year to get dollars per megawatt-hour.
- 😀 Fuel costs, when applicable, are converted from their unit of measure (e.g., dollars per mmBTU) to dollars per megawatt-hour using the plant's heat rate, which accounts for efficiency.
Q & A
What are the main cost components for a power plant?
-The main cost components for a power plant are capital costs, fixed operation costs, variable operation costs, and fuel costs.
What are capital costs in the context of a power plant?
-Capital costs are the costs associated with building or buying a power plant. These costs include the initial purchase price and any financing costs.
What are fixed costs for a power plant?
-Fixed costs are the costs to keep the plant operational regardless of its electricity output. These costs do not vary with how much electricity is generated.
How do variable costs differ from fixed costs?
-Variable costs scale with the power output of the plant. They range from zero when the plant is not running to a maximum when the plant is running at full capacity.
Why are fuel costs considered a separate category for some power plants?
-Fuel costs are considered a separate category for power plants like coal, natural gas, and nuclear plants because these plants require large amounts of fuel, making fuel costs a significant and separate expense.
Why do renewable power plants like wind and solar have zero fuel costs?
-Renewable power plants such as wind and solar have zero fuel costs because they generate electricity from natural resources, like wind and sunlight, which do not incur a cost.
What is the Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE)?
-The Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) is the cost to generate a single unit of electricity over the lifetime of the power plant, usually expressed in dollars per megawatt-hour or cents per kilowatt-hour.
How is the LCOE calculated?
-LCOE is calculated by summing the capital cost, fixed costs, variable costs, and fuel costs (if applicable), and then dividing by the plant’s expected energy output over its lifetime.
What is the significance of the discount rate in calculating LCOE?
-The discount rate is used to account for the time value of money in the capital cost component, reflecting the future cost of the plant in today's terms, often based on an interest rate or expected return on investment.
What is the role of a power plant’s heat rate in fuel cost calculation?
-The heat rate is a measure of a power plant’s efficiency. It converts the fuel cost (typically in dollars per mm BTU) into a cost per megawatt-hour by adjusting for the plant's energy efficiency.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

High-Low Method to Separate Mixed Cost into Fixed Cost & Variable Cost

Long-run Average Total Cost and Economies of Scale

Akuntansi Manajemen Pertemuan 6 Perilaku Biaya Aktivitas

ANALISIS PERILAKU BIAYA
Cost Classifications - Managerial Accounting- Fixed Costs Variable Costs Direct & Indirect Costs

Biaya Produksi (Bagian 3) : Kombinasi Input Optimal
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
