Cara Kerja Turbin Gas Pesawat/Komersil
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed explanation of how gas turbine engines work, commonly used in power generation and aircraft. It introduces the Brayton cycle, the engine's core operational principle, which converts heat into mechanical energy. The process includes intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust stages. The video explains the starting mechanism, air compression, combustion process, and how the turbine converts combustion energy into kinetic energy. Additionally, it touches on the efficiency of gas turbines and innovative methods to enhance performance, such as combined cycles with steam turbines. The video concludes with a brief look at auxiliary systems.
Takeaways
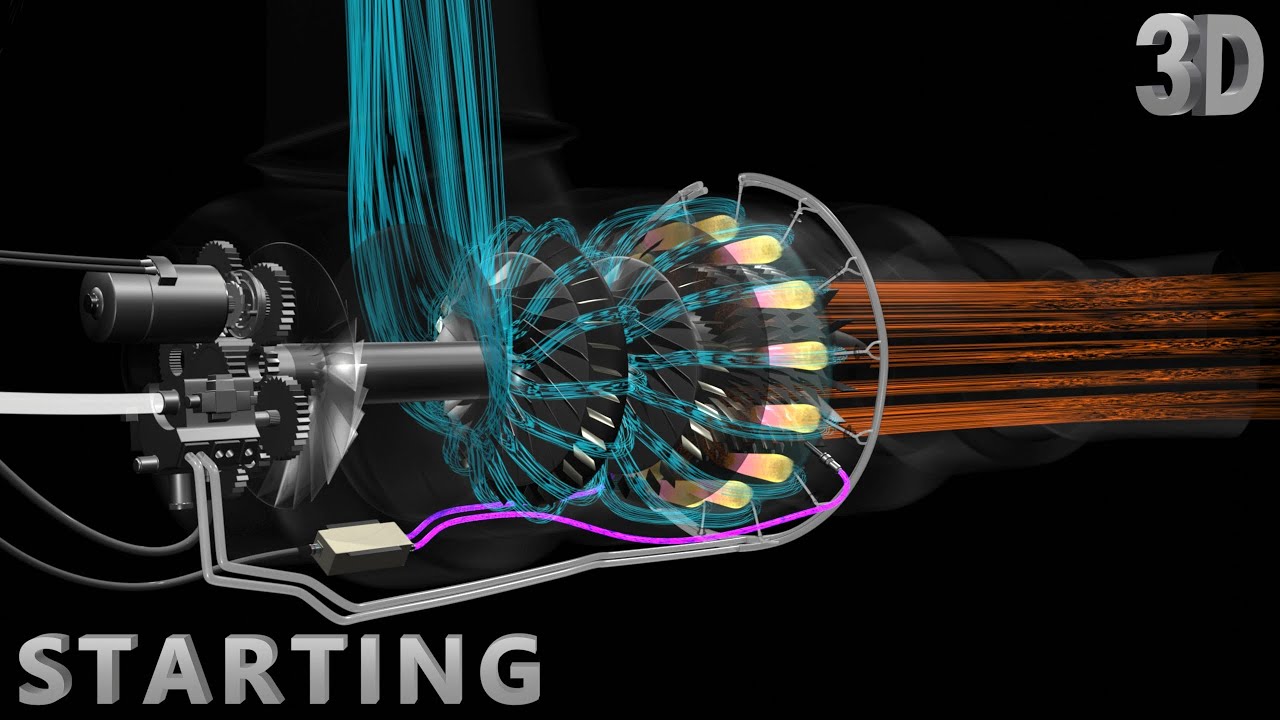
- 😀 Gas turbine engines are a type of internal combustion engine, used in both power generation and aircraft propulsion.
- 😀 The gas turbine engine operates based on the Brayton Cycle, which involves intake, compression, combustion, expansion, and exhaust stages.
- 😀 The Brayton Cycle consists of four stages: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust, which occur under ideal conditions like isentropic compression and isobaric combustion.
- 😀 The compression process in a gas turbine engine is achieved using an axial compressor, which compresses atmospheric air to high pressure for efficient combustion.
- 😀 Air entering the compressor is first filtered, then guided and compressed to increase its pressure, which is necessary for the combustion process.
- 😀 Combustion in a gas turbine engine is continuous, unlike the intermittent combustion seen in gasoline and diesel engines.
- 😀 The gas turbine's igniter initially sparks the combustion, but after ignition, combustion continues without further ignition sparks, thanks to the oxygen and fuel mix.
- 😀 The high-speed hot gases from combustion expand rapidly, driving the power turbine, which is connected to the compressor shaft, allowing the system to become self-sustaining after reaching a certain speed.
- 😀 The energy from combustion not only powers the compressor but can also be used to generate electricity, rotate pumps, or drive other machinery.
- 😀 The efficiency of a gas turbine engine typically ranges from 25-40%, but innovations like combined cycles can improve efficiency to over 60%, as seen with companies like Mitsubishi and General Electric.
Q & A
What is a gas turbine engine and how does it work?
-A gas turbine engine is an internal combustion engine that works by converting heat energy into mechanical energy. This energy can be converted into electrical energy by using a generator. The engine operates based on the Brayton cycle, which consists of intake, compression, combustion, expansion, and exhaust stages.
What is the Brayton cycle, and how is it related to gas turbine engines?
-The Brayton cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that describes the operation of a gas turbine engine. It involves four stages: intake, compression, combustion, and expansion. The cycle is named after George Brayton, who perfected it in the 1800s, and is central to how gas turbines function, converting heat into mechanical energy.
How does the air compression process work in a gas turbine engine?
-In a gas turbine engine, air from the atmosphere is sucked in by the axial compressor. The compressor has multiple stages of rotating blades (rotors) and stationary blades (stators) that work together to increase the air pressure. The further back in the compressor, the higher the compression ratio, which typically ranges from 10-18 for industrial turbines or 24-60 for aeroderivative turbines.
What role does the combustion chamber play in a gas turbine engine?
-The combustion chamber is where the compressed air mixes with fuel, and combustion occurs. The fuel is injected by a fuel injector, and the combustion process is initiated by an igniter. Once started, the combustion continues without the need for the igniter, providing a continuous energy source to power the turbine.
What is the difference between a gas turbine engine's combustion process and that of gasoline or diesel engines?
-Unlike gasoline or diesel engines, which have intermittent combustion cycles, a gas turbine engine has continuous combustion. After the initial spark from the igniter, the combustion process continues without further intervention, resembling the constant burning of a stove.
What happens to the hot gases produced in the combustion chamber?
-The hot gases produced in the combustion chamber expand rapidly and pass through nozzles that direct them toward the power turbine. The expanding gases cause the turbine to rotate, converting the thermal energy into kinetic energy.
How does the power turbine function in a gas turbine engine?
-The power turbine is connected to the same shaft as the axial compressor, allowing it to convert the energy from the hot, expanding combustion gases into mechanical energy. This energy drives the compressor and can also be used to rotate other equipment, such as a generator or pump.
What is the role of the exhaust in a gas turbine engine?
-Once the combustion gases pass through the power turbine, they are expelled through the exhaust system. The exhaust gases are released into the atmosphere after their energy has been used to rotate the turbine.
What is the efficiency of a typical gas turbine engine, and how can it be improved?
-The efficiency of a typical gas turbine engine ranges from 25-40%. However, some companies have innovated to combine cycles (e.g., a gas turbine and steam turbine) to increase overall efficiency, reaching up to 60% or more, as seen in some modern systems.
What is a combined cycle in the context of gas turbine engines?
-A combined cycle in a gas turbine system refers to the use of both a gas turbine and a steam turbine. The exhaust heat from the gas turbine is used to produce steam, which drives the steam turbine, improving the overall efficiency of the system by recovering energy that would otherwise be wasted.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Asynchronous Learning in Aircraft System

Gas Turbine Power Plant || Brayton Cycle In Hindi || Gear Institute

ATPL Aircraft General Knowledge - Class 1: Foundations.

Diffrence Between TurboJet, RamJet And ScramJet, Every Thing About Jet Engines

17 ATPL Training Gas Turbine Engines #17 Ignition Systems
How Auxiliary Power Units Work | Part 1 : Starting
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
