Google Cloud architecture
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the structure and offerings of Google Cloud, which is divided into three layers: networking and security, compute and storage, and big data and machine learning products. It highlights how these layers scale independently to support growing data needs, with services like Compute Engine, Kubernetes Engine, and BigQuery. The video also details the importance of Google's global network infrastructure, consisting of regions and zones, and how this network enables low-latency, high-throughput applications. Additionally, it covers Google Cloud's vast geographical presence, with over 120 zones across 40 regions, ensuring global service availability and data redundancy.
Takeaways
- 😀 Google Cloud's infrastructure is structured into three main layers: networking and security, compute and storage, and big data and machine learning products.
- 😀 The base layer of Google Cloud infrastructure supports applications through networking and security, which are crucial for scalability and protection.
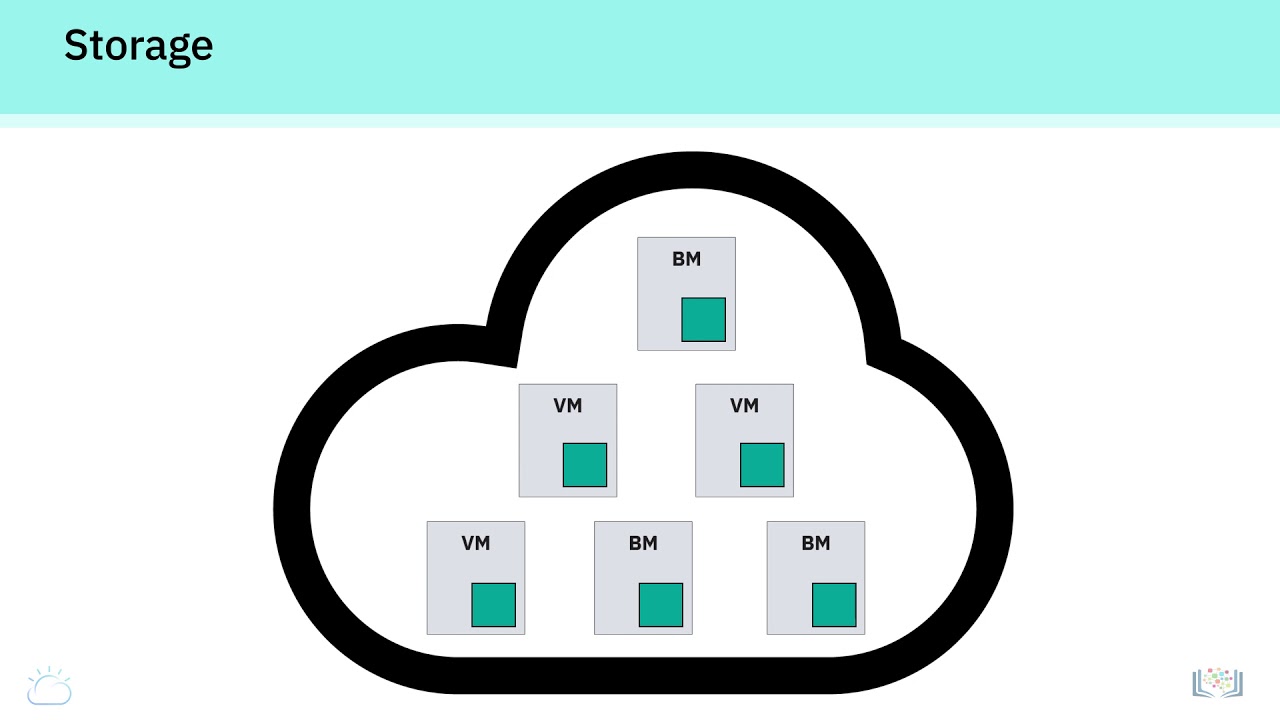
- 😀 Compute and storage in Google Cloud are decoupled, allowing them to scale independently based on demand.
- 😀 Google Cloud's big data and machine learning products help businesses process and deliver insights without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- 😀 Google offers a range of computing services including Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, App Engine, Cloud Run, and Cloud Run Functions.
- 😀 Managed storage options in Google Cloud include Cloud Storage, Cloud SQL, Spanner, Bigtable, and Firestore, with options for both relational and NoSQL databases.
- 😀 Google Cloud provides robust big data and machine learning tools like BigQuery, Dataproc, AutoML, and Vertex AI, among others.
- 😀 Google’s network is the largest of its kind and ensures low latency and high throughput by leveraging content caching nodes worldwide.
- 😀 Google Cloud operates in five major geographic locations: North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Australia, with regions and zones for resource deployment.
- 😀 Google Cloud’s multi-region support, like Spanner’s multi-region configurations, helps ensure low-latency access and redundancy in case of regional issues.
- 😀 Google Cloud currently operates 121 zones in 40 regions, providing global service coverage with continuous expansion.
Q & A
What are the three main layers of Google Cloud infrastructure?
-The three main layers of Google Cloud infrastructure are networking and security, compute and storage, and big data and machine learning. These layers work together to support and scale Google Cloud's services.
Why does Google Cloud decouple compute and storage services?
-Google Cloud decouples compute and storage services so they can scale independently based on the specific needs of the user. This provides greater flexibility and efficiency in resource management.
What are the key compute services offered by Google Cloud?
-Google Cloud's key compute services include Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, App Engine, Cloud Run, and Cloud Run Functions. Each service is designed to cater to different application deployment and management needs.
What types of databases does Google Cloud offer?
-Google Cloud offers both relational and NoSQL databases. Relational databases include Cloud SQL and Spanner, while NoSQL options include Bigtable and Firestore.
How does Google Cloud help with big data and machine learning?
-Google Cloud provides a variety of tools for big data processing and machine learning, such as BigQuery, Dataproc, Dataflow, Pub/Sub, Looker, AutoML, and Vertex AI. These tools enable users to process large datasets and develop machine learning models.
What makes Google Cloud's global network unique?
-Google Cloud's network is the largest of its kind, offering high throughput and low latency for applications. The network uses over 100 content caching nodes worldwide to ensure quick responses by serving content from the closest location to the user.
How are Google Cloud's regions and zones structured?
-Google Cloud infrastructure is organized into regions and zones. Regions represent independent geographic areas, and each region consists of multiple zones, where resources are deployed. This setup helps ensure redundancy and resource availability.
What is the benefit of multi-region configurations in Google Cloud?
-Multi-region configurations, such as those available with Spanner, allow data to be replicated across multiple zones in different regions. This improves availability and reduces latency by enabling users to read data from locations closer to them.
What happens if a zone becomes unavailable in Google Cloud?
-If a zone becomes unavailable, any resources deployed in that zone will also be unavailable. However, users can mitigate this risk by deploying resources across multiple zones to ensure continuity and redundancy.
How does Google Cloud ensure high availability during disasters?
-Google Cloud allows users to specify the location of their resources, including across multiple regions. This geographical flexibility helps protect applications and data from downtime in case of regional issues such as natural disasters.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
Google Cloud infrastructure

What is Google Cloud?

Cloud Providers Compared: A Comprehensive Guide to AWS, Azure, and GCP

Top 50+ GOOGLE CLOUD Services Explained in 7 Minutes

Google Cloud Platform Tutorial - Part #1 | Introduction to GCP | Cloud Computing Basics | @SCALER
3 1 1 Overview of Cloud infrastructure
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
