Pharmacology – MENSTRUAL CYCLE AND HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES (MADE EASY)
Summary
TLDRThis lecture covers the menstrual cycle and the pharmacology of hormonal contraceptives. It explains the phases of the menstrual cycle, including the follicular and luteal phases, the roles of hormones like GnRH, FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone, and how these regulate ovulation and the uterine lining. The second part of the lecture focuses on hormonal contraceptives, comparing combined methods (estrogen and progestin) and progestin-only methods. It discusses how these contraceptives prevent pregnancy through hormone suppression, ovulation inhibition, and cervical mucus thickening, highlighting different pill formulations and examples of common contraceptive drugs.
Takeaways
- 😀 The menstrual cycle is a regular, repetitive monthly occurrence of ovulation throughout a female’s reproductive life.
- 😀 The menstrual cycle involves a complex feedback system between the hypothalamus, pituitary, ovary, and uterus.
- 😀 The average menstrual cycle is 28 days, but it can vary between individuals and cycles.
- 😀 The cycle is divided into two phases: the follicular phase and the luteal phase, each lasting approximately 14 days.
- 😀 The follicular phase begins with the release of GnRH from the hypothalamus, stimulating FSH and LH secretion from the pituitary.
- 😀 FSH stimulates the maturation of oocytes in the ovaries, while LH causes theca cells to produce androgens, which are converted to estrogens.
- 😀 Estrogen has two main effects: it causes uterine lining growth and provides negative feedback to suppress FSH and LH production.
- 😀 During the luteal phase, the corpus luteum produces progesterone, which thickens the uterine lining and prepares it for potential pregnancy.
- 😀 If fertilization doesn't occur, the corpus luteum breaks down, causing a drop in estrogen and progesterone, leading to menstrual bleeding.
- 😀 Hormonal contraception methods, such as combined and progestin-only methods, prevent pregnancy by altering hormone levels to suppress ovulation or fertilization.
- 😀 Combined birth control pills (monophasic and multiphasic) deliver estrogen and progestin to prevent ovulation, with monophasic providing consistent doses and multiphasic varying doses to mimic natural hormone fluctuations.
Q & A
What is the menstrual cycle and how is it defined?
-The menstrual cycle is defined as the regular, repetitive monthly occurrence of ovulation throughout a female's reproductive life. It involves a complex feedback system among the hypothalamus, pituitary, ovary, and uterus.
What are the two phases of the menstrual cycle, and how long does each typically last?
-The menstrual cycle is divided into two phases: the follicular phase and the luteal phase. Each phase typically lasts about 14 days, though this can vary among individuals.
How does GnRH influence the menstrual cycle?
-Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is released by the hypothalamus in a pulsatile manner, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH, initiating the menstrual cycle.
What roles do FSH and LH play in the menstrual cycle?
-FSH stimulates the maturation of ovarian follicles, while LH triggers ovulation by causing the mature follicle to rupture and release the egg.
How does estrogen affect the uterus during the follicular phase?
-Estrogen causes the uterine lining (endometrium) to grow thicker in preparation for a potential pregnancy. This phase is also referred to as the proliferative phase.
What is the role of progesterone in the luteal phase?
-Progesterone helps the uterine lining become thicker and more vascular, supports the glands in the uterine wall to produce fluids for embryo nutrition, and causes the cervix to secrete thick mucus, which serves as a barrier to sperm and bacteria.
What happens if fertilization does not occur after ovulation?
-If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum breaks down, causing a dramatic drop in estrogen and progesterone levels, which leads to the breakdown of the uterine lining and menstrual bleeding (menses).
What is the difference between combined hormonal contraceptives and progestin-only contraceptives?
-Combined hormonal contraceptives contain both synthetic estrogen and progestin, while progestin-only contraceptives contain only synthetic progestin. Both prevent ovulation but have different methods of doing so and may be used based on individual health considerations.
How do monophasic birth control pills work?
-Monophasic birth control pills deliver the same amount of estrogen and progestin every day for 21 days, followed by 7 days of either a suspension or placebo pills. This continuous hormonal administration inhibits ovulation and mimics a menstrual cycle.
How do progestin-only contraceptives prevent pregnancy?
-Progestin-only contraceptives primarily work by thickening cervical mucus and causing endometrial atrophy, which makes it difficult for sperm to enter the uterus and for the fertilized egg to implant. They are less effective at suppressing ovulation compared to combined methods.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Reproductive Hormone Cycles

Fisiologi Hormon Siklus Mensturasi - FSH, Estrogen, LH, Progesteron

Pharmacology - CANCER DRUGS - HORMONAL THERAPY (MADE EASY)

Why 93% Of Women Never Lose Belly Fat

CICLO MENSTRUAL COMPLETO (FISIOLOGIA DE GUYTON) - MENSTRUAÇÃO - FISIOLOGIA HUMANA - OVULAÇÃO
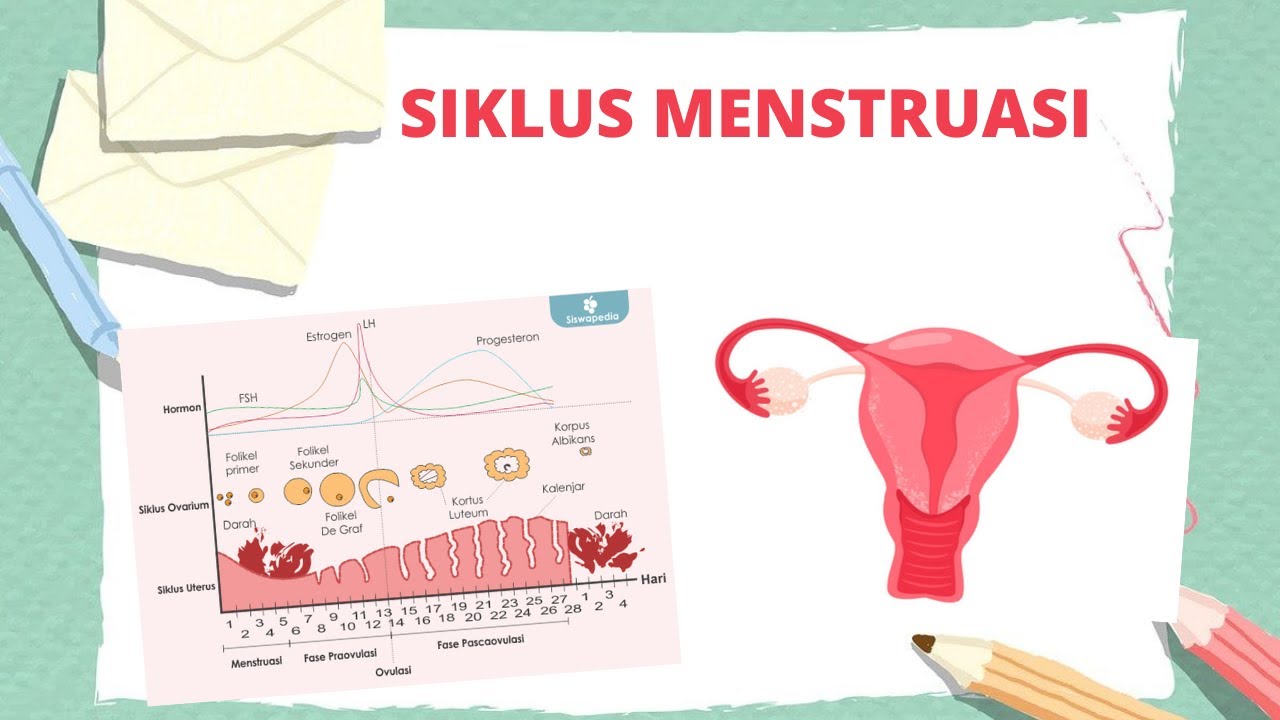
Siklus menstruasi - Grafik siklus menstruasi dan penjelasannya
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
