MACAM-MACAM TUMPUAN (ROL, SENDI DAN JEPIT) MEKANIKA TEKNIK KELAS X SMK BANGUNAN
Summary
TLDRIn this video script, the topic of structural supports in engineering is explored, focusing on three types of supports: roller, hinge (or pin), and fixed (or clamp). The script explains the differences between these supports, their functions, and their reactions to various forces, such as vertical, horizontal, and moments. Roller supports allow horizontal movement but only resist vertical forces, while hinge supports resist both vertical and horizontal forces. Fixed supports are the most stable, as they can resist vertical, horizontal, and rotational forces. Real-life applications like bridges and roofs are also discussed, illustrating how each type of support works in practice.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lesson focuses on understanding the types of supports (tumpuan) used in building structures, specifically roll, pin, and fixed supports.
- 😀 Roll support can only resist vertical forces and is commonly used in bridges, with a characteristic feature being the presence of a wheel under the structure.
- 😀 Roll supports cannot resist horizontal forces or twisting (moments). They are designed to allow horizontal movement.
- 😀 Pin support (sendi) is also used in building structures and can resist both vertical and horizontal forces, but it cannot resist twisting or rotational forces.
- 😀 Pin supports do not have wheels and are commonly used in jointed areas of structures like bridges.
- 😀 Fixed supports (jepit) are the most stable type of support, as they can resist vertical forces, horizontal forces, and moments (twisting).
- 😀 Fixed supports prevent any movement or twisting of a structure, making them crucial in maintaining structural integrity.
- 😀 The lesson emphasizes the importance of choosing the right support type for different structural components, depending on the required stability and movement tolerance.
- 😀 Real-world examples of roll, pin, and fixed supports are illustrated with bridges and trusses, showing how these supports adapt to expansion or contraction due to temperature changes.
- 😀 The script explains the critical role of these supports in preventing structural damage, such as cracking or warping, due to movement or stress.
- 😀 The lesson encourages students to understand the difference between these supports and apply this knowledge when analyzing or constructing buildings and bridges.
Q & A
What are the three types of supports mentioned in the video?
-The three types of supports are roller, hinge (sendi), and fixed (jepit).
What is the main characteristic of the roller support?
-The roller support has wheels and can only resist vertical forces, not horizontal forces or moments. It can move horizontally.
Why can the roller support only resist vertical forces?
-The roller support is designed with wheels, which allow horizontal movement. As a result, it cannot resist horizontal forces or moments, but only vertical forces.
What is the function of the hinge (sendi) support in a structure?
-The hinge support can resist both vertical and horizontal forces but cannot resist moments (torsional forces). It acts like a pivot point.
What distinguishes the hinge (sendi) from the roller support?
-The hinge support does not have wheels and can resist both vertical and horizontal forces, while the roller support can only resist vertical forces.
What is the most stable support type according to the video?
-The most stable support type is the fixed support (jepit), which can resist vertical, horizontal forces, and moments.
Why is the fixed support considered the most stable?
-The fixed support is considered the most stable because it can resist forces from all directions—vertical, horizontal, and moments. This makes it capable of holding the structure firmly in place.
How do roller and hinge supports work together in construction, such as in bridges or trusses?
-In structures like bridges or trusses, roller and hinge supports are used to accommodate the expansion and contraction due to temperature changes. The roller allows horizontal movement, while the hinge can resist both vertical and horizontal forces.
What would happen if a fixed support was used instead of a roller or hinge support in certain structures?
-If a fixed support was used instead of a roller or hinge, the structure might experience excessive stress or damage, as the fixed support cannot accommodate movement due to expansion or contraction of the materials.
What are some examples of structures that use these supports?
-Examples of structures that use these supports include bridges, trusses, and buildings. Roller and hinge supports are commonly used in bridges, while fixed supports are used in certain parts of buildings, like columns and beams.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

VIDEO PEMBELAJARAN ANALISIS STRUKTUR 1 MATERI GAYA DALAM PADA KONSTRUKSI BALOK SEDERHANA

Mekanika Statis Tentu: Jenis Tumpuan
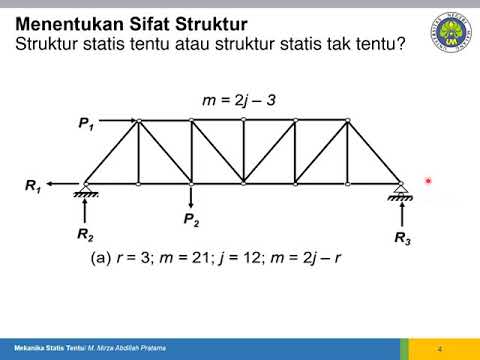
Mekanika Statis Tentu: Struktur Statis Tentu atau Struktur Statis Tak Tentu?
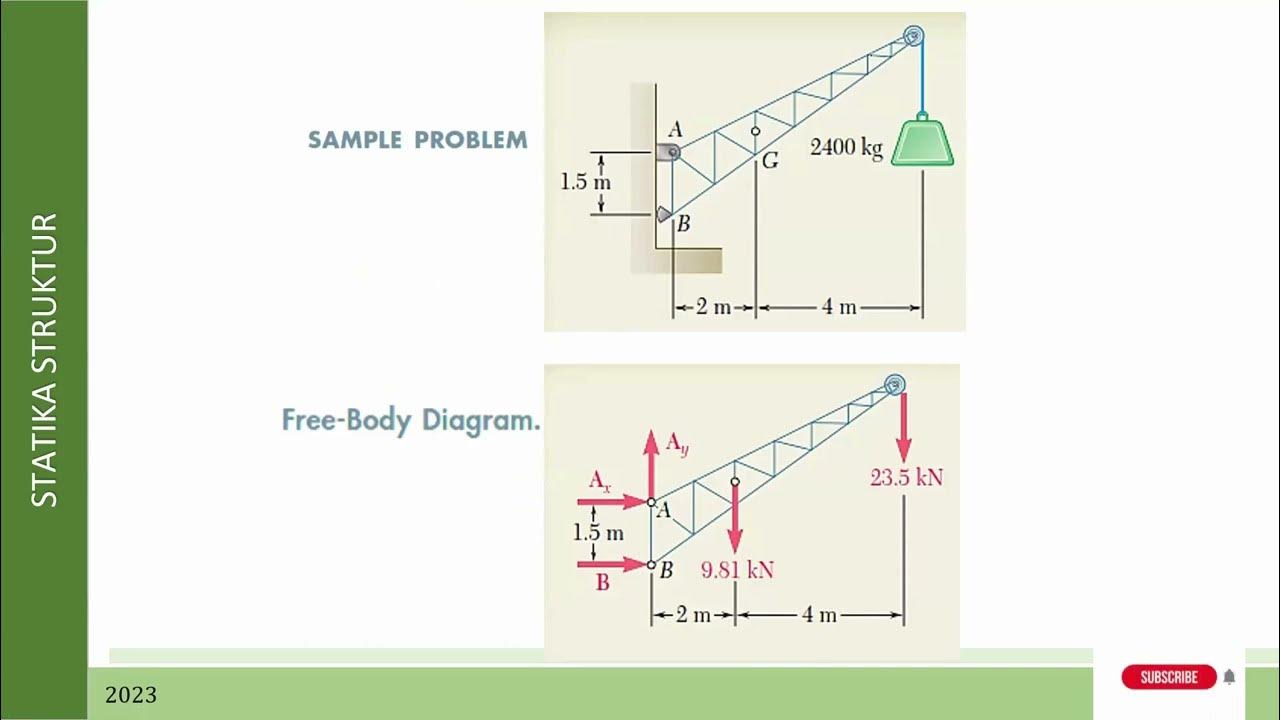
Teori Dasar Struktur Truss: Persamaan/Rumus, Reaksi Tumpuan, Gaya tarik atau tekan (T atau C)
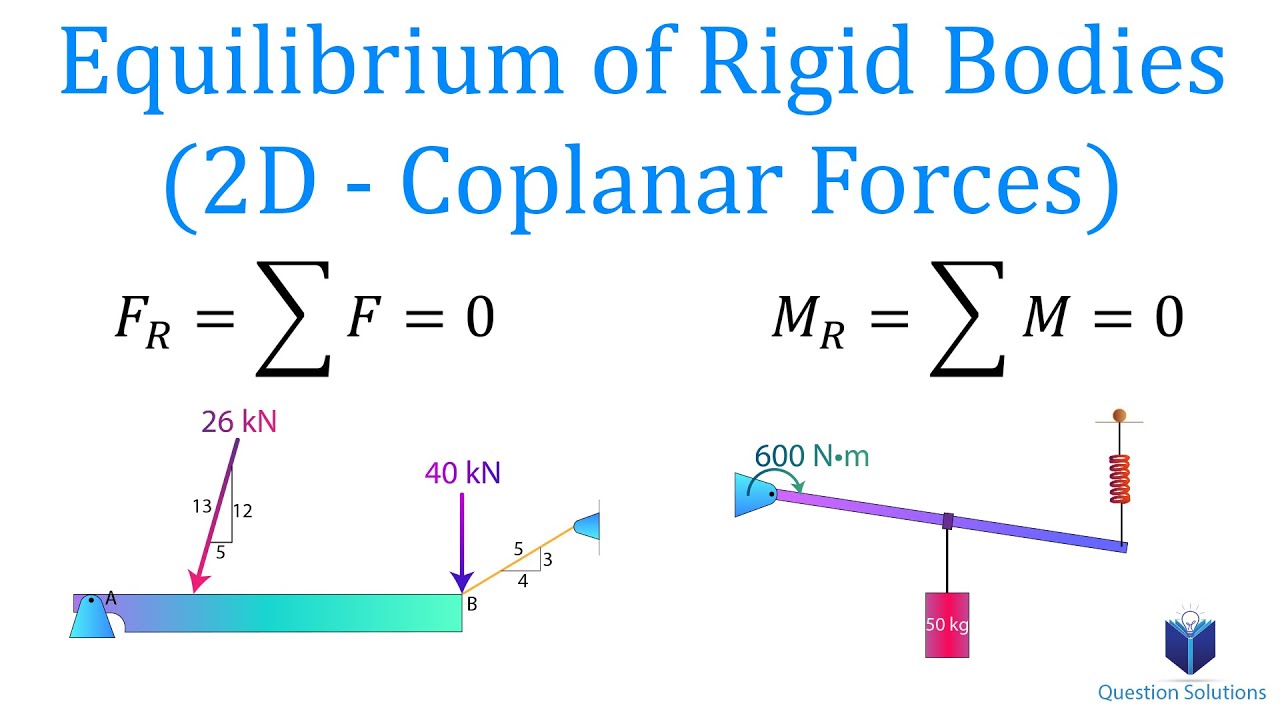
Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies (2D - Coplanar Forces) | Mechanics Statics | (Solved examples)

S-10 Pengenalan Truss
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
