Resumão: SISTEMA ARTICULAR
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Professor Natália Renc provides an in-depth overview of the human body's joint system, covering the three main types of articulations: synovial, fibrous, and cartilaginous. She explains how synovial joints allow the most movement, with complex structures including capsules, synovial fluid, and articular cartilage. Fibrous joints, such as sutures and gomphosis, offer limited or no movement, while cartilaginous joints, like the pubic symphysis, allow slight movement. The video also touches on additional resources for further learning, such as study materials and membership benefits, encouraging viewers to engage and ask questions for more personalized insights.
Takeaways
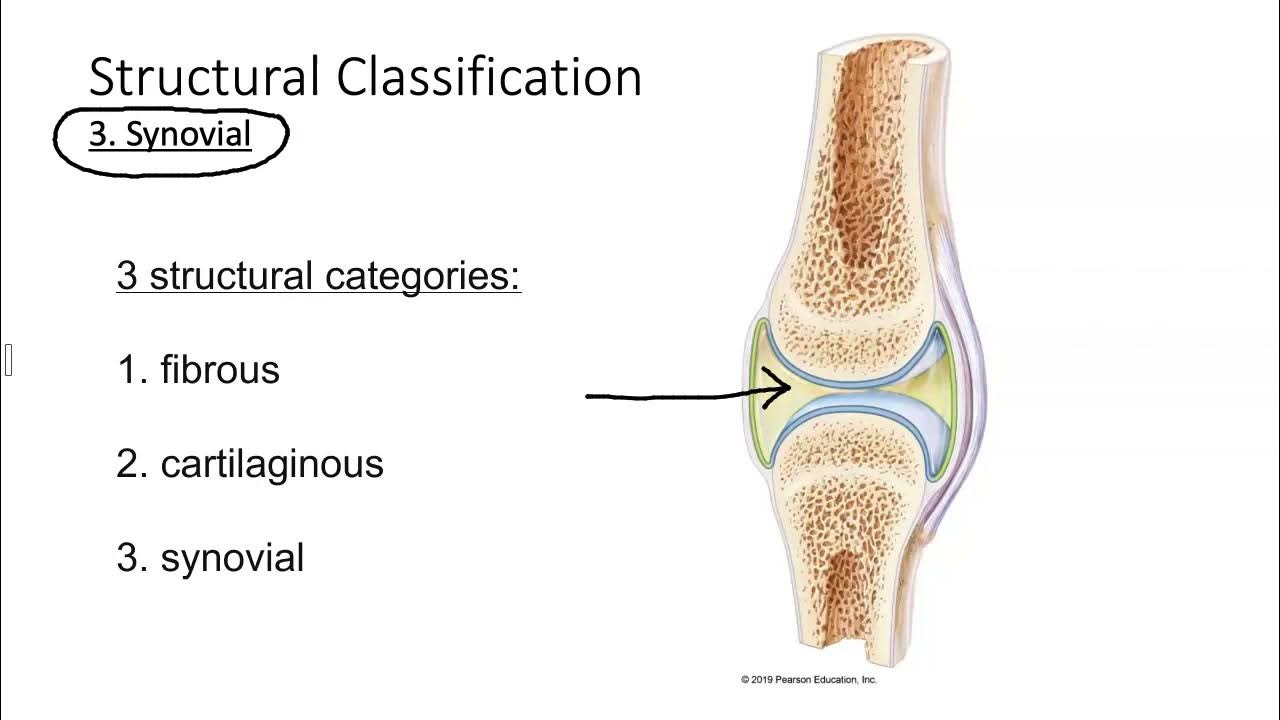
- 😀 Joints are the union or junctions between two or more bones in the human body.
- 😀 The main types of joints are synovial, fibrous, and cartilaginous joints.
- 😀 Synovial joints (diarthroses) are the most mobile and complex joints in the body.
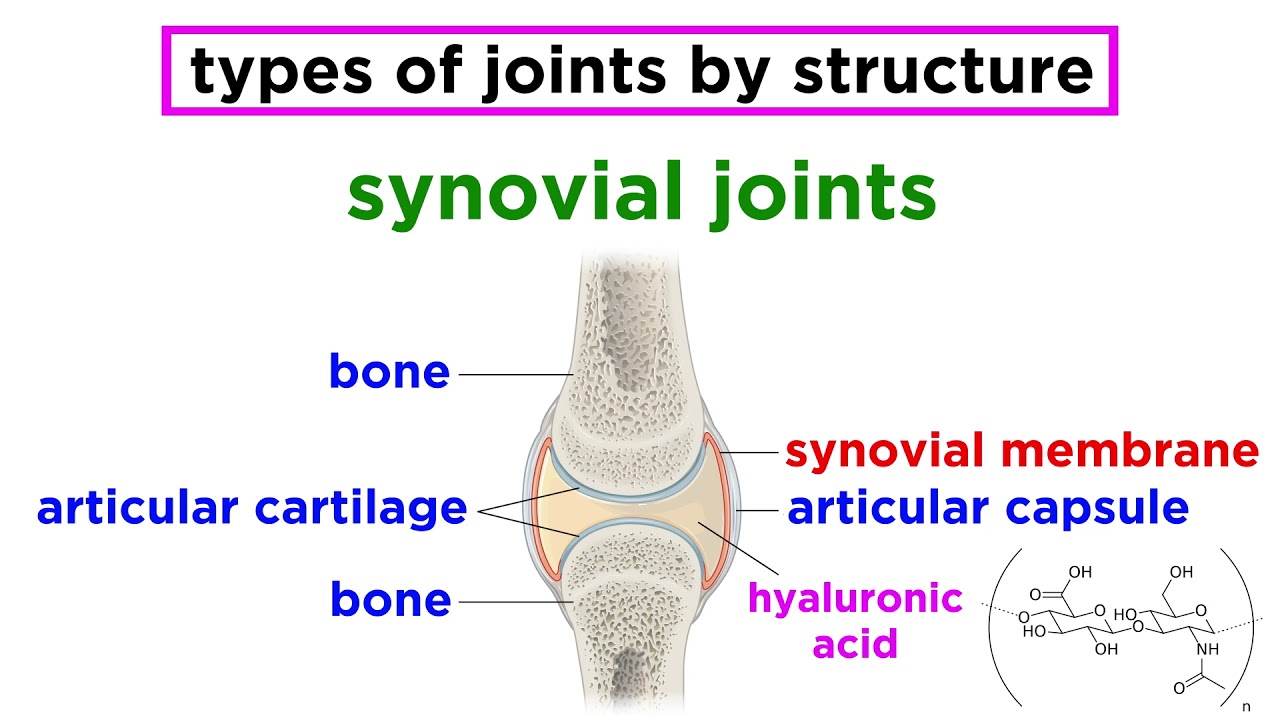
- 😀 Synovial joints are characterized by a synovial capsule, synovial fluid, and articular cartilage.
- 😀 Ligaments in synovial joints help control and limit movement to specific directions.
- 😀 Fibrous joints (synarthroses) are united by fibrous tissue and allow minimal or no movement.
- 😀 Examples of fibrous joints include sutures, syndesmoses, and gomphoses.
- 😀 Cartilaginous joints (amphiarthroses) allow slight movement and are joined by cartilage.
- 😀 Two types of cartilaginous joints are synchondroses (united by hyaline cartilage) and symphyses (united by fibrocartilage).
- 😀 Synchondroses are often temporary, like the epiphyseal plate in growing bones.
- 😀 Symphyses are strong joints that allow limited movement, such as the pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs.
Q & A
What are the three main types of joints in the human body?
-The three main types of joints in the human body are synovial joints, fibrous joints, and cartilaginous joints.
What are synovial joints also known as, and what is their main characteristic?
-Synovial joints are also known as diarthroses. They are characterized by a large range of motion and a more complex structure to support various movements.
What is the role of synovial fluid in synovial joints?
-Synovial fluid is produced by the articular capsule and fills the joint cavity. Its primary role is to lubricate the joint, reducing friction and allowing smooth movement.
How are the bones in synovial joints connected?
-In synovial joints, the bones are connected by a capsule called the articular capsule, and the surfaces of the bones are covered by articular cartilage.
What are the primary components of fibrous joints?
-Fibrous joints are connected by fibrous tissue. These joints typically allow little to no movement, depending on the length of the fibrous tissue connecting the bones.
What are the types of fibrous joints mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions three types of fibrous joints: sutures (such as cranial sutures), syndesmoses (like the interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna), and gomphosis (the joint between a tooth and its socket).
What is the defining feature of cartilaginous joints?
-Cartilaginous joints are characterized by the bones being united by cartilage, either hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage.
What are the two types of cartilaginous joints, and what differentiates them?
-The two types of cartilaginous joints are synchrondroses (primary cartilaginous joints) and symphyses (secondary cartilaginous joints). Synchondroses are usually temporary, like the epiphyseal plate, and are made of hyaline cartilage. Symphyses are more permanent and are composed of fibrocartilage, such as in the pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs.
What is the significance of ligaments in synovial joints?
-Ligaments in synovial joints help to stabilize the joint by restricting movements to the correct range and direction, ensuring that the bones move appropriately.
Where can we find synovial, fibrous, and cartilaginous joints in the human body?
-Synovial joints are found in areas like the knees, elbows, and shoulders, where a large range of motion is required. Fibrous joints are found in places like the skull (sutures) and between certain long bones (syndesmoses). Cartilaginous joints are found in the spine (intervertebral discs) and between the pubic bones (pubic symphysis).
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)