STATISTIKA : UJI NORMALITAS
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker provides an in-depth explanation of the Lilliefors normality test, a statistical method used to test if a sample comes from a normally distributed population. The process involves formulating hypotheses, calculating sample statistics (mean and standard deviation), computing Z-scores, and finding critical values using a Z-table. The test statistic (L) is compared to the critical value, and based on the result, a decision is made to either accept or reject the null hypothesis. The speaker demonstrates this process with an example, concluding that the sample in question likely comes from a normal distribution.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Lilliefors test is used to assess whether a sample comes from a normally distributed population.
- 😀 The null hypothesis (H₀) assumes the sample is from a normally distributed population, while the alternative hypothesis (H₁) assumes it is not.
- 😀 The significance level (α) for the hypothesis test is set at 5% or 0.05.
- 😀 To perform the Lilliefors test, the test statistic (L) is calculated using the formula L = max |F(Z_i) - Z_i|.
- 😀 The first step in the process is calculating the sample mean (X̄) and standard deviation (S).
- 😀 The Z-scores for each data point are computed using the formula Z_i = (X_i - X̄) / S.
- 😀 Data points need to be sorted in ascending order before calculating the Z-scores.
- 😀 After calculating the Z-scores, the corresponding values from the Z-table are used to compute the F(Z) values.
- 😀 The Lilliefors critical value for a sample size of 7 and α = 0.05 is found using a specific critical value table.
- 😀 If the calculated L value is smaller than the critical value from the table, the null hypothesis (H₀) is accepted, indicating the sample comes from a normally distributed population.
- 😀 In this case, the calculated L value of 0.1841 is smaller than the critical value of 0.300, leading to the acceptance of the null hypothesis and concluding the sample is normally distributed.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the script?
-The main topic of the script is about performing a normality test using the Lilliefors method for a given sample of data.
What is the Lilliefors test used for?
-The Lilliefors test is used for testing the normality of a sample when the data is not in a frequency distribution.
What are the two hypotheses mentioned in the script?
-The null hypothesis (H0) states that the sample comes from a population with a normal distribution, while the alternative hypothesis (H1) states that the sample does not come from a population with a normal distribution.
What statistical test is used in the Lilliefors method?
-The statistical test used in the Lilliefors method is the maximum absolute difference between the sample’s cumulative distribution function (CDF) and the expected cumulative distribution function (FZ).
What is the significance level (α) used in the example?
-In the example, the significance level (α) is 5% or 0.05.
What does the 'L' value represent in the Lilliefors test?
-The 'L' value in the Lilliefors test represents the maximum absolute difference between the observed and expected cumulative distribution values for the sample.
How is the Z-score calculated in the Lilliefors method?
-The Z-score is calculated using the formula: (X - X̄) / S, where X is each sample value, X̄ is the sample mean, and S is the sample standard deviation.
What role does the sample size (n) play in the Lilliefors test?
-The sample size (n) is crucial for calculating both the mean and the standard deviation, and it affects the critical value from the Lilliefors table.
What is the critical region for rejecting the null hypothesis in the Lilliefors test?
-The critical region for rejecting the null hypothesis occurs when the L value is greater than the critical value (0.300) obtained from the Lilliefors table.
What is the conclusion of the test if the L value does not fall within the critical region?
-If the L value does not fall within the critical region, the null hypothesis (H0) is accepted, meaning the sample data likely comes from a population with a normal distribution.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

UJI NORMALITAS DATA PERHITUNGAN MANUAL (METODE LILLIEFORS)

Uji Normalitas Menggunakan SPSS
Normally distributed errors - finite sample inference

Uji Normalitas Lilliefors | cara cepat uji normalitas lilliefors di Excel | Uji normalitas excel
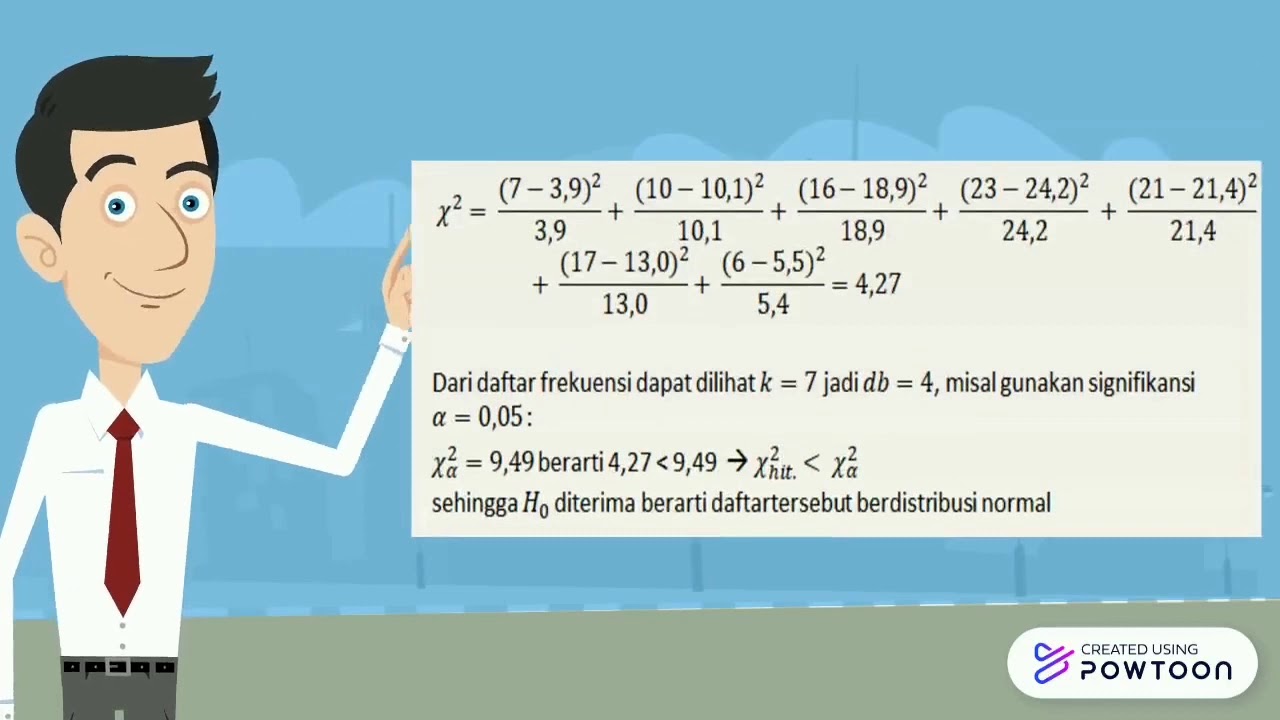
Uji Normalitas dan Homogenitas
Pertemuan 6 Uji Mean One Sample T-Test
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
