Hukum Hess dengan Data Perubahan Entalpi Pembentukan Standar - Swasti
Summary
TLDRIn this chemistry lesson, the instructor discusses how to calculate changes in enthalpy of a reaction using Hess's Law, focusing on the standard enthalpy of formation. The lesson covers the application of Hess's Law through examples, demonstrating how to determine enthalpy changes from given data, such as the enthalpy of formation of reactants and products. Various examples are provided, including combustion reactions, reactions involving gases like propane and ethene, and how to handle incomplete combustion. The video concludes with practice problems for students to work on independently, helping them solidify their understanding of enthalpy calculations in chemical reactions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Hess's Law states that the heat change in a reaction is independent of the path it takes, depending only on the initial and final states.
- 😀 The enthalpy change of a reaction (ΔH) can be determined by subtracting the sum of the enthalpy of formation of the reactants from that of the products.
- 😀 Standard enthalpy of formation refers to the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is formed from its elements in their standard states.
- 😀 The standard enthalpy of formation for elemental gases like O2 is considered zero because they are in their most stable form.
- 😀 A chemical reaction can be analyzed by using the equation: ΔH = ΣΔH_f (products) - ΣΔH_f (reactants).
- 😀 When calculating enthalpy changes for combustion reactions, the coefficients in the balanced equation must be considered.
- 😀 For combustion reactions, incomplete combustion produces CO (carbon monoxide) and H2O, while complete combustion yields CO2 and H2O.
- 😀 Hess's Law can be applied by using data on standard enthalpies of formation, as shown in the sample problems of the script.
- 😀 In the provided examples, the enthalpy changes for various reactions like combustion and formation are calculated step by step using known values.
- 😀 A formula is used to solve for unknown enthalpies of formation, which involves manipulating the equation based on the given data.
- 😀 The video encourages viewers to try practice problems at the end to reinforce the concepts of enthalpy change and Hess's Law.
Q & A
What is Hess's Law, and how does it relate to enthalpy changes?
-Hess's Law states that the heat change during a chemical reaction is the same, regardless of the number of steps in the reaction, as long as the initial and final states are the same. It means the enthalpy change of a reaction depends only on the initial and final states of the system and not on the path taken.
How can enthalpy changes be calculated according to Hess's Law?
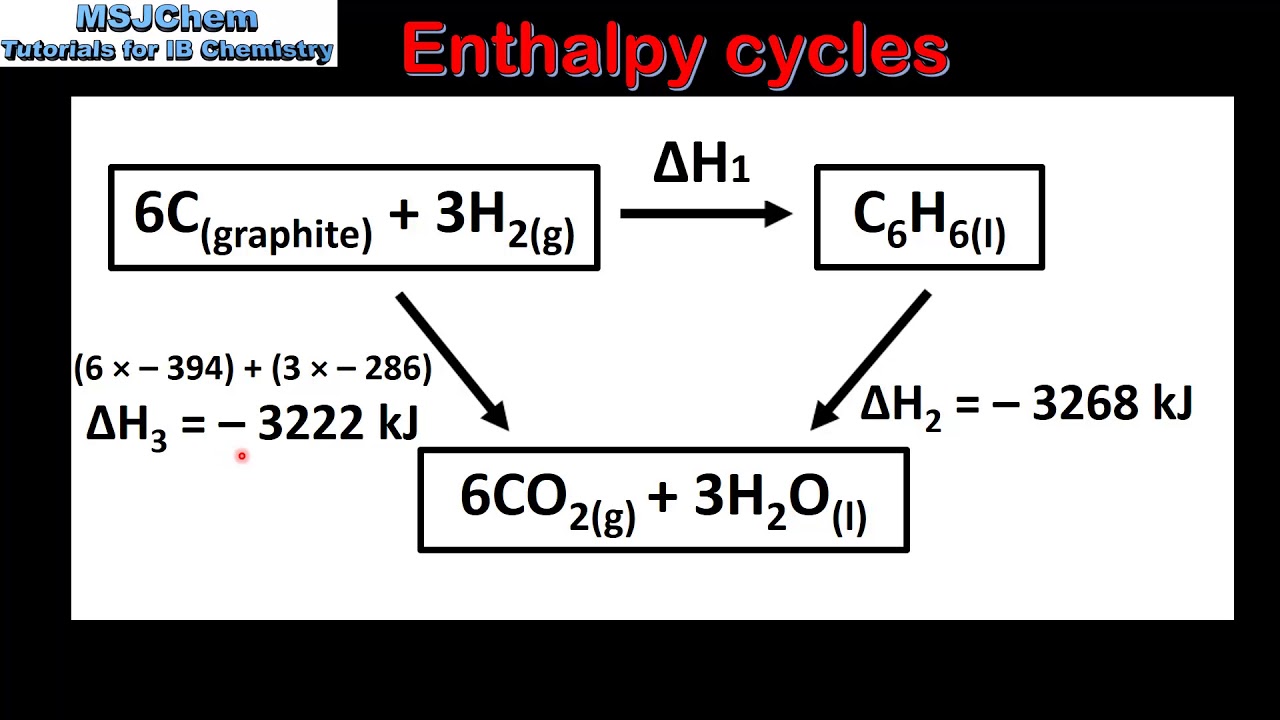
-Enthalpy changes can be calculated using three methods: based on standard enthalpies of formation, using a cycle diagram, and by combining multiple reactions. In the first method, the enthalpy of the reaction is the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the products minus the sum of the enthalpies of formation of the reactants.
What is the formula used to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction?
-The formula to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction is: ΔH_reaction = ΣΔHf(products) - ΣΔHf(reactants), where ΔHf represents the standard enthalpy of formation of each substance.
In the example given, how is the enthalpy change for the combustion of propane (C3H8) calculated?
-The enthalpy change for the combustion of propane is calculated by taking the sum of the enthalpies of formation of CO2 and H2O (products) and subtracting the sum of the enthalpies of formation of C3H8 and O2 (reactants). Since the enthalpy of formation of O2 is zero, it is not included in the calculation.
What is the enthalpy of formation of elemental oxygen (O2)?
-The enthalpy of formation of elemental oxygen (O2) is zero because it is considered a reference substance in its natural state.
How do you calculate the enthalpy change for the incomplete combustion of ethene (C2H4)?
-To calculate the enthalpy change for the incomplete combustion of ethene, you first balance the equation and then apply Hess's Law. The enthalpy change is the sum of the enthalpies of formation of CO2 and H2O (products) minus the sum of the enthalpies of formation of C2H4 and O2 (reactants).
Why is the enthalpy of formation of oxygen gas (O2) considered zero in calculations?
-The enthalpy of formation of oxygen gas (O2) is considered zero because it is a pure elemental form of oxygen, which is the reference point for standard enthalpies of formation.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction where NH3 reacts with O2 to produce NO2 and H2O?
-To find the enthalpy change for this reaction, you apply Hess's Law, using the standard enthalpies of formation for NH3, O2, NO2, and H2O. The enthalpy change for the reaction is the sum of the enthalpies of formation of NO2 and H2O (products) minus the enthalpies of formation of NH3 and O2 (reactants).
How do you calculate the enthalpy change for the combustion of acetylene (C2H2)?
-To calculate the enthalpy change for the combustion of acetylene, use the enthalpies of formation for CO2 and H2O. The enthalpy change is the difference between the sum of the enthalpies of formation of the products (CO2 and H2O) and the reactant (C2H2).
What is the enthalpy change for the combustion of 52 grams of C2H2 (acetylene)?
-To calculate the enthalpy change for the combustion of 52 grams of C2H2, first calculate the number of moles of C2H2 (52 grams / 26 g/mol = 2 moles). Then multiply the enthalpy change for the combustion of 1 mole of C2H2 (1082 kJ/mol) by the number of moles (2 moles), resulting in 2164 kJ.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

HUKUM HESS, ENTALPI PEMBENTUKAN DAN ENERGI IKATAN

Termokimia part 4- HUKUM HESS - Kimia SMA kelas 11 semester 1
5.2 Enthalpy cycles (SL)

Penentuan Entalpi Reaksi Berdasarkan Entalpi Pembentukan Standar | Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti

HUKUM HESS : Menentukan perubahan entalpi reaksi dengan Hukum Hess

LEI DE HESS (TERMOQUÍMICA) | Resumo de Química para o Enem
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
