HUKUM HESS, ENTALPI PEMBENTUKAN DAN ENERGI IKATAN
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script discusses the application of Hess's Law in thermodynamics, focusing on calculating reaction enthalpy changes. It presents examples involving the reaction of NH3 with HCl to form NH4Cl, demonstrating how to determine the enthalpy change using initial and final states. The script further illustrates how to manipulate chemical equations to align with known enthalpy values and calculate the enthalpy change for reactions such as S + O2 to SO2 and SO3. It also covers the calculation of reaction enthalpy using standard enthalpy formation data for C3H8 combustion and the use of bond energy data to determine the enthalpy change for the combustion of CH4.
Takeaways
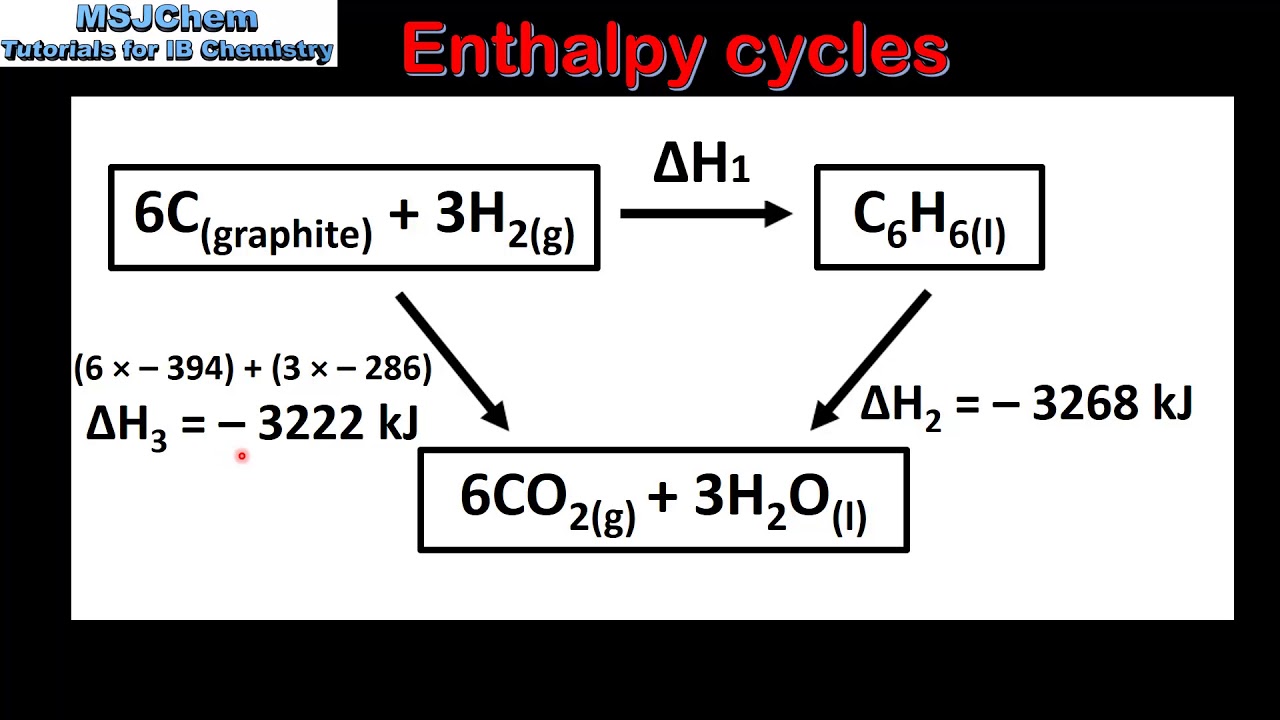
- 🔍 The script discusses the application of Hess's Law in calculating the enthalpy change of chemical reactions.
- 📚 It explains that the enthalpy change of a reaction depends only on the initial and final states, not the path taken.
- 🧪 The script provides an example of calculating the enthalpy change for the reaction between NH3 and HCl to form NH4Cl.
- 📐 It demonstrates how to adjust the direction of reactions and coefficients to match the given thermochemical equations.
- 🔢 The calculation involves summing the enthalpy changes of the reactants and products, taking into account their stoichiometric coefficients.
- 🌡 The script also covers the calculation of enthalpy change using standard enthalpies of formation for the combustion of C3H8.
- ⚖️ It highlights that the enthalpy of formation for diatomic gas molecules like O2, H2, and N2 is zero, simplifying calculations.
- 🔥 Another example provided involves the reaction of CH4 with O2 to form CO2 and H2O, emphasizing the importance of identifying the types of bonds in the reactants and products.
- 📈 The script explains that the enthalpy change of a reaction can be found by subtracting the energy of bond formation from the energy of bond breaking.
- 📝 It concludes with a detailed calculation for the enthalpy change of the combustion reaction of CH4, incorporating bond energies and stoichiometric coefficients.
Q & A
What is the first example problem discussed in the script?
-The first example problem discusses the calculation of the enthalpy change for the reaction NH3 + HCl to form NH4Cl.
What is the significance of the term 'Delta H' in the context of the script?
-In the script, 'Delta H' refers to the change in enthalpy, which is a measure of the heat absorbed or released in a chemical reaction.
How is the enthalpy change calculated for the reaction NH3 + HCl?
-The enthalpy change for the reaction NH3 + HCl is calculated by considering the standard enthalpies of formation of the reactants and products, and it is found to be -176 kJ.
What is the second example problem in the script about?
-The second example problem involves determining the enthalpy change for the reaction of sulfur and oxygen to form sulfur trioxide.
How does the script explain the application of Hess's Law?
-The script explains Hess's Law by demonstrating how to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction using the standard enthalpies of formation of reactants and products.
What is the role of stoichiometry in calculating the enthalpy change of a reaction?
-Stoichiometry is crucial in calculating the enthalpy change as it determines the coefficients of reactants and products, which are used to calculate the total enthalpy change.
What is the significance of the term 'exothermic' in the script?
-The term 'exothermic' is used in the script to describe a reaction that releases heat, such as the reaction NH3 + HCl forming NH4Cl.
How does the script handle the calculation when the reaction direction is reversed?
-When the reaction direction is reversed, the script instructs to reverse the sign of the enthalpy change to maintain the correct calculation.
What is the third example problem presented in the script?
-The third example problem is about calculating the enthalpy change for the combustion of propane (C3H8) using standard enthalpies of formation.
What is the purpose of identifying the type of bonds in the molecules involved in a reaction?
-Identifying the type of bonds in the molecules is necessary to calculate the energy changes associated with bond breaking and formation, which are used to determine the enthalpy change of the reaction.
How does the script use bond energies to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction?
-The script uses bond energies by summing the energy required to break the bonds in the reactants and subtracting the energy released in forming the bonds in the products to find the enthalpy change.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)