BIOLOGIA - Lezione 2 - Le Biomolecole
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive overview of key biomolecules essential for life, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It explains the structure, function, and importance of each class, detailing their roles in energy storage, cell structure, and communication. The script also covers the process of polymer formation and key examples such as glucose, triglycerides, and DNA. Furthermore, it introduces ATP as the cell’s energy currency. Ideal for learners, the video delivers foundational knowledge of biochemistry in an accessible and engaging manner.
Takeaways
- 😀 Biomolecules are essential for life and are either formed by living organisms or are used by them. They are typically large molecules, known as macromolecules or polymers, made of smaller units called monomers.
- 😀 Carbohydrates are the first class of biomolecules. They serve as energy sources and storage in humans and other organisms. Examples include glucose and starch.
- 😀 Lipids (fats and oils) are the second class of biomolecules. They also serve as energy reserves and play crucial roles in insulation and signaling. Examples include triglycerides and phospholipids.
- 😀 Proteins, formed by amino acids, are crucial for many functions such as structural support, movement, immune defense, transport, and enzyme catalysis.
- 😀 Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are key biomolecules responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. DNA holds the instructions for building an organism, while RNA helps in protein production.
- 😀 Biomolecules are formed through condensation reactions, where monomers are joined by the removal of a water molecule, while hydrolysis reactions break them down by adding water.
- 😀 Carbohydrates are divided into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. The most common polysaccharides are starch in plants and glycogen in animals.
- 😀 Proteins have a wide variety of functions. Some proteins serve as enzymes, speeding up chemical reactions. Others transport substances like oxygen (hemoglobin) or protect the body (antibodies).
- 😀 Lipids, including triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids, are vital for energy storage, forming cell membranes, and signaling in the body.
- 😀 The ATP molecule is a key energy carrier in cells, storing and transferring energy. It is made up of ribose, adenine, and three phosphate groups, playing an essential role in metabolism.
Q & A
What are biomolecules and why are they important for life?
-Biomolecules are large molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen, which are essential for life. They play critical roles in the structure, function, and regulation of cells, tissues, and organs in living organisms.
What is the role of carbohydrates in biological systems?
-Carbohydrates serve as a primary energy source for living organisms. They also function as energy reserves and are involved in structural support, particularly in plant cell walls (e.g., cellulose) and in storing energy (e.g., starch and glycogen).
Can you explain the difference between monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides?
-Monosaccharides are simple sugars like glucose, oligosaccharides consist of a few sugar molecules, and polysaccharides are long chains of sugar molecules. Examples include starch (polysaccharide) and sucrose (oligosaccharide).
How do lipids function in biological systems?
-Lipids, such as fats and oils, are primarily used for long-term energy storage, insulation, and forming cellular membranes. They are hydrophobic, meaning they do not dissolve in water.
What is the significance of proteins in living organisms?
-Proteins are made of amino acids and have diverse functions, including providing structural support, enabling movement (e.g., muscle proteins), facilitating immune response (e.g., antibodies), and catalyzing biochemical reactions (e.g., enzymes).
What is the relationship between amino acids and proteins?
-Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Proteins are formed when amino acids are linked together in specific sequences, determining their structure and function.
How do nucleic acids like DNA and RNA function in cells?
-DNA carries the genetic information necessary for the functioning and reproduction of cells, while RNA helps translate that information into proteins. RNA also has additional roles such as in gene regulation.
What is ATP and what role does it play in metabolism?
-ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a nucleotide that functions as a carrier and store of energy in cells. It releases energy when needed by breaking one of its phosphate bonds and is involved in processes like muscle contraction and protein synthesis.
What is the process of polymerization in biomolecules?
-Polymerization is the process by which smaller monomer units are chemically bonded to form larger, more complex polymers. In biomolecules, monomers like amino acids, sugars, and nucleotides are linked together to form proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids.
What is the difference between condensation and hydrolysis in the context of biomolecules?
-Condensation is the process where monomers are linked together by releasing a water molecule, forming a polymer. Hydrolysis is the opposite process, where a water molecule is added to break down polymers into their monomers.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Beginners Guide to MACROMOLECULES

La Química de los Alimentos: Cómo los Compuestos Influyen en tu Nutrición y Salud
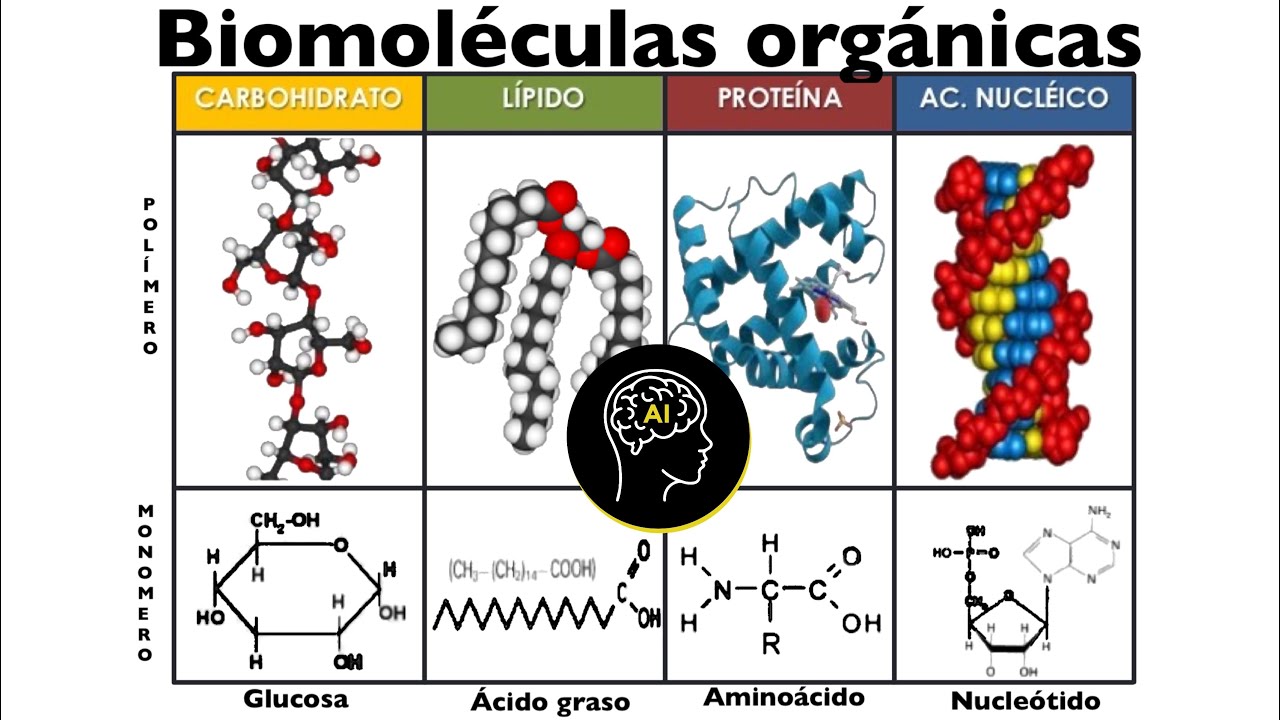
Biomoléculas presentes en células (orgánicas): carbohidratos, lípidos, proteínas y ácidos nucleicos

Biomoléculas (atualizado em 2023)

Biomolecules (Updated 2023)

PHYSICAL SCIENCE - BIological Macromolecules
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
