An Overview of Memory - CompTIA A+ 220-1101 - 3.2
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth overview of RAM (Random Access Memory) and memory modules in computers. It explains the role of RAM in loading and running applications, distinguishes between DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) and SO-DIMM (Small Outline DIMM), and explores the evolution of memory types from DDR2 to DDR5. The video highlights key features such as speed, capacity, compatibility, and installation processes, emphasizing the importance of understanding the different memory standards for optimal computer performance. It also covers physical aspects like notches to ensure proper installation and prevent compatibility issues.
Takeaways
- 😀 RAM (Random Access Memory) is temporary, high-speed memory used by applications and documents when they are loaded into your system.
- 😀 RAM is not the same as storage (SSD or hard drive); it is used for immediate data processing by the CPU.
- 😀 Modern memory slots in most computers are standardized, enabling faster data transfer between RAM and the CPU.
- 😀 DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module) is the standard memory module used in most desktop computers, allowing 64-bit data transfer.
- 😀 Laptop and mobile devices typically use SO-DIMM (Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module), which is about half the size of a DIMM.
- 😀 RAM modules, like DIMMs and SO-DIMMs, are made of dynamic RAM (D-RAM), which needs to be constantly refreshed to maintain data integrity.
- 😀 Random Access Memory allows for quick data retrieval from any part of the module without needing to sequentially access data.
- 😀 Modern systems use synchronous memory, which relies on a system clock to regulate data transfers in and out of RAM.
- 😀 Notches on RAM modules (DIMM and SO-DIMM) are designed to prevent incorrect installation, ensuring compatibility with the system's memory slot.
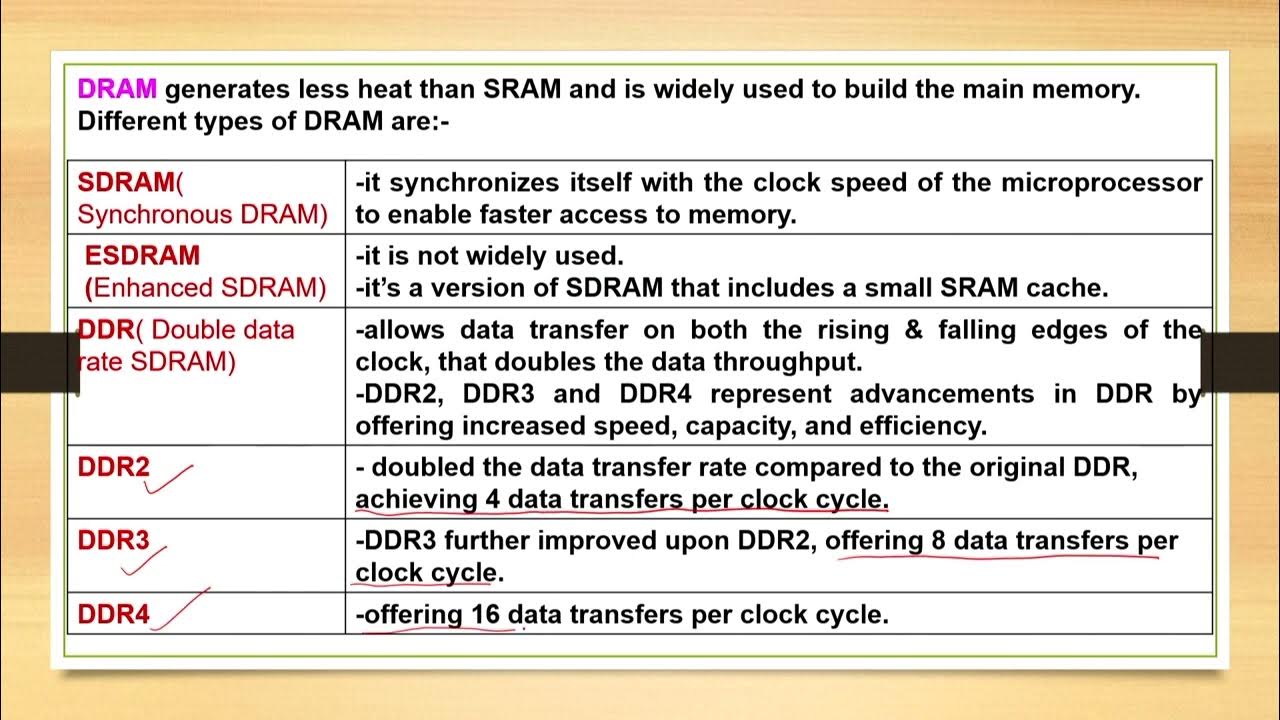
- 😀 Memory types, such as DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5, differ in terms of speed and capacity, with newer versions offering faster data transfer and larger capacities.
- 😀 DDR3 supports up to 16GB per module, DDR4 supports up to 64GB, and DDR5 also supports up to 64GB but with even faster data transfer rates.
- 😀 Each type of RAM is not backward compatible, meaning DDR4 and DDR5 cannot be used in systems designed for older memory types like DDR3 or DDR2.
Q & A
What is the main difference between RAM and storage devices like SSDs and hard drives?
-RAM is temporary, high-speed memory used by the CPU to store data for quick access while running applications. Storage devices like SSDs and hard drives are permanent storage solutions where data is saved long-term, even when the computer is turned off.
What does the term 'RAM' refer to in the context of a computer system?
-RAM stands for Random Access Memory. It is a high-speed, temporary memory used by the computer to store and quickly access data needed by running applications and the operating system.
What is the role of memory slots in a computer?
-Memory slots allow memory modules (DIMMs or SO-DIMMs) to be installed on the motherboard, enabling the system to transfer data quickly between the memory and the CPU, which is essential for system performance.
What is a DIMM and how does it function in a computer?
-A DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module) is a type of memory module that fits into memory slots on the motherboard. It has connectors on both sides, allowing for efficient data transfer between the memory and the CPU, impacting overall system speed.
What is the difference between a DIMM and a SO-DIMM?
-A SO-DIMM (Small Outline DIMM) is a smaller version of a DIMM, typically used in laptops and mobile devices where space is limited. It is half the width of a standard DIMM but functions in the same way.
Why is RAM referred to as 'dynamic' and 'random'?
-RAM is referred to as 'dynamic' because it needs to be constantly refreshed to retain data. It is 'random' because any part of the memory can be accessed directly without needing to go through the rest of the data sequentially.
What does the clock cycle in a computer's memory system do?
-The clock cycle regulates the flow of data into and out of the memory modules, synchronizing the transfer of data with the other components of the system to ensure smooth operations.
How do notches on memory modules prevent incorrect installations?
-The notches on memory modules are designed to ensure that only the correct type of memory can be installed into a specific memory slot. For example, DDR3 and DDR4 modules have differently placed notches to prevent them from being installed in incompatible slots.
What is the significance of DDR memory in modern computers?
-DDR (Double Data Rate) memory allows for faster data transfer by transmitting data twice in each clock cycle, which significantly improves the speed and efficiency of modern computers compared to older SDR (Single Data Rate) memory.
What are the key differences between DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 memory?
-Each generation of DDR memory offers improvements in speed and capacity. DDR2 is slower and has lower capacity than DDR3, which doubled the data rate. DDR4 further increases speed and supports larger capacities (up to 64GB per module), while DDR5 offers even faster speeds and remains at 64GB per module, with additional improvements in efficiency.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)