Konsep Node Luar Ruang
Summary
TLDRThis lecture discusses the concept and challenges of outdoor wireless network infrastructure in the context of increasing connectivity demands. It covers the role of outdoor nodes in extending network reach, enhancing capacity, and ensuring stable connections in public spaces. Key topics include weather resistance, signal range, power over Ethernet (PoE), antenna strength, and the importance of strategic node placement. The lecture also highlights the technical components required for building outdoor network infrastructures, such as routers, switches, and enclosures, and addresses issues like interference, maintenance, security, and regulatory approvals.
Takeaways
- 😀 Outdoor network nodes play a critical role in extending wireless coverage in public and commercial spaces, enhancing connectivity in outdoor areas like parks and campuses.
- 😀 Weatherproofing is essential for outdoor nodes, with devices often rated IP67 or IP68 to withstand extreme weather conditions such as rain, dust, and humidity.
- 😀 Outdoor network nodes offer wider signal range compared to indoor devices, reducing the need for additional repeaters or access points in large, open spaces.
- 😀 Power over Ethernet (PoE) simplifies the installation of outdoor nodes by providing both data and power through a single Ethernet cable, ideal for locations without nearby power sources.
- 😀 High-quality antennas, including omnidirectional and directional types, are crucial for maintaining strong and stable signal coverage in outdoor environments.
- 😀 Challenges of outdoor network nodes include weather-related damage, signal interference from physical obstacles, bandwidth congestion in high-traffic areas, and security risks like theft or vandalism.
- 😀 To mitigate weather damage, outdoor devices with high durability standards (e.g., IP67) reduce the need for frequent repairs and lower long-term maintenance costs.
- 😀 Using less congested frequencies, such as 5 GHz, minimizes interference, especially in crowded environments where many devices are competing for bandwidth.
- 😀 Strategic placement of outdoor nodes in secure locations, like high poles or monitored areas, reduces the risks of theft or damage and ensures optimal signal reach.
- 😀 Key components for building an outdoor network infrastructure include outdoor access nodes, powerful antennas, PoE switches/injectors, weatherproof enclosures, and secure mounting structures.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the transcript?
-The main topic discussed is the concept of outdoor wireless network nodes and the challenges associated with building wireless infrastructure in outdoor environments.
Why is outdoor network infrastructure important in the current connectivity era?
-Outdoor network infrastructure is crucial because it expands the reach of wireless networks to open spaces, such as parks, public areas, and campuses, where connectivity demands are increasing.
What are the primary challenges when building outdoor wireless networks?
-The challenges include weather conditions, physical obstructions like tall buildings and trees, interference from nearby devices, and the need for robust security and maintenance protocols.
What are some key features of outdoor nodes?
-Outdoor nodes are designed to be weatherproof, with features like high-power antennas for extended signal range, Power over Ethernet (PoE) for efficient installation, and protection against extreme weather conditions.
How does Power over Ethernet (PoE) benefit outdoor installations?
-PoE allows outdoor nodes to receive both power and data through a single Ethernet cable, which simplifies installation, reduces costs, and eliminates the need for separate power sources, making it ideal for remote or hard-to-reach locations.
What are the differences between omnidirectional and directional antennas in outdoor nodes?
-Omnidirectional antennas spread signals in all directions, while directional antennas focus the signal in a specific direction, which can be useful for targeting particular areas and extending the signal range.
What is the role of the enclosure in outdoor nodes?
-The enclosure protects the node from harsh weather conditions, such as rain, dust, and extreme temperatures. It typically meets IP67 or IP68 standards for water and dust resistance.
How can interference in outdoor wireless networks be minimized?
-Interference can be minimized by choosing less congested frequencies (such as 5 GHz), using powerful antennas, and ensuring that outdoor nodes are installed in locations where interference from nearby devices and structures is minimal.
What are the main components required to build outdoor wireless infrastructure?
-Key components include outdoor access nodes, antennas, Power over Ethernet (PoE) systems, enclosures, switches, routers, backhaul connections, installation poles or towers, security systems, and network management software.
What are the security challenges related to outdoor wireless networks, and how can they be addressed?
-Outdoor wireless networks are vulnerable to vandalism or theft. To mitigate these risks, security measures such as strong protective covers, surveillance cameras, and installation in hard-to-reach locations should be employed.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Wireless Networking Explained | Cisco CCNA 200-301
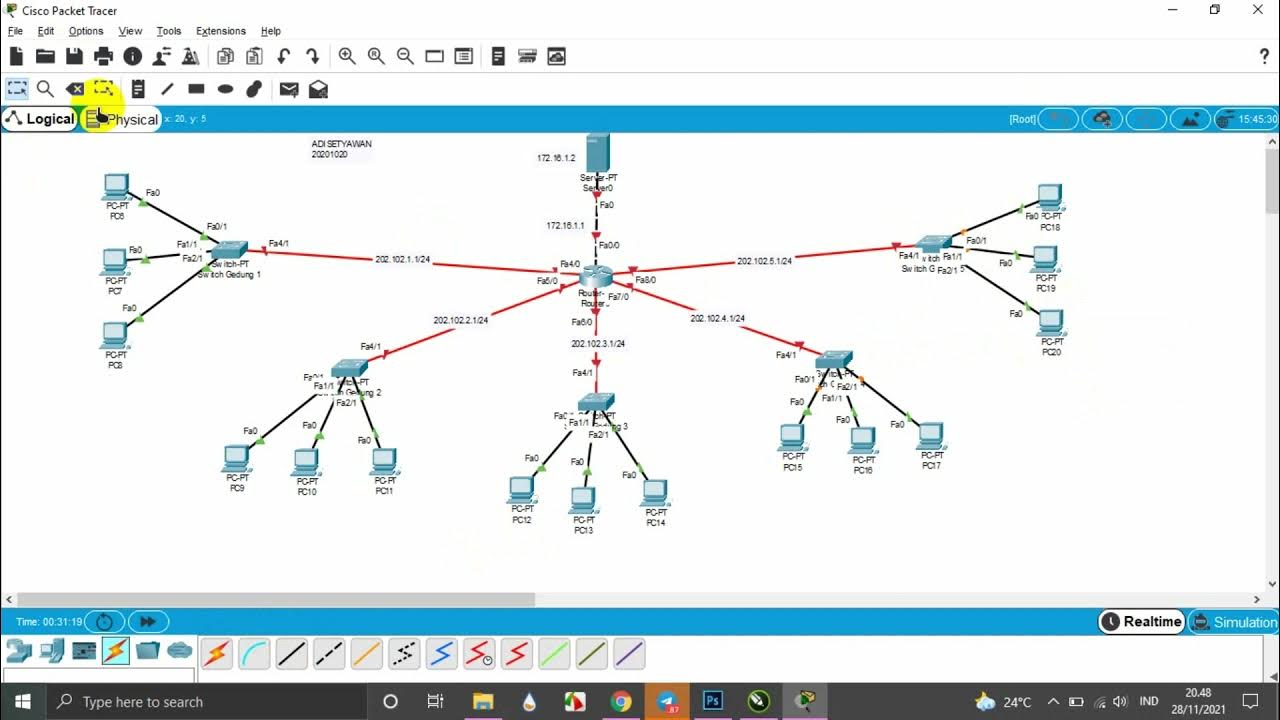
TUTORIAL MEMBUAT TOPOLOGI JARINGAN STAR DI GEDUNG 5 LANTAI MENGGUNAKAN CISCO PAKET TRACER

Membangun Jaringan Nirkabel - Teknik Komputer dan Jaringan

Jaringan Nirkabel {Wireless)

Introducing Next-Generation Wireless for Warehouse Operations

Wireless Networking - CompTIA Network+ N10-009 - 1.5
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
