Dasar Elektronika : Transistor
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed introduction to transistors, a fundamental component in modern electronics. It explains the transistor's structure, consisting of three parts: emitter, base, and collector, and highlights how these elements function in amplification and switching. The lesson covers different types of transistors (NPN and PNP), their behavior in active and saturated states, and the effects of biasing. Key applications in electronics such as radios, televisions, and computers are also discussed. The video concludes by encouraging students to simulate transistor performance and analyze its behavior using provided tools.
Takeaways
- 😀 Transistors are crucial components in modern electronics, used in devices like TVs, radios, and computers.
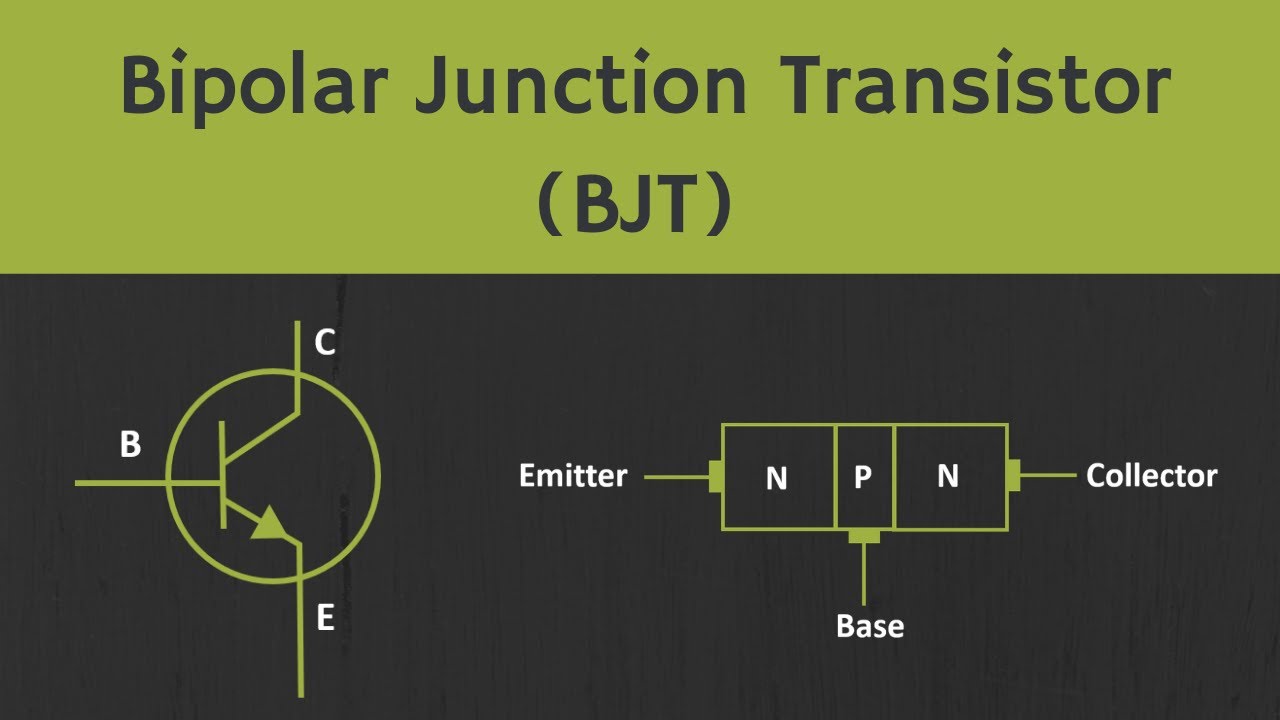
- 😀 A transistor consists of three main parts: emitter, base, and collector.
- 😀 Transistors function as amplifiers, switches, and signal processors, enabling efficient electrical control.
- 😀 There are two main types of transistors: NPN and PNP, which differ in their construction and current flow.
- 😀 The transistor's active region allows it to amplify signals by controlling the current between the emitter and collector.
- 😀 In the saturation region, the transistor acts as a switch, with the collector current reaching its maximum.
- 😀 The cutoff region occurs when the transistor is off, and no current flows through the collector.
- 😀 Biasing is essential for transistor operation, with forward bias allowing current flow and reverse bias causing leakage current.
- 😀 A transistor’s biasing can be forward or reverse, impacting its amplification and current flow properties.
- 😀 Transistors have applications in amplification, switching, and generating oscillations for electronics like oscillators and signal processing.
- 😀 Simulations of transistor behavior can help in understanding their operational characteristics and designing efficient circuits.
Q & A
What is the main function of a transistor in electronics?
-The main function of a transistor in electronics is to act as an amplifier or a switch, controlling the flow of electrical signals in various devices like radios, televisions, and computers.
What are the three terminals of a transistor and their functions?
-The three terminals of a transistor are the emitter (E), which supplies current to the transistor; the base (B), which controls the flow of current between the emitter and collector; and the collector (C), which collects current from the transistor.
How does a transistor amplify a signal?
-A transistor amplifies a signal by controlling a larger current through the collector with a smaller current at the base. This results in an output signal that is stronger than the input.
What are the two main types of transistors and how are they different?
-The two main types of transistors are NPN and PNP. NPN transistors consist of a layer of N-type material between two layers of P-type material, while PNP transistors have a P-type material between two N-type materials. Their operation is reversed, with current flowing in opposite directions.
What is biasing in a transistor and why is it important?
-Biasing in a transistor refers to the process of applying a voltage to the base terminal to set the operating point of the transistor. Proper biasing is crucial for ensuring the transistor operates in the correct region (active, saturation, or cutoff) and performs optimally.
What are the different operating regions of a transistor?
-The three operating regions of a transistor are: the **active region**, where the transistor acts as an amplifier; the **saturation region**, where the transistor acts as a switch, fully 'on'; and the **cutoff region**, where the transistor is fully 'off' and no current flows.
What happens when a transistor is forward biased?
-When a transistor is forward biased, current flows from the emitter to the base, allowing the transistor to conduct and amplify the input signal. This creates a larger current in the collector, which is the output signal.
What is the result of reverse biasing in a transistor?
-Reverse biasing in a transistor prevents current from flowing through the emitter-collector path, causing leakage current. This can lead to higher temperatures and potential damage to the transistor if the leakage current is too large.
How can a transistor be used as a switch in a circuit?
-A transistor can be used as a switch by applying a small voltage to the base. If the base-emitter junction is forward biased, the transistor turns 'on,' allowing current to flow between the collector and emitter. If reverse biased, the transistor turns 'off,' blocking current flow.
What are some common applications of transistors in electronics?
-Transistors are widely used in applications such as signal amplification, voltage regulation, switching circuits, rectifiers (converting AC to DC), and oscillators for generating periodic waveforms in devices like radios, computers, and televisions.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)