Everything About Circle Theorems - In 3 minutes!
Summary
TLDRIn this engaging tutorial on circle theorems, viewers learn essential concepts including chords, semicircles, tangents, subtended angles, and relationships between angles in segments. The video illustrates how various geometric principles apply to different shapes within a circle, emphasizing key properties like the right angles formed by tangents and radii. It also presents practical examples, encouraging viewers to solve a related problem while highlighting the interconnectedness of angles. The friendly host invites questions and encourages subscriptions, making complex math accessible and interactive for learners.
Takeaways
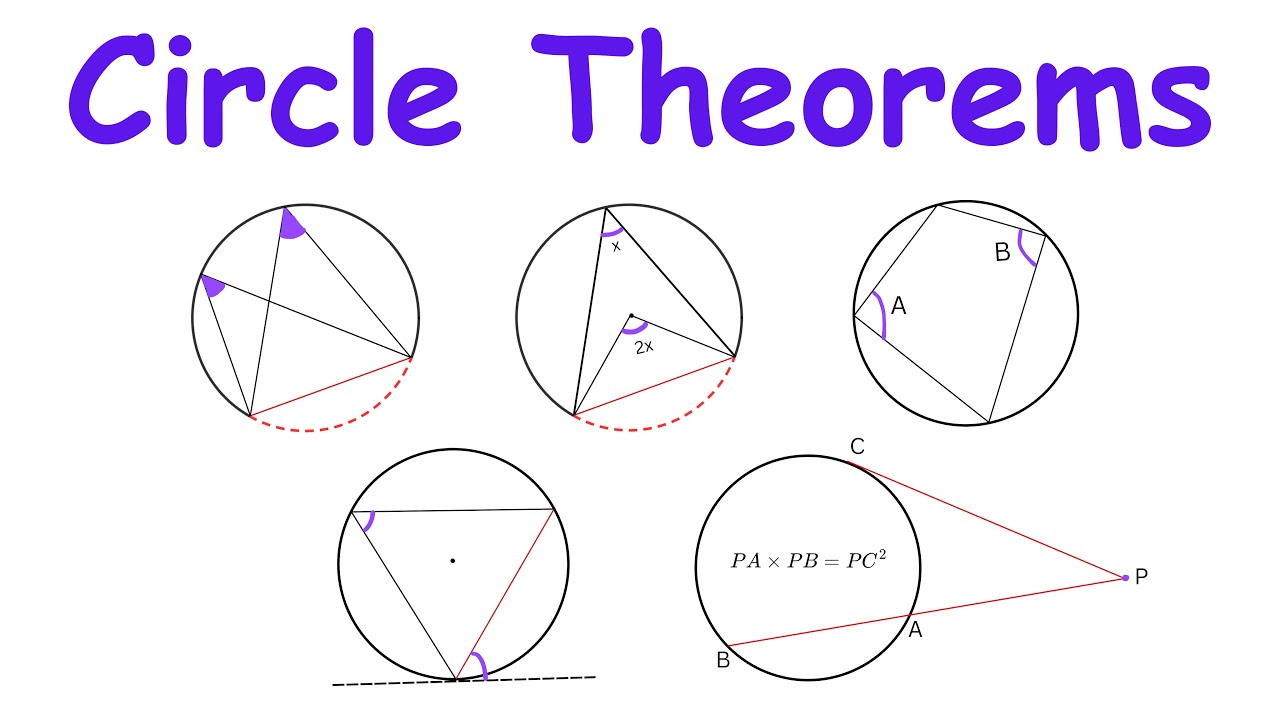
- 😀 A circle theorem helps determine angles within a circle that contains other shapes.
- 🔷 A chord is a line segment that connects two points on a circle, lying below the diameter.
- ⚪ The perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through the center of the circle.
- 🔺 Any triangle inscribed in a semicircle will always have an angle of 90° at the circumference.
- 📏 A tangent to a circle forms a right angle (90°) with the radius at the point of contact.
- 👀 The subtended angle is the angle formed by a line from an object to the edge of the circle.
- ⚖ Angles in the same segment subtended by the same arc are equal.
- 🔄 In a cyclic quadrilateral, opposite angles add up to 180°.
- 🔗 The lengths of two tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
- 📐 The angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment.
Q & A
What is a circle theorem?
-A circle theorem is essentially about finding angles within a circle that has another shape inside it. These shapes are usually not drawn to scale, which can make solving them more challenging.
What is a chord in the context of a circle?
-A chord is a line that lies below the diameter and connects two points on the circumference of the circle.
What is the significance of a perpendicular bisector of a chord?
-The perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through the center of the circle, indicating that it divides the chord into two equal parts.
What happens to the angle formed at point B in a semicircle with a triangle inscribed?
-The angle at point B becomes 90°, regardless of the type of triangle inscribed within the semicircle.
How is a tangent defined in relation to a circle?
-A tangent is a line that touches the outside edge of a circle. When this line meets the radius, it forms a 90° angle.
What is a subtended angle?
-A subtended angle is formed by an object, such as a tree, when viewed from a specific point, with the angle measured at that point.
What is the relationship between angles in the same segment of a circle?
-Angles in the same segment that are subtended by the same arc are equal.
What is a cyclic quadrilateral?
-A cyclic quadrilateral is a four-sided shape with all corners touching the circumference of the circle. The opposite angles of this shape add up to 180°.
What is the Alternate Segment Theorem?
-The angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment, which helps in solving various geometric problems.
How can you solve for angle D in a mathematical problem involving circles and triangles?
-You would first calculate angle A by taking 180° - 70° and dividing by 2 to find 55°. Then, using the properties of isosceles triangles and the 90° angle created by the radius and tangent, you can solve for angle D.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Every Theorem on Circle with Proofs.| Theorem on Circles.| Class 9 |NCERT.
11 Most Important Circle Theorems You Need To Know!
Pembahasan Soal Lingkaran | Menghitung Besar Sudut Antara Dua Tali Busur pada Lingkaran

12-5 Angle Relationships in Circles

THEOREMS INVOLVING CHORDS, ARCS, CENTRAL ANGLES || GRADE 10 MATHEMATICS Q2

Lingkaran kelas 11 / Video Teorema Lingkaran
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
