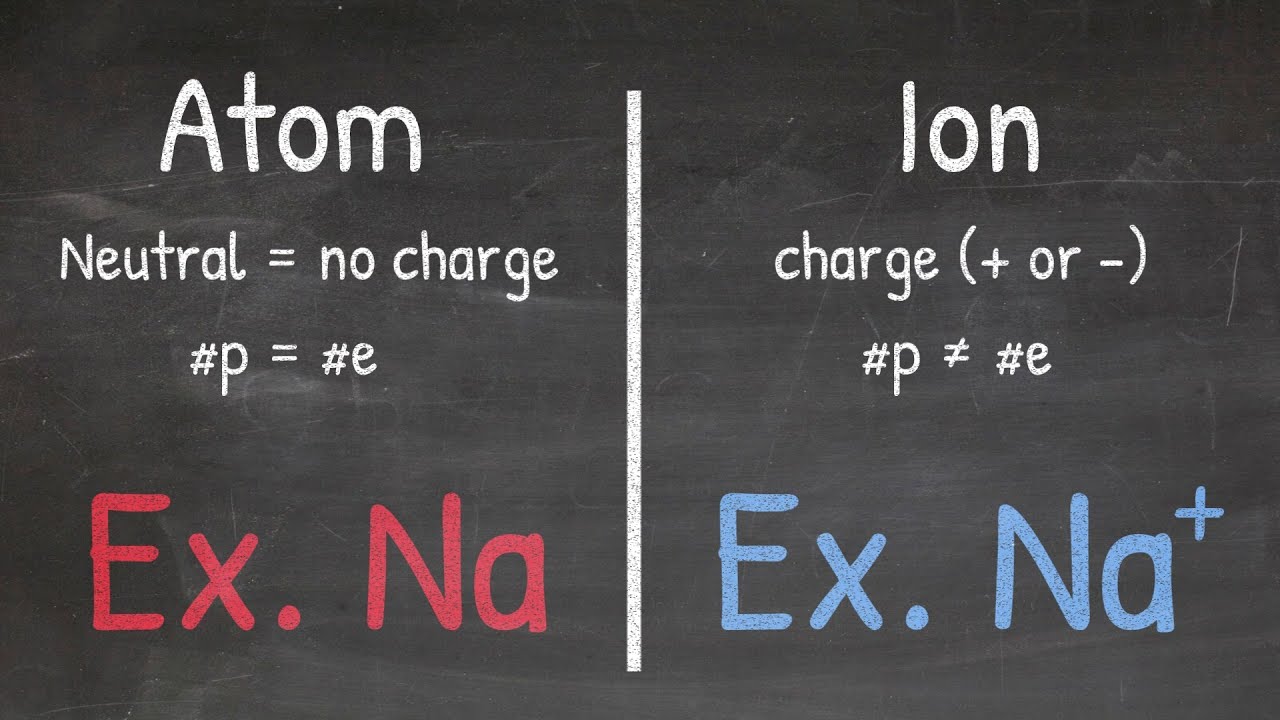Polyatomic Ions (EisleyChem)
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses polyatomic ions, which are particles composed of multiple atoms that have a charge. These ions typically involve covalent bonding between non-metal atoms, like in a carbonate ion with carbon and oxygen. The excess or deficiency of electrons gives the ion a negative or positive charge, respectively, though polyatomic ions are often anionic. Despite covalent bonding within the ion, the overall particle reacts ionically due to its charge, attracting other ions through electrostatic forces.
Takeaways
- 🔋 Polyatomic ions are unique particles that display multiple types of bonding.
- ⚛️ Polyatomic ions consist of more than one atom and carry a charge, hence the 'ion' in the name.
- 🌿 Non-metals, like carbon and oxygen, typically form covalent bonds in polyatomic ions.
- 💡 Covalent bonds in polyatomic ions involve the sharing of electrons between atoms with a small difference in electronegativity.
- 🧲 Polyatomic ions often have an excess of electrons, which gives them a negative charge.
- ⚖️ Some polyatomic ions can have a deficiency of electrons, resulting in a positively charged (cationic) ion, though most are anionic.
- 🔗 The atoms within a polyatomic ion are covalently bonded, but the ion as a whole acts ionically due to its charge.
- 📉 Carbonate is an example of a polyatomic ion, with carbon and oxygen atoms forming the ion.
- 🌀 The overall negative charge of the ion leads to electrostatic attraction to other positively charged ions.
- 🧬 Even though the atoms within the ion are covalently bonded, the entire ion behaves as a charged entity in reactions.
Q & A
What defines a polyatomic ion?
-A polyatomic ion is a charged particle made up of more than one atom, where the atoms are covalently bonded but the group as a whole carries a charge.
How do polyatomic ions differ from simple ions?
-Polyatomic ions consist of multiple atoms bonded together, whereas simple ions are typically composed of a single atom with a charge.
What type of bonding typically occurs within polyatomic ions?
-Covalent bonding typically occurs within polyatomic ions, where electrons are shared between atoms with small differences in electronegativity.
What creates the charge in a polyatomic ion?
-The charge in a polyatomic ion is usually caused by an excess or deficiency of electrons, leading to a net positive (cationic) or negative (anionic) charge.
Can polyatomic ions be both positive and negative?
-Yes, polyatomic ions can be either positive (cations) or negative (anions), though they are more commonly anionic.
What is an example of a polyatomic ion mentioned in the transcript?
-The carbonate ion (CO3^2−) is mentioned as an example of a polyatomic ion, made up of carbon and oxygen atoms.
How do atoms in a polyatomic ion behave electrostatically?
-The entire polyatomic ion, with its net charge, behaves electrostatically, meaning it can attract or repel other ions based on its charge.
What type of atoms typically make up polyatomic ions?
-Polyatomic ions are typically made up of non-metal atoms that form covalent bonds with each other.
Why are polyatomic ions usually anionic?
-Polyatomic ions are usually anionic because they often have an excess of electrons, resulting in a negative charge.
How do polyatomic ions interact with other ions?
-Polyatomic ions interact with other ions ionically due to their net charge, meaning they are attracted to oppositely charged ions through electrostatic forces.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)