Kesetimbangan Kimia • Part 3: Tetapan Kesetimbangan Pada Reaksi Berkaitan / Hukum Hess
Summary
TLDRThis video script is a chemistry lesson focusing on chemical equilibrium, specifically discussing how to calculate equilibrium constants (Kc). It covers the reversal of reaction equations, the effect of multiplying reaction coefficients on Kc values, and combining multiple equilibrium reactions. The lesson uses examples to illustrate how to manipulate equations to find the desired Kc, applying principles similar to Hess's Law. The instructor also encourages viewers to check their work for accuracy.
Takeaways
- 🔄 When a chemical equilibrium reaction equation is reversed, the equilibrium constant expression is also reversed.
- 🔢 If the initial equilibrium constant is given, reversing the reaction changes its value accordingly, such as from 20 to 1/20.
- 📉 Reversing a reaction changes the positions of reactants and products, which in turn affects the equilibrium constant expression.
- 🔄 The script uses the example of NH3 gas in equilibrium with N2 and H2 gases to illustrate the concept of reversing reactions.
- 📈 Multiplying the equilibrium constant by a number 'n' raises the equilibrium constant to the power of 'n', reflecting changes in reaction coefficients.
- 🔢 For instance, if the reaction coefficient is multiplied by 2, the equilibrium constant is squared.
- 🧪 The script explains that when multiple equilibrium reaction equations are combined, the resulting equilibrium constant is the product of the individual constants.
- 📐 It uses the example of combining reactions involving O2 and N2O gases to demonstrate this principle.
- 🔍 The script emphasizes the importance of understanding how to manipulate equilibrium constants when reactions are reversed or combined, similar to Hess's Law.
- 📝 It provides a step-by-step guide on how to calculate the equilibrium constant for a desired reaction using known reactions and their constants.
- 🔎 The process involves reversing and combining known reactions to match the target reaction, then calculating the new equilibrium constant based on the changes.
Q & A
What is the relationship between the equilibrium constant and the reaction equation if the reaction is reversed?
-If the reaction equation is reversed, the equilibrium constant (K) is also reversed. For example, if the initial K is 20, then when the reaction is reversed, the new K becomes 1/20.
How does the equilibrium constant change if the reaction equation is multiplied by a certain number?
-If the reaction equation is multiplied by a certain number (n), the equilibrium constant is raised to the power of that number. For instance, if the original K is 1.9 * 10^4 and the reaction is multiplied by 2, the new K becomes (1.9 * 10^4)^2.
What happens to the equilibrium constant when multiple reaction equations are added together?
-When multiple reaction equations are added, the equilibrium constant is the product of the equilibrium constants of the individual reactions. For example, if two reactions have equilibrium constants K1 and K2, the combined reaction's equilibrium constant is K1 * K2.
Can you provide an example of how to calculate the equilibrium constant for a reaction where NH3 gas is in equilibrium with N2 and H2 gases?
-Sure. If NH3 gas is in equilibrium with 1/2 N2 gas and 3/2 H2 gas, the equilibrium constant (K) is calculated based on the concentrations of the products and reactants raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients.
What is the significance of the equilibrium constant in understanding chemical reactions?
-The equilibrium constant (K) is significant because it provides a quantitative measure of the extent to which a reaction proceeds at equilibrium. It helps predict whether a reaction will favor the products or reactants under given conditions.
How does the equilibrium constant change if the stoichiometric coefficients in the reaction equation are altered?
-If the stoichiometric coefficients in the reaction equation are altered, the equilibrium constant will change accordingly. For example, if a coefficient is doubled, the equilibrium constant will be raised to the power of two.
What is the principle behind combining multiple equilibrium reactions to find the equilibrium constant for a new reaction?
-The principle behind combining multiple equilibrium reactions is based on Hess's Law, which states that the total enthalpy change for a reaction is the same, whether the reaction is carried out in one step or several steps.
Can you explain the process of finding the equilibrium constant for a reaction involving N2O4 gas in equilibrium with NO2 gas?
-To find the equilibrium constant for the reaction involving N2O4 gas in equilibrium with NO2 gas, you would need to consider the stoichiometry of the reaction and the equilibrium constants of related reactions, then apply Hess's Law to combine them appropriately.
What is the role of the equilibrium constant in determining the direction a reaction will proceed?
-A large equilibrium constant indicates that the reaction favors the formation of products, while a small equilibrium constant suggests that the reaction favors the reactants. The equilibrium constant helps determine the direction a reaction will proceed spontaneously.
How can you determine if a calculated equilibrium constant is reasonable based on the given data?
-To determine if a calculated equilibrium constant is reasonable, you should compare it with the equilibrium constants of related reactions and check if the reaction's direction and the stoichiometry align with the expected chemical behavior.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Kesetimbangan Kimia • Part 1: Konsep, Hukum, Tetapan Kesetimbangan Kc dan Kp

Menghitung Tetapan Kesetimbangan Berdasarkan Konsentrasi (Kc) | Kesetimbangan Kimia | Kelas 11

Reaksi Kesetimbangan | Tetapan Kesetimbangan Kc | Kimia kelas 11

PENGERTIAN DAN TETAPAN KESETIMBANGAN (Kc)

Kesetimbangan Kimia| Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti
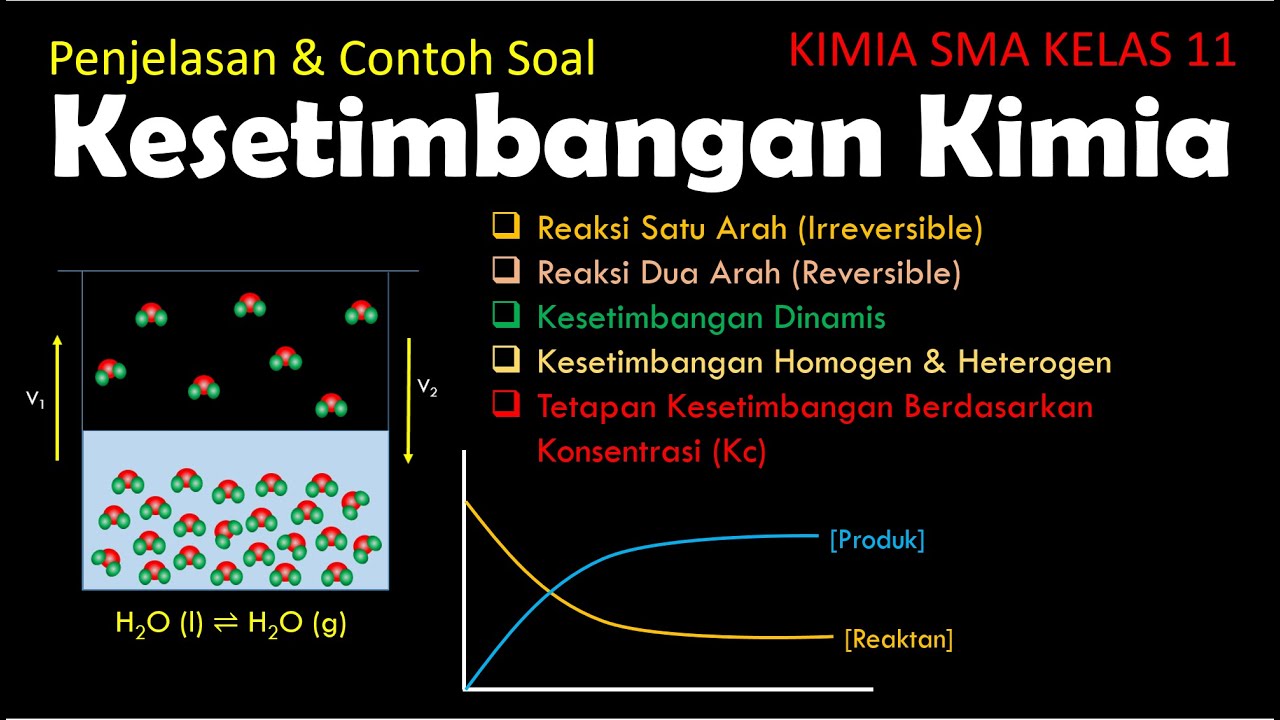
KESETIMBANGAN KIMIA ( KIMIA SMA KELAS 11 )
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
