HUKUM HESS
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses Hess's Law, a fundamental concept in thermochemistry, which states that the total enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the path taken and depends only on the initial and final states. The script uses the example of carbon combustion to illustrate how a single-step reaction can be broken into multiple steps, with the total enthalpy change remaining constant. It also explains how to adjust coefficients and manipulate equations to calculate the enthalpy change for different reactions, providing insights into the calculation of enthalpy changes for complex reactions.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The Hess's Law is a fundamental principle in thermochemistry, introduced by Germain Hess in 1848.
- 🔥 Hess's Law states that the total enthalpy change for a chemical reaction is the same, regardless of whether the reaction occurs in one step or several steps.
- 🌡 The law is based on experimental observations that not all chemical reactions occur in a single step.
- 🔍 An example given is the combustion of carbon, which can occur in a single step to form carbon dioxide or in two steps, first forming carbon monoxide.
- 📐 The enthalpy change for the combustion of carbon to carbon dioxide is the same whether it occurs in one or two steps, totaling -394 kJ.
- 📉 For reactions occurring in multiple steps, the overall enthalpy change is the sum of the enthalpy changes for each individual step.
- 🧪 Coefficients of identical substances in a balanced equation are adjusted based on their positions; opposite sides reduce each other, while the same side sums up.
- 📚 The law is applied to calculate the enthalpy change for the formation of SO3, showing that the enthalpy change remains consistent across different pathways.
- 📝 Hess's Law can be used to solve problems by manipulating known reactions to match the desired reaction conditions.
- 🔋 An example calculation is provided for the production of acetylene (C2H2) from its elements, demonstrating the application of Hess's Law to find the enthalpy change for a reaction not directly measured.
Q & A
Who is the scientist credited with Hess's Law?
-Hess's Law is credited to the German scientist Germain Hess.
What is the main concept of Hess's Law?
-Hess's Law states that the total enthalpy change for a chemical reaction is the same, regardless of the number of steps the reaction is carried out in.
What is an example of a reaction that can occur in more than one step according to the transcript?
-The combustion of carbon to form carbon dioxide can occur in two steps: first, carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon monoxide, and then carbon monoxide reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide.
What is the enthalpy change for the single-step reaction of carbon combustion as mentioned in the transcript?
-The enthalpy change for the single-step reaction of carbon combustion to form carbon dioxide is -394 kilojoules.
How does the enthalpy change for a reaction in multiple steps compare to the single-step reaction according to Hess's Law?
-According to Hess's Law, the total enthalpy change for a reaction that occurs in multiple steps is the sum of the enthalpy changes for each step, and it should be equal to the enthalpy change of the reaction if it occurred in a single step.
What does the transcript say about the coefficients of substances in a reaction?
-The transcript explains that if the same substance appears on both sides of a reaction, its coefficients are subtracted if they are on opposite sides and added if they are on the same side.
How is the enthalpy change for a reaction calculated when the reaction occurs in multiple steps?
-The enthalpy change for a reaction that occurs in multiple steps is calculated by summing the enthalpy changes of each individual step.
What is the significance of the diagram mentioned in the transcript for understanding Hess's Law?
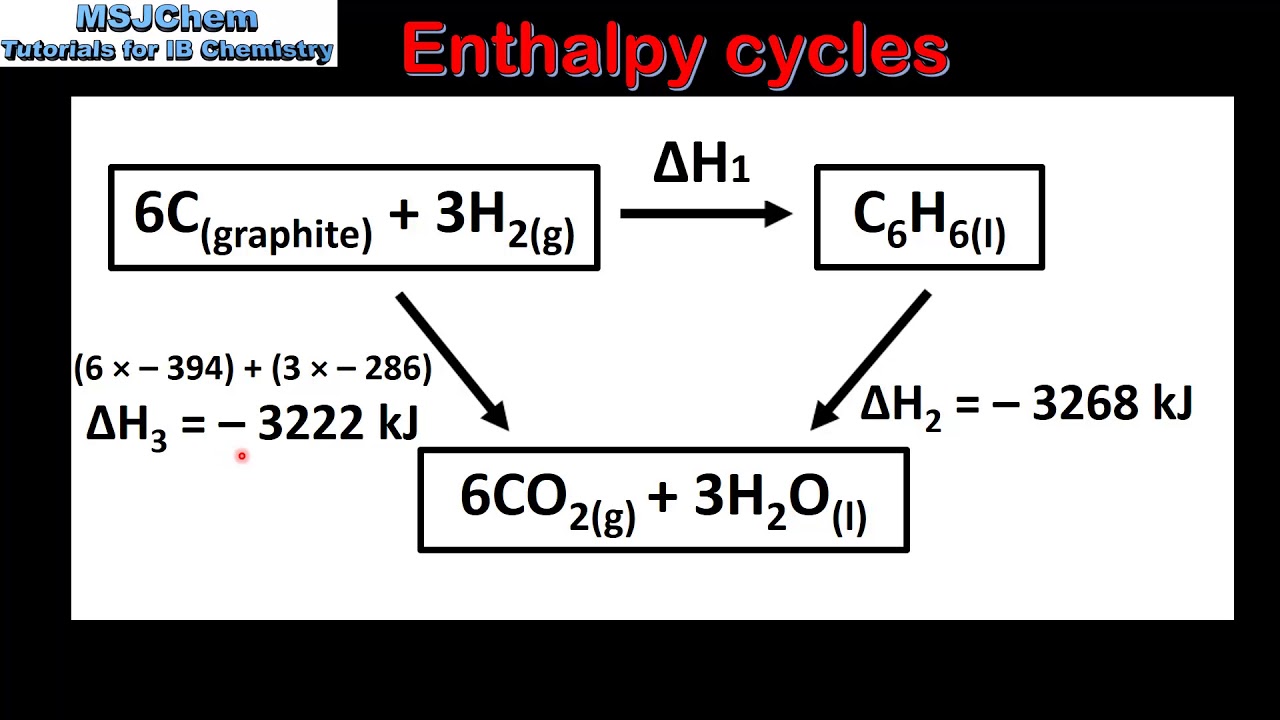
-The diagram helps visualize how the enthalpy change is calculated for reactions that occur in a single step versus multiple steps, illustrating the principle that the total enthalpy change is the same regardless of the reaction pathway.
Can you provide an example of how to apply Hess's Law to calculate the enthalpy change for a reaction involving SO3 formation as described in the transcript?
-Yes, the transcript provides an example where the formation of SO3 can occur in a single step with a ΔH of -794 kJ, or in two steps with ΔH1 of -539.8 kJ for the first step and ΔH2 for the second step. According to Hess's Law, ΔH for the overall reaction is the sum of ΔH1 and ΔH2.
What is the final enthalpy change calculated for the two-step reaction of SO3 formation in the transcript?
-The final enthalpy change for the two-step reaction of SO3 formation is calculated to be -250 kJ, after applying Hess's Law and considering the enthalpy changes of both steps.
How does the transcript describe the process of calculating the enthalpy change for the reaction of acetylene (C2H2) formation?
-The transcript describes a process where multiple reactions are adjusted (reversed or multiplied by factors) to match the desired reaction for acetylene formation. The total enthalpy change is then calculated by summing the adjusted enthalpy changes of these reactions.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Termokimia part 4- HUKUM HESS - Kimia SMA kelas 11 semester 1

HUKUM HESS : Menentukan perubahan entalpi reaksi dengan Hukum Hess
5.2 Enthalpy cycles (SL)

HUKUM HESS, ENTALPI PEMBENTUKAN DAN ENERGI IKATAN

Practice Problem: Hess's Law

Termokimia (1) | Entalpi Dan Perubahan Entalpi | Persamaan Termokimia | Hukum Hess
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
