Corak Kehidupan dan Hasil-hasil Budaya Masyarakat Masa Praaksara Indonesia
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the evolution of human culture and lifestyle from the Paleolithic to the Metal Age. It outlines the progression from a nomadic hunting and gathering existence to settled farming communities, highlighting the development of tools and the emergence of complex social structures. The script explores the cultural advancements, such as the use of fire, cave paintings, and the introduction of metal tools, which significantly impacted daily life and the belief systems of early humans.
Takeaways
- 🌿 The Paleolithic culture was characterized by a nomadic lifestyle, with early humans relying on hunting and gathering for survival.
- 🐘 Hunting large animals like horses, pigs, and buffalo was crucial for sustenance during the Paleolithic era.
- 🗺️ Migration was influenced by climate change, natural disasters, and the availability of food and water sources.
- 🔥 Early humans used simple stone tools like hand axes and developed basic communication through sounds and gestures.
- 🏞️ The Mesolithic culture saw the use of more advanced tools made from stone, bone, and shell, and a shift towards a more settled lifestyle near water sources.
- 🔥 The discovery of fire was a significant cultural achievement during the Mesolithic period, aiding in cooking and providing light.
- 🌾 The Neolithic culture marked the beginning of farming and animal husbandry, leading to more permanent settlements and the domestication of animals like chickens, buffalo, dogs, and pigs.
- 🏺 Pottery and more sophisticated stone tools were developed during the Neolithic period, indicating a more advanced level of craftsmanship.
- 🌱 The belief system during the Neolithic period included animism and dynamism, with practices related to honoring ancestors and life after death.
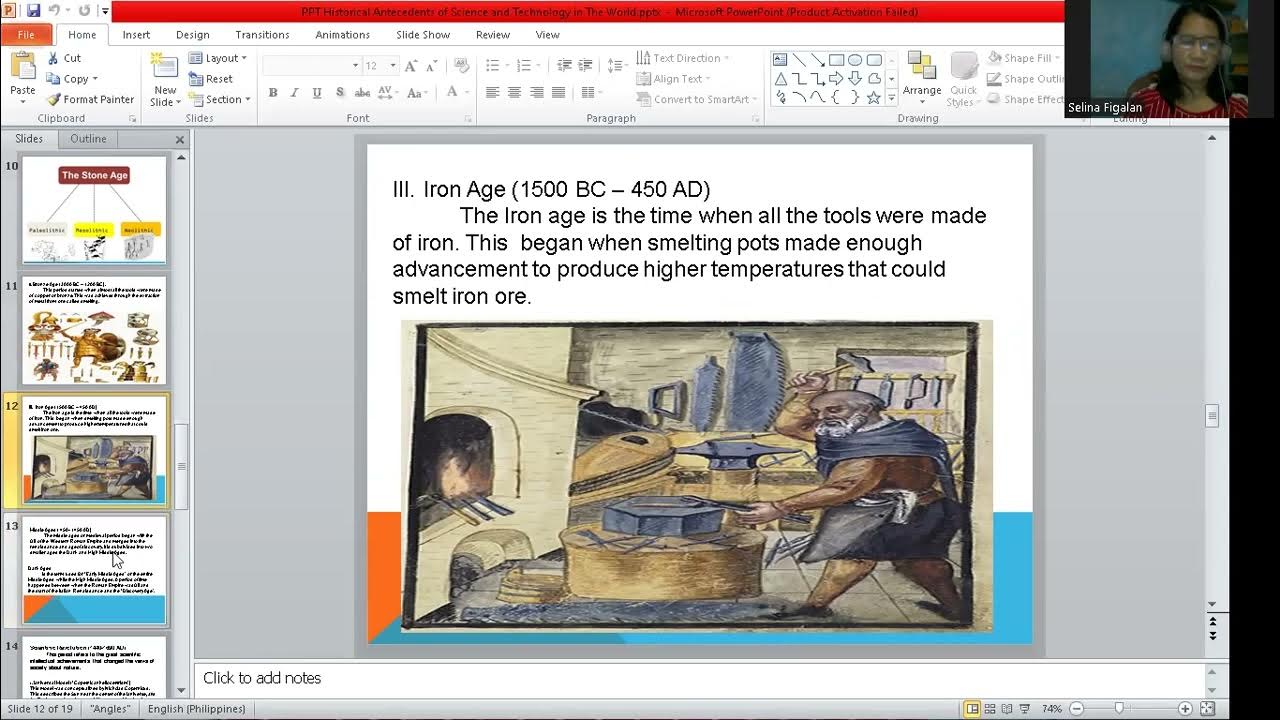
- 🛠️ The Perundagian or Megalithic culture introduced metal tools, signifying a significant advancement in technology and a more organized society.
- 🏰 The Perundagian period also saw the rise of trading, with communities exchanging goods that held magical or symbolic meanings.
Q & A
What are the four periods of human culture discussed in the script?
-The four periods of human culture discussed are the Paleolithic culture (hunting and gathering at a simple level), Mesolithic culture (hunting and gathering advanced food), Neolithic culture (period of farming), and the Metal culture (Perundagian or Megalithic culture).
How did early humans obtain their food during the Paleolithic period?
-During the Paleolithic period, early humans' food depended entirely on nature and was obtained by hunting and gathering food.
What factors influenced the migration of early humans during the hunting and gathering period?
-Migration was influenced by climate change, natural disasters, and threats from carnivorous animals. A long dry season or prolonged rainy season could also affect their movement.
What type of tools were used by early humans in the Paleolithic culture?
-In the Paleolithic culture, early humans used stone tools such as hand axes, flakes, and bone tools like spatulas and spearheads made from jagged bones.
How did the Mesolithic culture differ from the Paleolithic in terms of tool usage?
-In the Mesolithic culture, in addition to stone tools, they were able to make tools from bones and shells, and there was a division of labor with men hunting and women gathering food.
What is significant about the discovery of fire in the Mesolithic period?
-The discovery of fire in the Mesolithic period was significant as it allowed for cooking food, which improved nutrition and health, and provided warmth and protection.
What changes occurred in the Neolithic culture regarding agriculture and animal husbandry?
-In the Neolithic culture, humans became familiar with farming activities, including cutting and burning trees to create fields, raising livestock such as chickens, buffalo, dogs, and pigs, and making handicrafts.
How did the community housing pattern change from the Mesolithic to the Neolithic period?
-The community housing pattern changed from a nomadic lifestyle in the Mesolithic period to living in more permanent structures, especially near water sources, during the Neolithic period.
What types of tools were prominent in the Neolithic culture?
-In the Neolithic culture, square pickaxes and oval axes were prominent stone tools, and pottery objects began to be known, indicating the development of more advanced techniques for making and decorating pottery.
How did the introduction of metal tools mark the beginning of the Perundagian period?
-The introduction of metal tools marked the beginning of the Perundagian period as it signified a significant advancement in tool-making, with the creation of tools to support and facilitate daily activities and work.
What were the beliefs and ceremonies associated with the Metal culture?
-In the Metal culture, there was a growing belief in the influence of ancestral spirits on human life and religious ceremonies. Ancestors were believed to protect and accompany the journey of human life, and offerings were made to ensure their spirits' well-being.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Sejarah Indonesia : Kebudayaan Zaman Pra Aksara

Manusia Prasejarah | Pembagian Zaman Batu dan Logam (Arkeologi & Geologi) | IPS Kelas 8
Historical Antecedents of Science and Technology in the World

sejarah perkembangan agama hindu di dunia

ZAMAN PALEOLITIKUM

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman Materi IPS Kelas 7 Tema 2 Keberagaman Lingkungan Sekitar
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
