History's Worst Software Error
Summary
TLDRThe script recounts the tragic history of the Therac-25, a radiation therapy machine that caused severe injuries and deaths due to software errors. It highlights the importance of rigorous software testing and ethical decision-making in medical technology. The Therac-25's malfunctions, including a deadly bug known as 'Malfunction 54', led to the machine's withdrawal and the dissolution of the manufacturer's medical division.
Takeaways
- 😔 Katie Yarborough was the first victim of the Therac-25, a radiation therapy machine with fatal software flaws.
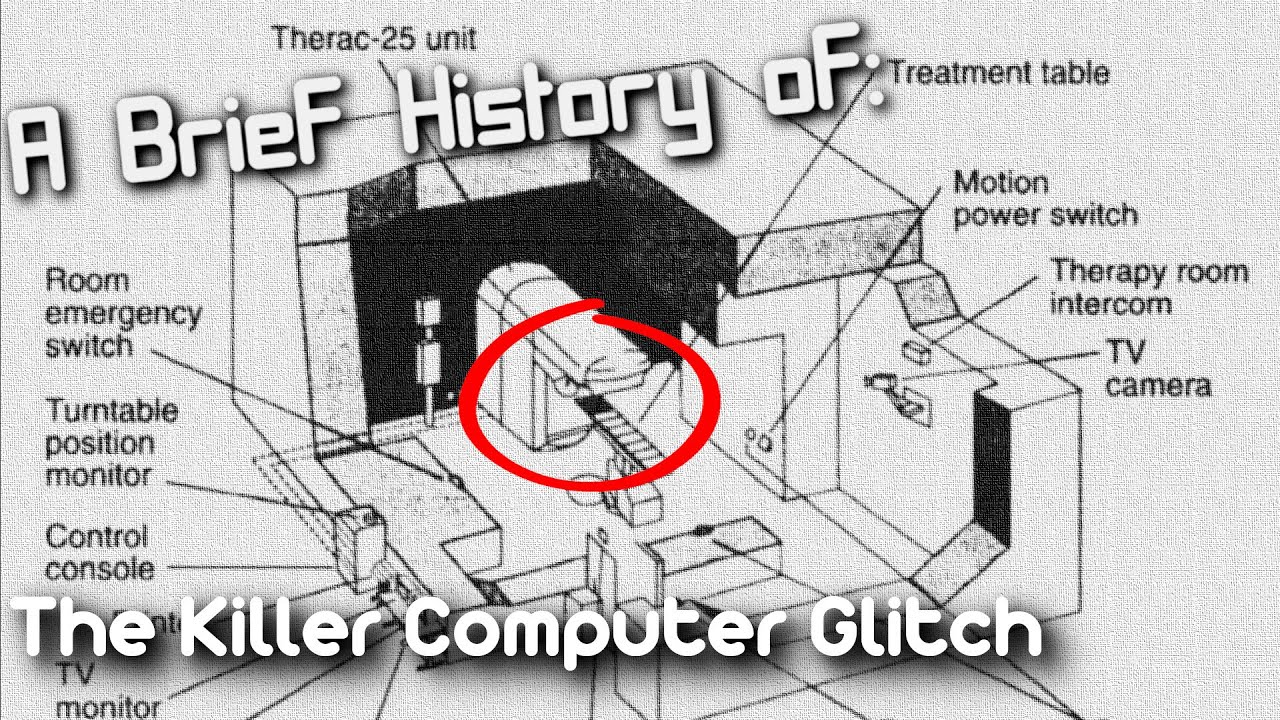
- 🔬 Therac-25 was a state-of-the-art linear accelerator designed for cancer treatment, but it was primarily controlled by software.
- 💡 The concept of radiotherapy involves using high-energy radiation to target and destroy cancer cells.
- 🛠️ Therac-25 was developed by AECL Medical and was smaller and more software-dependent than its predecessors.
- 🚫 A critical oversight in the 1983 safety analysis excluded any evaluation of the Therac-25's software.
- 🔍 The software, based on the older Therac-20 model and written by a single individual, had significant errors that were not addressed.
- 🚨 Multiple patients were severely injured or killed due to software malfunctions that caused overdoses of radiation.
- 🤖 Therac-25's software had a critical flaw known as 'Malfunction 54', which allowed unfiltered radiation beams to hit patients.
- 🛑 AECL initially denied the possibility of overdoses and did not acknowledge the software issues until forced by evidence and lawsuits.
- 🔄 Therac-25's design relied on software without hardware fail-safes, leading to a series of tragic accidents.
- 📚 The Therac-25 case is now a cautionary tale in ethics and computer science, highlighting the importance of rigorous software testing and safety measures.
Q & A
What was the name of the woman who experienced the first known software-related accident in the medical field?
-Katie Yarborough.
What was the medical device involved in the accidents described in the script?
-The device involved was the Therac-25, a linear accelerator used for cancer treatment.
What was the year when Katie Yarborough's accident with the Therac-25 occurred?
-Katie Yarborough's accident occurred in 1985.
How did the Therac-25 work in terms of delivering radiation to patients?
-The Therac-25 worked by using a double pass accelerator to direct high-energy electrons and/or X-rays into patients' lymph nodes.
What was the estimated radiation dose Katie Yarborough received instead of the prescribed 200 rads?
-Katie Yarborough received an estimated dose of 20,000 rads, which was hundreds of times more than the prescribed amount.
What was the name of the company that developed the Therac-25?
-The Therac-25 was developed by AECL Medical, a division of Atomic Energy of Canada Limited.
What was the main issue with the Therac-25's software that led to the accidents?
-The main issue with the Therac-25's software was the lack of proper safety checks and the potential for errors like arithmetic overflow, which allowed unfiltered beams of radiation to strike patients.
What was the 'Malfunction 54' error that was repeatedly mentioned in the script?
-Malfunction 54 was an undefined error in the Therac-25's software that, when encountered, allowed the machine to deliver a powerful, unfiltered beam of radiation to patients, causing severe injuries or death.
What was the corrective action plan (CAP) that AECL eventually submitted to the FDA after the accidents?
-The corrective action plan included 23 software changes and six hardware safety features, including a dose per pulse monitor to shut down dangerous doses even if all software safety checks failed.
What was the final outcome for AECL Medical after the Therac-25 accidents?
-AECL Medical dissolved their medical division in 1988, and lawsuits from the families of the victims were settled out of court.
How is the Therac-25 incident viewed today in the context of medical technology and ethics?
-Today, the Therac-25 incident is considered a staple of ethics and computer science classes as a case study of what can go wrong when new technology is trusted implicitly and ethical decision-making fails.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

THERAC-25: O PIOR erro de SOFTWARE da HISTÓRIA

how a simple programming mistake ended 6 lives
A Brief History of: The killer Therac-25 Radiotherapy machine (Short Documentary)

Technology and Society - Chapter 4 - Engineering Ethics Course

Medical Mistakes: The Affects on Families

The Minamata Disaster | The town that was poisoned
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
