Second Law of Thermodynamics and entropy | Biology | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the Second Law of Thermodynamics, emphasizing the universal increase in entropy, or disorder. It illustrates the concept with the vastness of the universe, represented by galaxies captured by the Hubble telescope, and explains entropy as the number of possible states a system can take. Using examples like diffusion and billiard balls, the video clarifies the irreversibility of processes that increase entropy, highlighting the continuous rise in the universe's disorder due to heat and friction in everyday activities.
Takeaways
- 🔥 The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the entropy of the universe only increases, signifying a move towards greater disorder.
- 🌌 Entropy can be understood as the measure of disorder within a system, which correlates to the number of possible states the system can occupy.
- 🔄 A closed system, such as the universe, is one that does not interact with its surroundings thermodynamically, making the universe the ultimate closed system.
- 🔥 Open systems, like a campfire, interact with their surroundings by releasing heat and light, thus not being isolated.
- 🧊 An ice cooler is an example of an approximate closed system in everyday life, attempting to isolate its contents from external heat.
- 🔬 In research labs, there are better approximations of closed systems, but even these cannot be completely isolated from the universe.
- 🌐 The diffusion of particles, such as gas molecules spreading out to fill a container, is a clear example of entropy increasing.
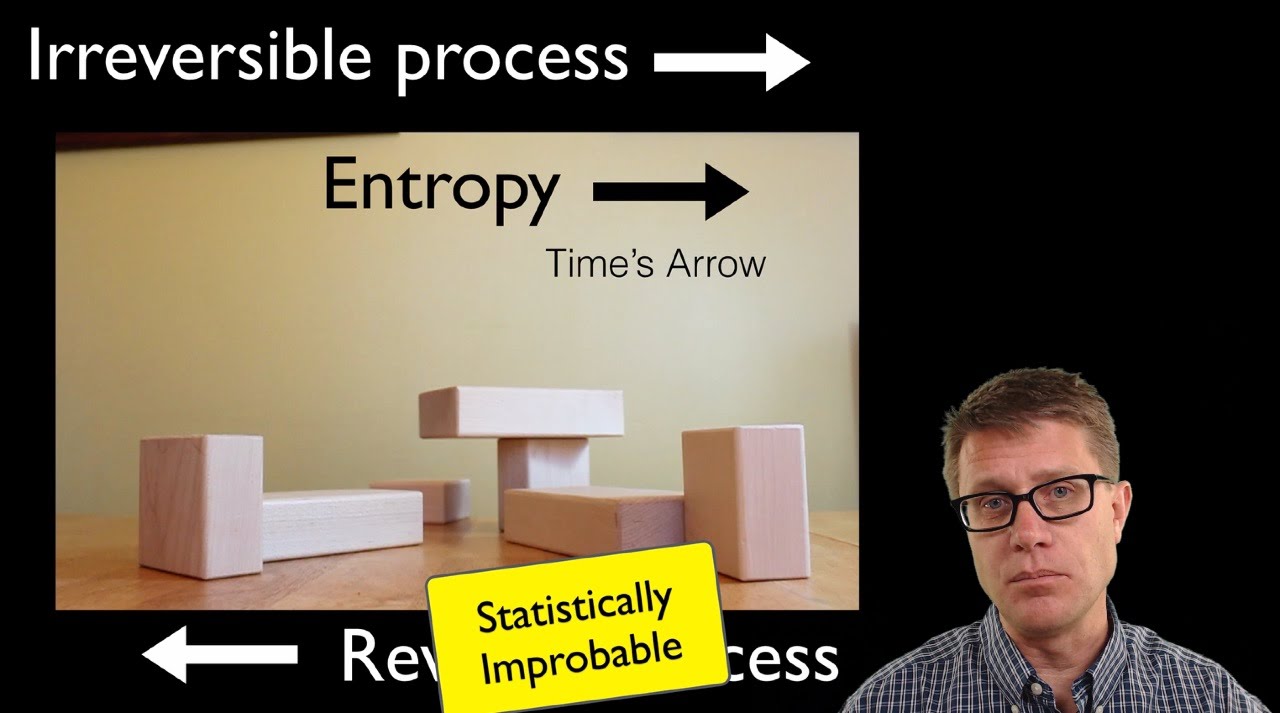
- 🔁 Irreversible processes, like diffusion, lead to an increase in entropy because it is highly improbable for the system to return to its previous state.
- 🎱 Even seemingly reversible processes, like billiard balls colliding, contribute to entropy increase when viewed at a microscopic level due to heat generation and molecular excitation.
- ♨️ Everyday activities, including watching videos and using computers, generate heat, which dissipates and adds to the universe's entropy.
Q & A
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics?
-The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the entropy of the universe only increases, meaning the disorder or the number of possible states a system can take on is always on the rise.
What is entropy and how is it related to the disorder of a system?
-Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system, which can be defined as the number of states that a system could take on. Higher entropy indicates a greater level of disorder or more possible states.
What is the difference between an open and a closed system in thermodynamics?
-An open system is one that interacts thermodynamically with its surroundings, such as a campfire releasing heat and light. A closed system, on the other hand, is isolated from the rest of the universe, with no thermodynamic interaction outside of it, making the universe the ultimate closed system.
Can you give an example of an everyday closed system?
-An ice cooler is an example of an everyday closed system. It is designed to thermodynamically isolate the inside from the outside environment, although it is not a perfect closed system as heat will eventually transfer into it from the surroundings.
Why is the process of diffusion considered an irreversible process?
-Diffusion is considered irreversible because it involves a transition from a state of lower entropy (fewer possible states) to a state of higher entropy (more possible states), and it is highly unlikely that the system will spontaneously revert to its original state due to the vast number of molecules involved.
How does the concept of entropy relate to the macroscopic and microscopic views of a system?
-Macroscopically, some processes may appear reversible, like the collision of billiard balls. However, microscopically, these processes are irreversible because they result in an increase in entropy due to factors like heat generation and molecular excitation, which do not return to their original states.
What is the significance of the statement 'the entropy of the universe only increases'?
-The statement signifies that the universe is constantly moving towards a state of greater disorder. This is a fundamental principle that governs the direction of natural processes and the eventual fate of the universe.
How does the increase in entropy relate to the concept of irreversibility in thermodynamics?
-The increase in entropy is directly related to the irreversibility of thermodynamic processes. When entropy increases, it means that the system has transitioned to a state with more possible configurations, making it highly improbable to return to its previous state.
Can you provide an example of how everyday activities contribute to the increase of the universe's entropy?
-Everyday activities like watching a video, using a computer, or even moving one's hands generate heat, which dissipates into the universe. This heat release adds to the number of possible states the universe can take on, thus increasing its entropy.
What is the role of heat in the context of entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics?
-Heat plays a crucial role as it is often the driving force behind the increase in entropy. The dissipation of heat into the universe from various sources contributes to the increase in the number of states the universe can occupy, adhering to the Second Law of Thermodynamics.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)