12 - Solving & Graphing Inequalities w/ One Variable in Algebra, Part 1
Summary
TLDRThis algebra lesson focuses on solving one-variable inequalities, starting with simple problems and progressing to more complex ones. The instructor explains that solving inequalities follows the same rules as equations but with a crucial difference: when multiplying or dividing by a negative number, the direction of the inequality sign must be reversed. The lesson covers various inequality types, demonstrates solving steps, and emphasizes graphing solutions on a number line with open and closed circles to represent inclusive or exclusive endpoints. The goal is to find a range of values that satisfy the inequality, verifying solutions by substituting back into the original inequality.
Takeaways
- 📚 Start by understanding the basics of solving inequalities with one variable, progressing from simple to complex problems for thorough practice.
- 🔍 The rules for solving inequalities are similar to solving equations, involving moving terms to one side and isolating the variable.
- 📉 Inequalities represent a range of values rather than a single solution, which is a key difference from equations.
- 📌 When graphing inequalities, use open circles for 'greater than' or 'less than' and closed circles for 'greater than or equal to' or 'less than or equal to' to indicate inclusion or exclusion of the boundary value.
- 📈 To graph an inequality, shade the appropriate side of the number line based on whether the inequality is 'greater than' or 'less than'.
- ⚠️ A crucial rule when solving inequalities is to flip the inequality sign when multiplying or dividing by a negative number.
- 🔢 Practice checking solutions by substituting values back into the inequality to ensure they satisfy the original condition.
- 🔄 Inequalities can involve various variables, but the process of solving them remains consistent regardless of the variable used.
- 📝 When solving compound inequalities, collect like terms on one side and constants on the other, then isolate the variable.
- 📉 After isolating the variable, the solution to an inequality is a range of values that can be represented on a number line.
- 🚀 These foundational skills in solving one-variable inequalities are essential for tackling more complex inequalities with multiple variables in the future.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the algebra lesson in the provided transcript?
-The main focus of the lesson is solving inequalities that involve one variable, starting with simple problems and gradually increasing in complexity.
How are inequalities different from equations in terms of solutions?
-Inequalities have a range of solutions, whereas equations typically have a single solution. Inequalities use less than, greater than, less than or equal to, or greater than or equal to signs instead of an equal sign.
What is the first step in solving an inequality like 'X - 7 > -5'?
-The first step is to isolate the variable, which involves adding 7 to both sides of the inequality to get 'X > 2'.
How do you represent the solution of the inequality 'X > 3' on a number line?
-You place an open circle at 3 on the number line and shade everything to the right, indicating that X can be any number greater than 3 but not including 3 itself.
What is the rule for dividing or multiplying both sides of an inequality by a negative number?
-When dividing or multiplying both sides of an inequality by a negative number, you must flip the direction of the inequality sign.
What does the inequality 'X ≥ 2' mean in terms of the range of values for X?
-'X ≥ 2' means that X can be any number greater than or equal to 2, including 2 itself.
How do you graph the solution for 'X ≤ -2' on a number line?
-You place a closed circle at -2 on the number line and shade everything to the left, indicating that X can be any number less than or equal to -2.
What is the difference between using an open circle and a closed circle when graphing inequalities?
-An open circle indicates that the number at that point on the number line is not included in the solution, while a closed circle indicates that the number is included.
In the transcript, what is an example of an inequality that involves dividing by a negative number?
-An example given is '-5x < 10', which after dividing both sides by -5, becomes 'x > -2', and the direction of the inequality sign is flipped.
How do you check if a particular number is a solution to an inequality?
-You substitute the number into the original inequality and check if the resulting statement is true, indicating that the number is part of the solution set.
What is the final step in solving the inequality '3x - 1 ≥ -4' as per the transcript?
-The final step is to divide both sides by 3, which gives 'x ≥ -1' after flipping the inequality sign due to division by a positive number.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

SOLVING ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS | GRADE 6
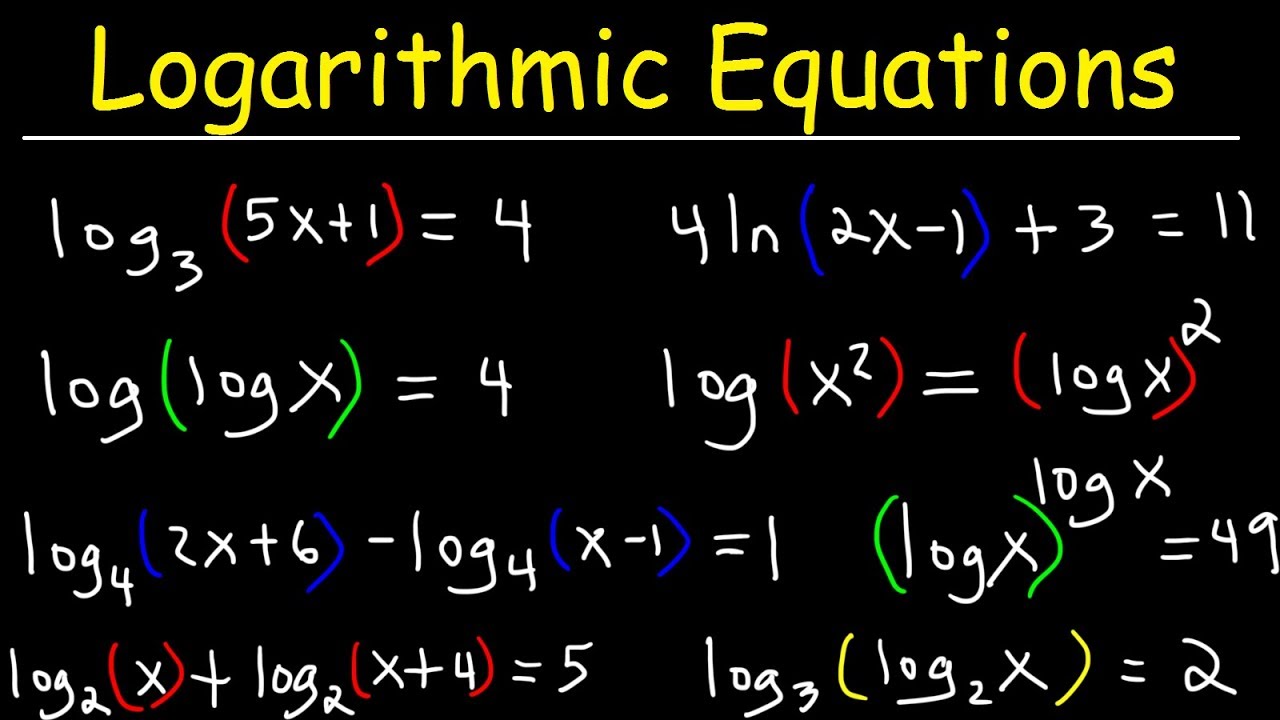
Solving Logarithmic Equations

Absolute value inequalities | Linear equations | Algebra I | Khan Academy
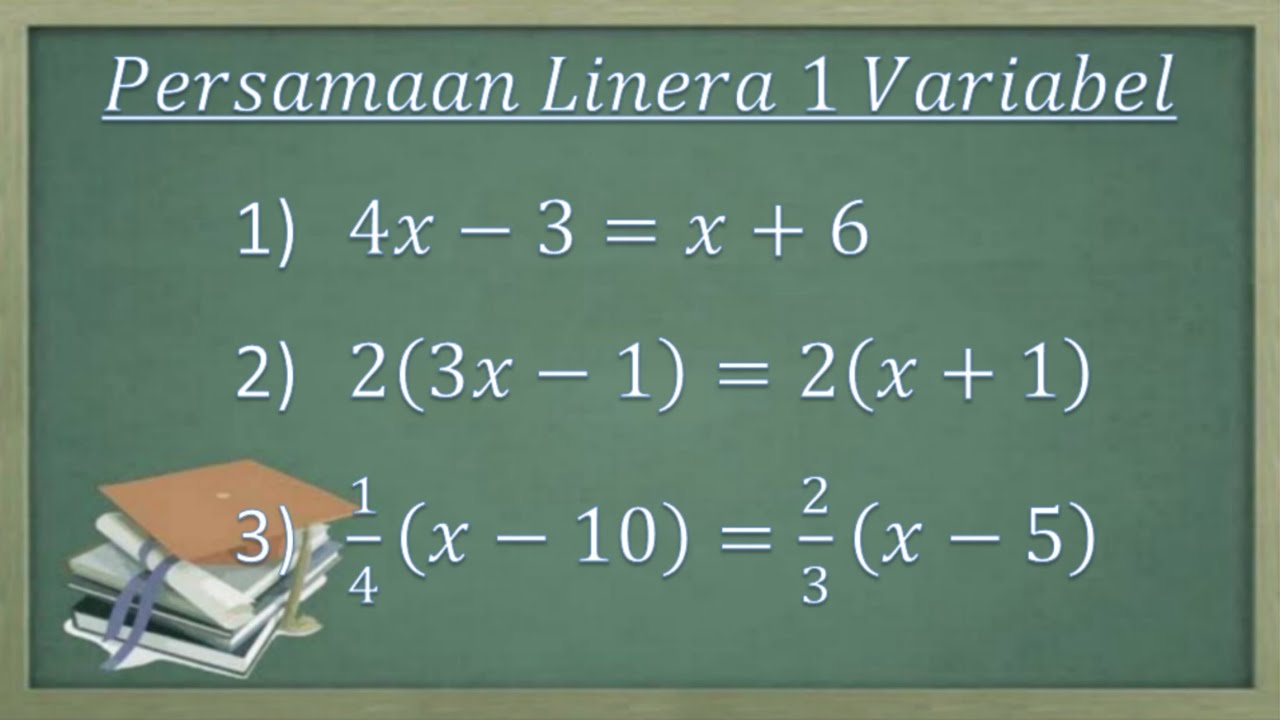
Sistem persamaan Linear satu variabel. Cara menentukan himpunan penyelesaiannya

1 PENGERTIAN ALJABAR - ALJABAR - KELAS 7 SMP

Matematika Kelas 8 Bab 3 Persamaan Linier Satu Variabel - hal. 109 - 111 - Kurikulum Merdeka
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
