Engine Fuel Systems Part 1 - Aircraft Gas Turbine Engines #19
Summary
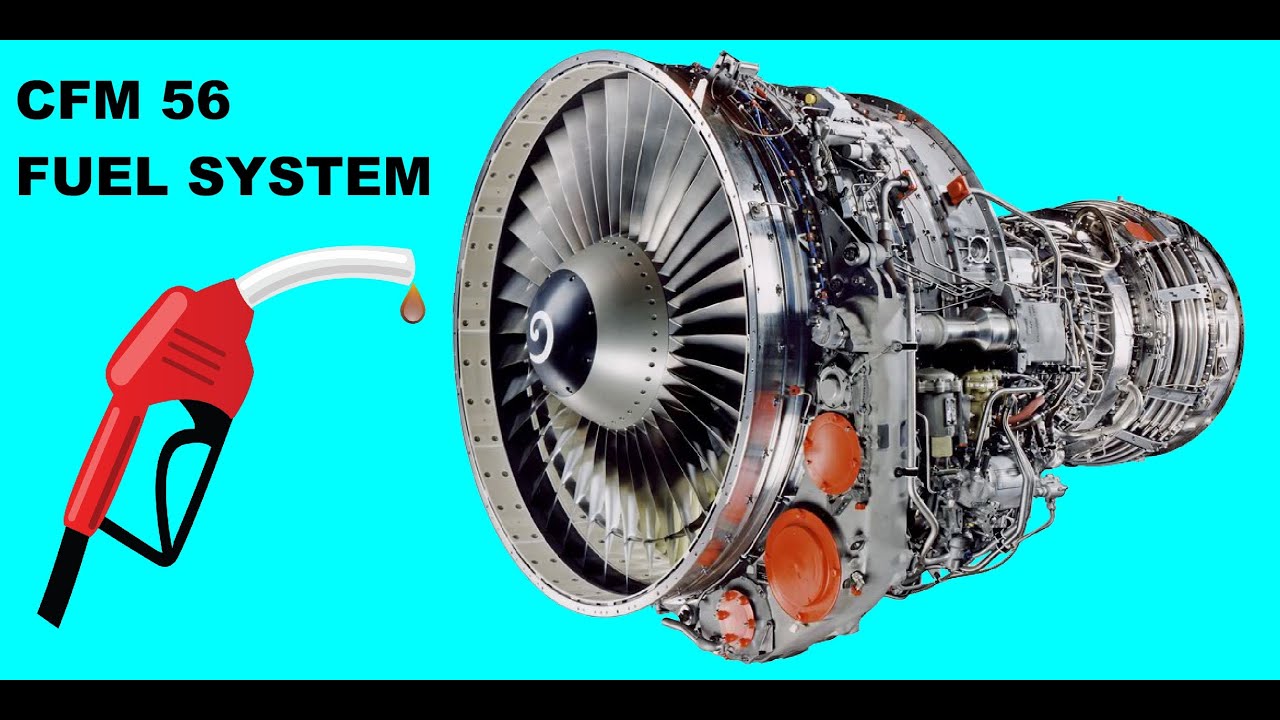
TLDRThe script delves into the engine fuel system of aircraft, detailing its components and functions. It explains how the system receives low-pressure fuel from the airframe tanks, increases pressure for combustion, and includes mechanisms like booster pumps, low-pressure fuel pumps, oil coolers, and fuel heaters to ensure efficient and safe operation. The focus is on the intricacies of the fuel control unit, which adjusts fuel flow according to various engine requirements, highlighting the importance of components like the high-pressure fuel pump and the hydro-mechanical fuel control systems.
Takeaways
- 🛩️ The engine fuel system is a critical part of the aircraft's fuel supply, receiving low-pressure fuel from the airframe fuel system and increasing it to a usable pressure for the engine.
- 🔧 The booster pumps in the wing and center tanks pass fuel to the engine through non-return valves, ensuring a continuous supply even if the engine fire control handle is activated.
- 🔄 The low-pressure fuel system can be used to shut off the fuel supply for maintenance or in case of engine fire, but it takes longer to shut down the engine compared to using high-pressure fuel.
- 🚫 The low-pressure fuel system contains a significant amount of fuel in the pipeline, which can maintain supply to the burners for some time, unlike the high-pressure system.
- 🔧 The low-pressure fuel pump, also known as the backing pump, supports the fuel supply to the engine in case of booster pump failure and helps prevent cavitation in the high-pressure pump.
- 🔥 A fuel cooled oil cooler is used in most gas turbine engines to cool the oil and heat the fuel, preventing ice crystal formation that could block the fuel system.
- 🛠️ The oil feed line to the fuel cooled oil cooler includes a pressure maintaining valve to ensure oil leaks into the fuel system rather than fuel into the oil system in case of a leak, avoiding potential hazards.
- 🌡️ The fuel heater works with the fuel cool oil cooler to maintain a predetermined fuel temperature, using a Verna therm thermal actuator sensitive to temperature changes.
- 📏 The flow meter measures the instantaneous fuel flow and can totalize the amount of fuel used, with two types in use on large jet aircraft: the vane type and the mass flow measuring type.
- 🛡️ The fuel pressure is sensed after the low-pressure fuel filter, which protects sensitive control components from dirt or contamination, and is indicated on the flight deck for monitoring.
- ⚙️ The high-pressure fuel pump, driven by the engine accessory gearbox, uses a plunger or spur gear type design to supply the necessary fuel flow, with the output controlled by a servo piston from the fuel control unit.
Q & A
What are the two main sections of the aircraft's fuel system?
-The two main sections of the aircraft's fuel system are the airframe fuel system and the engine fuel system.
What is the primary function of the engine fuel system?
-The primary function of the engine fuel system is to receive low pressure fuel supply from the aircraft fuel tanks, increase the fuel pressure to a value usable by the fuel nozzles in the combustion chamber, and control the volume of fuel into the engine to meet its requirements.
What is the role of booster pumps in the airframe fuel system?
-Booster pumps in the airframe fuel system are responsible for passing fuel through non-return valves to the engine via the low-pressure fuel supply.
How can the low-pressure fuel be used in the event of a fire or component removal?
-The low-pressure fuel can be used to shut off the supply to the engine automatically if the engine fire control handle is activated or to facilitate the removal of a fuel system component by stopping the fuel supply.
What is the purpose of the low-pressure fuel pump in the engine fuel system?
-The low-pressure fuel pump, sometimes called the backing pump, is used to back up the fuel supply to the engine in case of a failure of both booster pumps in the wing tanks and to minimize the chance of cavitation at the inlet of the high-pressure pump.
What is the function of a fuel cooled oil cooler in gas turbine engines?
-A fuel cooled oil cooler serves the dual purpose of cooling the oil and heating the fuel, which helps to eliminate the formation of ice crystals that may block components downstream in the fuel system.
How does the pressure maintaining valve in the oil feed line to the fuel cooled oil cooler work?
-The pressure maintaining valve keeps the oil pressure in the cooler higher than the fuel pressure, ensuring that if an internal leak occurs, the oil leaks into the fuel system rather than the fuel leaking into the oil system.
What is the purpose of the fuel heater in the fuel system?
-The fuel heater assists in warming the fuel to eliminate ice crystals and maintain a predetermined fuel temperature through the use of compressed bleed air.
What are the two types of flow meters used on large jet aircraft?
-The two types of flow meters used on large jet aircraft are the vane type and the mass flow measuring type.
How does the high-pressure fuel pump function in the engine fuel system?
-The high-pressure fuel pump, which can be of different types such as plunger or spur gear type, is fitted and driven by the engine accessory gearbox and is responsible for supplying fuel under high pressure to the outlet.
What are the two types of hydro-mechanical fuel control systems used in gas turbine engines?
-The two types of hydro-mechanical fuel control systems used in gas turbine engines are the pressure control system and the proportional flow control system, with the latter being more popular due to its compactness and insensitivity to flow variations downstream of the throttle.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)