Triple bottom line (3 pillars): sustainability in business
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the concept of the triple bottom line, introduced by John Elkington in 1997, emphasizing the balance between economic, social, and environmental sustainability. It challenges the traditional overlapping circles representation by proposing a nested model where the economy is a subsidiary of the environment. The script suggests that businesses should integrate sustainability into their strategies without sacrificing financial success, recognizing that all human activities are ultimately dependent on nature's cycles, particularly photosynthesis.
Takeaways
- 📚 The triple bottom line concept was introduced by John Elkington in 1997, emphasizing the importance of considering social and environmental factors alongside financial performance in business.
- 🌐 It is often represented by three overlapping circles, symbolizing the intersection of economic, social, and environmental concerns in sustainability.
- 🤔 The visual representation of the triple bottom line raises questions about the relative importance and trade-offs between the economy, society, and environment.
- 🌿 Science reveals that nature operates in balanced cycles, powered by the sun, and that matter is conserved through processes like photosynthesis, which is crucial for structuring matter on Earth.
- 🔄 The principle of entropy suggests that everything tends towards dispersal, but photosynthesis counters this by creating structure from energy, highlighting the importance of plant life in the environment.
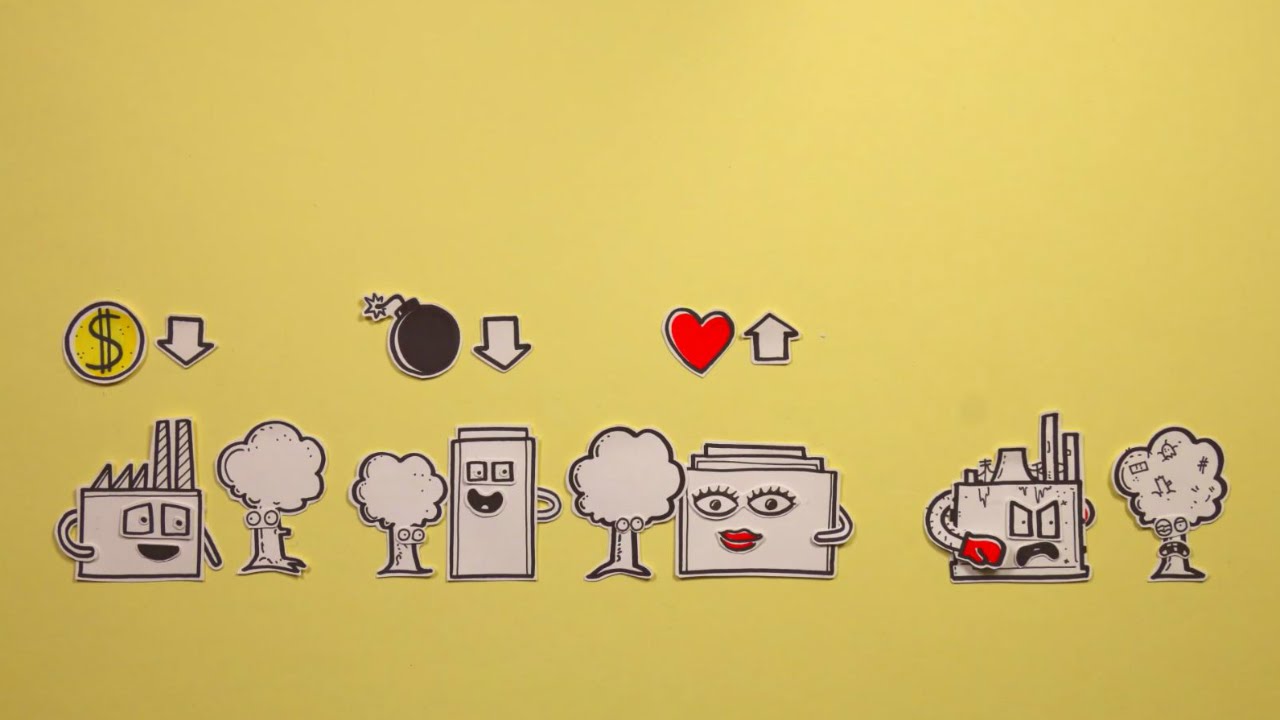
- 🌱 Plant cells, as part of the environmental circle, are foundational to the existence of both society and economy, suggesting a nested rather than overlapping relationship among the three aspects of the triple bottom line.
- 🏢 The economy is a subsidiary of the environment, meaning that sustainable business practices must align with social and environmental conditions to ensure long-term viability.
- 💡 Sustainability is not about prioritizing financial gain last, but integrating it as part of a strategy that also advances social and ecological goals.
- 💼 Businesses should view the economy as a means to meet human needs within ecological constraints, rather than as an end in itself.
- 🌳 Recognizing the dependency on photosynthesis for all levels of 'paying the bills' provides a new perspective on the importance of integrating sustainability into business operations.
- 👏 The video encourages viewers to subscribe and support the channel, highlighting the community aspect of creating and sharing educational content.
Q & A
What is the triple bottom line?
-The triple bottom line is a concept that measures the value of a company not only by its financial profit or loss but also by its social and environmental performance.
Who coined the term 'triple bottom line'?
-John Elkington, a global authority on corporate responsibility and sustainability, coined the term in 1997.
What does the overlapping circles image of the triple bottom line represent?
-The overlapping circles represent the intersection of economy, social realities, and environmental health, which are the three pillars of sustainability.
How does the triple bottom line concept help businesses?
-It helps businesses understand that long-term sustainability requires more than financial equity and encourages them to consider social and environmental impacts in their strategies.
What is the significance of the same size of the circles in the triple bottom line image?
-The same size of the circles might suggest that the economy, society, and environment are of equal importance or value in the context of sustainability.
How does the script suggest we should view the relationship between the economy, society, and environment?
-The script suggests viewing them as nested circles, where the economy is a subsidiary of the environment, indicating that economic activities are embedded within and dependent on the environment.
What is the role of plant cells in the context of the triple bottom line?
-Plant cells, through photosynthesis, are the original creators of structure from energy on our planet, making them fundamental to the environment and, by extension, to the economy and society.
What does the script imply about the priority of financial gain in business?
-The script implies that while financial gain is important, it should be part of a strategy that also considers social and ecological sustainability.
How does the script relate the concept of the triple bottom line to the laws of thermodynamics?
-It relates the concept by explaining that photosynthesis, which structures matter from energy, is essential to counteract the principle of entropy and maintain the cycles of nature.
What is the role of photosynthesis in the sustainability of our planet?
-Photosynthesis is crucial for structuring matter from energy, allowing for the creation of life and ecosystems, and is the process by which nature maintains its balance.
What is the script's perspective on the integration of sustainability into business practices?
-The script suggests that integrating sustainability is not only about financial success but also about aligning with social and ecological conditions to meet human needs within ecological constraints.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Konsep Dasar Pembangunan Berkelanjutan

What Is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)? | Business: Explained

How to be a sustainable entrepreneur Part 1

MODUL 11 UNIT 3 " GEOGRAFI" PAKET C SETARA SMA KELAS 12 - MEMBANGUN UNTUK MASA DEPAN
Little Green Bags: True Business Sustainability

What is SUSTAINABILITY? Explained By An Expert
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
