Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning by Professor Mayer, highlighting the multimedia principle for enhanced learning. It outlines three key assumptions: dual channels for audio and visual processing, limited capacity of these channels, and the necessity of active processing to integrate information with prior knowledge. The script also discusses three types of cognitive processing and emphasizes instructional design techniques to optimize learning through multimedia.
Takeaways
- 🎓 The importance of research in educational videos: High-quality educational videos are based on extensive research into the impact of multimedia on learning.
- 📚 Mayer's Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning: This theory, developed by Professor Mayer, is built on a set of principles derived from decades of research.
- 📈 Multimedia Principle: The use of words with graphics, known as multimedia, enhances learning more than words alone.
- 🧠 Cognitive Theory Foundation: Understanding multimedia learning requires a basis in cognitive theory, which the video aims to discuss.
- 🔍 Three Key Assumptions: Mayer's theory is based on the dual channel, limited capacity, and active processing assumptions.
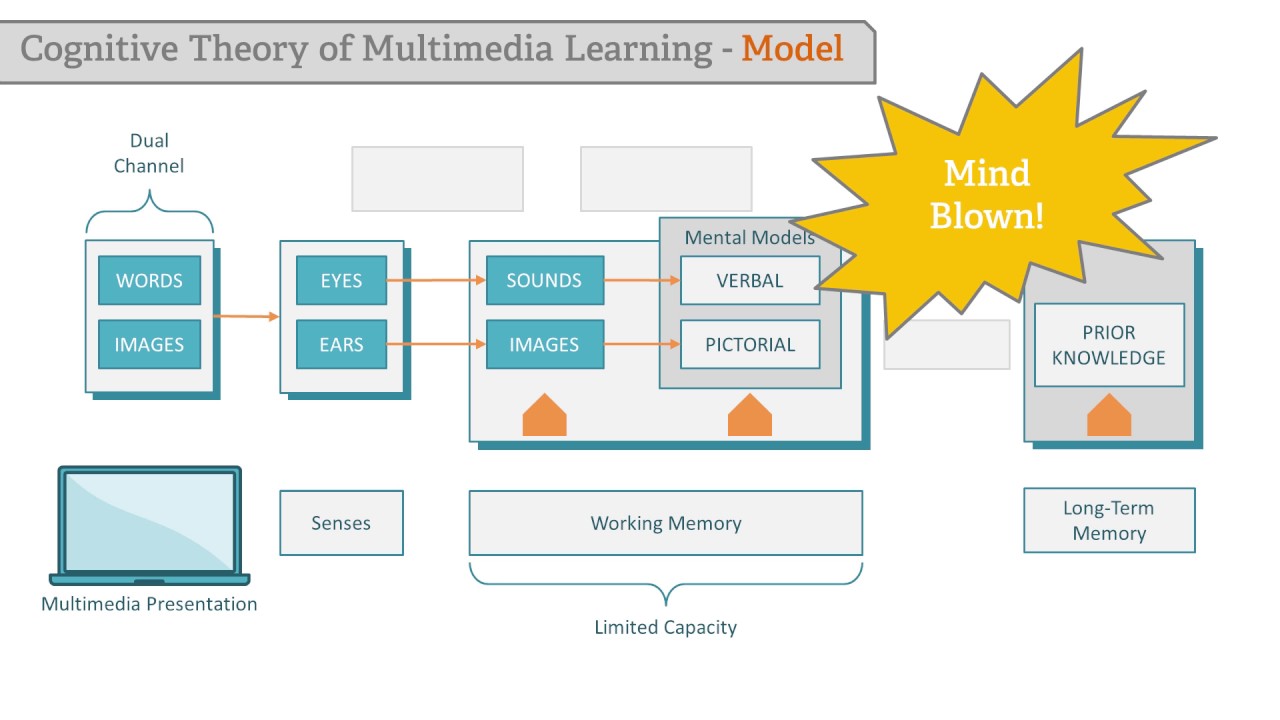
- 👁🗨 Dual Channel Assumption: Information is processed through separate channels for audio/visual and words/images, which are later combined.
- 🚫 Limited Capacity Assumption: Each channel has a limited capacity, and overloading them can hinder learning.
- 🤔 Active Processing Assumption: Learning requires active engagement to extract, organize, and integrate relevant information with prior knowledge.
- 🧐 Types of Processing: The brain performs extraneous, essential, and generative processing while learning from multimedia.
- 📉 Reducing Extraneous Processing: Instructional design should aim to minimize cognitive load from unnecessary processing.
- 📈 Managing Essential Processing: Efficiently organizing information intake to enhance learning without overloading cognitive capacity.
- 🌱 Fostering Generative Processing: Encouraging deeper understanding and retention by building upon existing knowledge structures.
- 🛠️ Mayer's Principles of Multimedia Design: A set of principles aimed at optimizing multimedia learning through instructional techniques.
Q & A
What is the main principle of multimedia learning as discussed in the video?
-The main principle of multimedia learning is the multimedia principle, which states that using words together with graphics, or multimedia, leads to better learning outcomes than using words alone.
What is the cognitive theory behind multimedia learning according to Professor Mayer?
-Mayer's Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning is based on three key assumptions: the dual channel assumption, the limited capacity assumption, and the active processing assumption.
What does the dual channel assumption suggest about how learners process information?
-The dual channel assumption suggests that learners process information through separate channels for audio and visual inputs, and that words and images are initially processed separately before being integrated.
How does the limited capacity assumption affect the design of educational multimedia?
-The limited capacity assumption implies that both the visual and auditory channels have a limited capacity for processing information at one time, which means that overloading these channels can hinder learning.
What is the active processing assumption and why is it important for learning?
-The active processing assumption states that learners must actively engage with the material by extracting relevant information and integrating it with their prior knowledge. This active engagement is crucial for effective learning.
What are the three types of cognitive processing that occur during multimedia learning?
-The three types of cognitive processing are extraneous processing, essential processing, and generative processing. Extraneous processing drains cognitive capacity without contributing to learning, essential processing involves organizing relevant information in working memory, and generative processing involves building upon prior knowledge.
How can instructional design techniques be used to enhance multimedia learning?
-Instructional design techniques can be used to reduce extraneous processing, manage essential processing for more efficient information intake, and foster generative processing for deeper understanding and retention.
What are Mayer's Principles of Multimedia Design and how do they relate to cognitive processing?
-Mayer's Principles of Multimedia Design are a set of guidelines derived from research that aim to reduce extraneous processing, manage essential processing, and foster generative processing, aligning with the cognitive theory of multimedia learning.
Can you provide an example of a principle that reduces extraneous processing?
-The coherence principle is an example that reduces extraneous processing by minimizing irrelevant information and focusing on the essential content.
What is the purpose of the segmenting principle in multimedia design?
-The segmenting principle aims to manage essential processing by breaking down complex information into smaller, more manageable segments, making it easier for learners to process and understand the material.
How does the personalization principle contribute to generative processing in multimedia learning?
-The personalization principle contributes to generative processing by making the material more relatable and engaging for the learner, which can encourage deeper reflection and integration of new information with existing knowledge.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)