Using similarity to estimate ratio between side lengths | High school geometry | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRIn this instructional video, the instructor guides viewers through a geometric problem involving the ratio of segment lengths in similar triangles. The focus is on identifying the correct pair of similar triangles among three given options by matching angle measures. Once identified, the instructor explains that the ratio of corresponding sides in similar triangles is constant. The example uses a 35-degree and 90-degree angle to establish similarity and approximates the ratio of segment PN to MN as roughly 0.6, suggesting choice B as the closest answer.
Takeaways
- 📐 The task is to approximate the ratio of the length of segment PN to the length of segment MN.
- 🔍 The solution involves identifying similar triangles among the given options.
- 🔢 Similarity in triangles is determined by having two angles in common, which implies the third angle is also the same.
- 📌 A 35-degree angle and a 90-degree angle are common in the triangles being compared.
- 🔎 Triangle two is identified as having a 35-degree angle, a 90-degree angle, and a 55-degree angle, making it similar to triangle PNM.
- 🌐 The angles in triangle PNM and triangle two add up to 180 degrees, confirming their similarity.
- 📏 The ratio of corresponding sides in similar triangles will be the same.
- 📊 PN corresponds to the side opposite the 35-degree angle, and MN corresponds to the side opposite the 55-degree angle.
- ✂️ The ratio of PN to MN is equivalent to the ratio of the corresponding sides in triangle two, which is 5.7 over 8.2.
- 🧩 It's important to note that the actual lengths of the sides are not 5.7 and 8.2, but the ratio is what is significant.
- 🔑 The final step involves approximating the ratio 5.7/8.2 to find the closest answer choice, which is suggested to be around 0.6.
Q & A
What is the main objective of the video script?
-The main objective is to approximate the ratio of the length of segment PN to the length of segment MN using the concept of similar triangles.
What is the significance of the 35-degree angle in the script?
-The 35-degree angle is significant because it is a common angle between triangle PNM and one of the given triangles, which helps in identifying the similar triangles.
How does the presence of a 90-degree angle contribute to the problem?
-The presence of a 90-degree angle indicates a right triangle, which is one of the criteria for identifying similar triangles in the context of this problem.
What mathematical concept is used to determine the similarity of triangles?
-The concept of angle-angle similarity is used, which states that if two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, the triangles are similar.
Why is it important to identify similar triangles in this context?
-Identifying similar triangles is important because it allows us to establish that the ratios of corresponding sides are equal, which is necessary to approximate the ratio of PN to MN.
What is the ratio of the red side to the blue side in the similar triangles?
-The ratio of the red side to the blue side in the similar triangles is 5.7 to 8.2, as these sides correspond to the segments PN and MN, respectively.
How does the instructor approximate the ratio of 5.7 to 8.2?
-The instructor approximates the ratio by dividing 57 by 82 and estimating that it is a little less than 0.7, suggesting a value around 0.6.
What is the purpose of the color coding in the script?
-The color coding is used to visually distinguish between the corresponding sides of the similar triangles, making it easier to identify which sides are being compared in the ratio.
Why can't the exact lengths of the sides be determined from the ratio alone?
-The exact lengths cannot be determined from the ratio alone because similarity only tells us that the ratios of corresponding sides are equal, not the actual lengths of the sides.
What is the conclusion the instructor reaches after approximating the ratio?
-The instructor concludes that the approximate ratio is between 0.57 and 1, and after a rough calculation, suggests that it is likely around 0.6, which corresponds to choice B in the given options.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Kekongruenan dan Kesebangunan [Part 4] - Kesebangunan Dua Segitiga
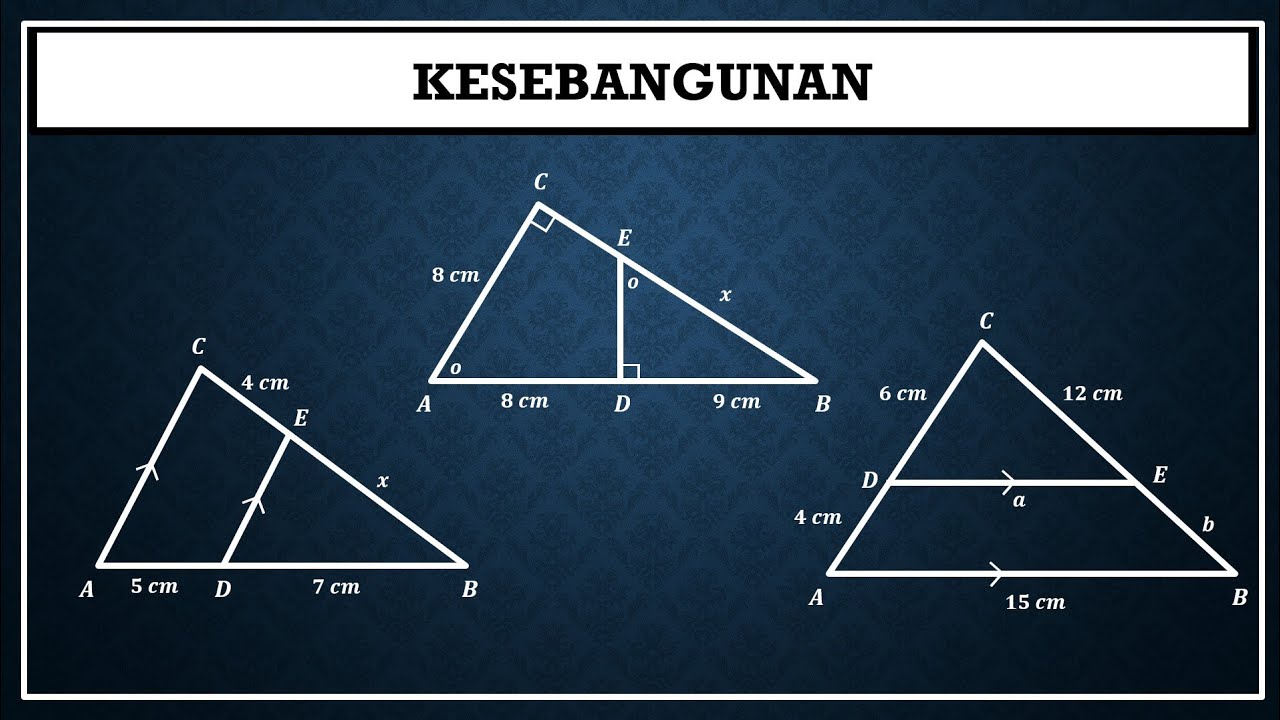
Kesebangunan pada segitiga
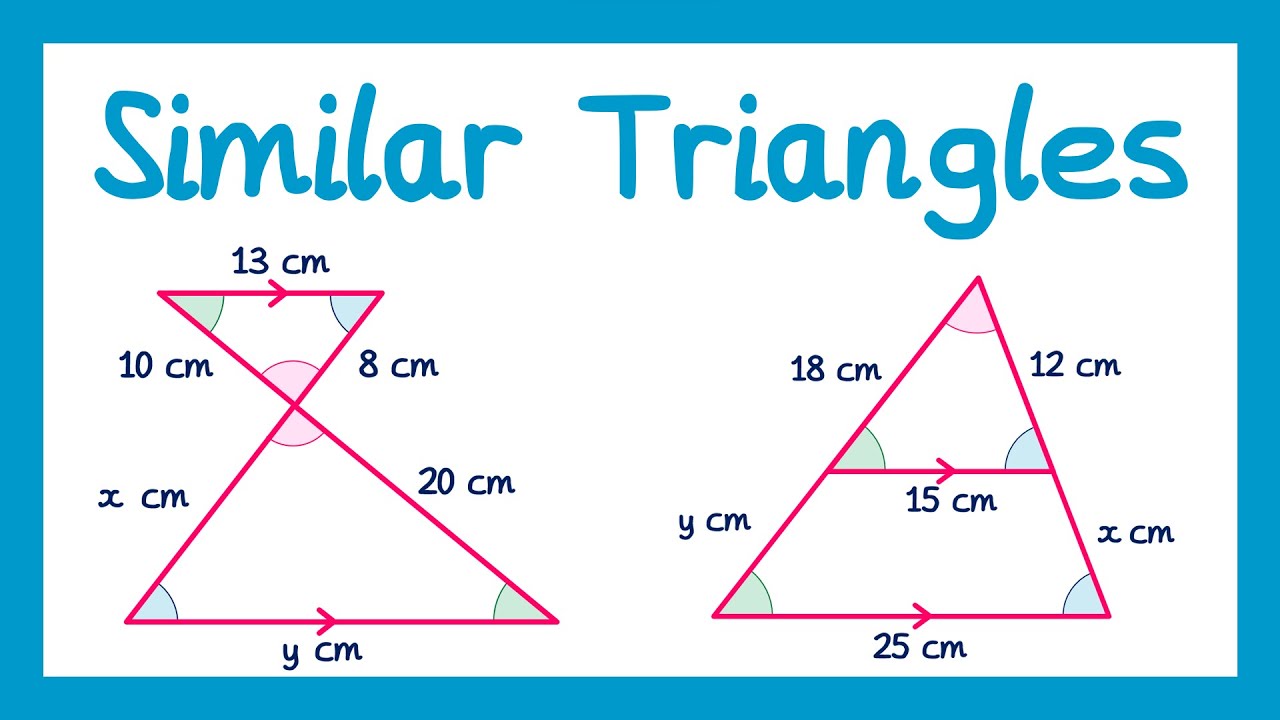
Similar Triangles - GCSE Maths

Triangles 5 | CAT Preparation 2024 | Geometry | Quantitative Aptitude

CRITERI DI CONGRUENZA DEI TRIANGOLI, criterios de congruencia de triangulos, triangoli congruenti

KESEBANGUNAN DUA BANGUN DATAR
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
