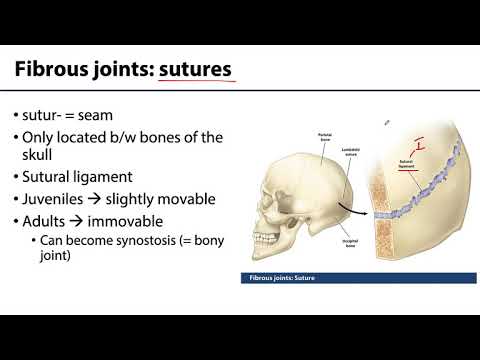
Labelled skull sutures
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the presenter explores the sutures of the human skull, explaining how these fibrous joints connect the various bones. The sutures, which evolved to minimize movement for brain protection, are named based on the bones they join. The video covers key sutures like the coronal, sagittal, and lambdoid, along with others like the squamosal and sphenozygomatic sutures. The presenter also highlights unique areas such as the terion, where several sutures meet, and the potential dangers of certain weak areas in the skull. Detailed yet accessible, this overview helps viewers understand the structure and naming conventions of skull sutures.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sutures in the skull are fibrous joints between bones that have evolved to allow minimal movement to protect the brain.
- 😀 The coronal suture connects the frontal bone to the parietal bones, forming a crown-like structure.
- 😀 The sagittal suture runs down the midline of the skull, joining the two parietal bones, and meets the coronal suture at the bregma.
- 😀 The lambdoid suture, shaped like the Greek letter lambda, connects the occipital bone to the parietal bones.
- 😀 The terion is a weak point where the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones meet, making it a vulnerable area of the skull.
- 😀 The squamosal suture connects the squamous part of the temporal bone to the parietal bone.
- 😀 The sphenoid bone connects to the temporal, parietal, and frontal bones, forming the sphenosquamosal, spheno-parietal, and spheno-frontal sutures.
- 😀 Sutural bones (or Wormian bones) may form in areas where sutures meet, typically where multiple sutures converge.
- 😀 The temporal bone has several sutures, including the temporozygomatic and frontozygomatic sutures, connecting it to other facial bones.
- 😀 The mastoid part of the temporal bone has a suture with the parietal bone called the parietal mastoid suture, while it also connects to the occipital bone at the occipital mastoid suture.
Q & A
What are the joints between the bones of the skull called?
-The joints between the bones of the skull are called sutures. These are fibrous joints that allow minimal movement to protect the brain.
Why do the bones of the skull have sutures instead of more flexible joints?
-The sutures are designed to minimize movement, which helps protect the delicate structures inside the skull, particularly the brain.
How do the bones of the skull connect at the sutures?
-The bones at the sutures have wiggly, interlocking edges that fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. Collagen fibers run across the joints to hold them in place.
What are Wormian or sutural bones?
-Wormian bones are small, extra bones that sometimes form within sutures, typically where multiple sutures meet. These bones are not common and don't have specific names.
What is the coronal suture, and which bones does it connect?
-The coronal suture runs across the skull, connecting the frontal bone to the two parietal bones. It is named for its crown-like appearance.
What is the sagittal suture, and what does it connect?
-The sagittal suture runs down the midline of the skull, connecting the two parietal bones. It's named after the sagittal plane, which divides the body into left and right halves.
What is the lambdoid suture and where is it located?
-The lambdoid suture is located at the back of the skull, connecting the occipital bone to the two parietal bones. It forms an upside-down 'V' shape and is named after the Greek letter lambda.
What is the terion, and why is it significant?
-The terion is the point where the sphenoid bone meets the frontal, parietal, and temporal bones. It is a weak spot in the skull and is associated with a risk of injury to the meningeal artery in case of a blow to the head.
What does the squamosal suture connect?
-The squamosal suture connects the squamous part of the temporal bone to the parietal bone. This suture is located laterally on the skull.
What is the significance of the mastoid process in relation to sutures?
-The mastoid process is part of the temporal bone and connects to the parietal bone through the parietal mastoid suture and to the occipital bone through the occipital mastoid suture. These sutures are often quite wiggly and variable.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)