Alternating and Direct Current | Electricity | Physics | FuseSchool
Summary
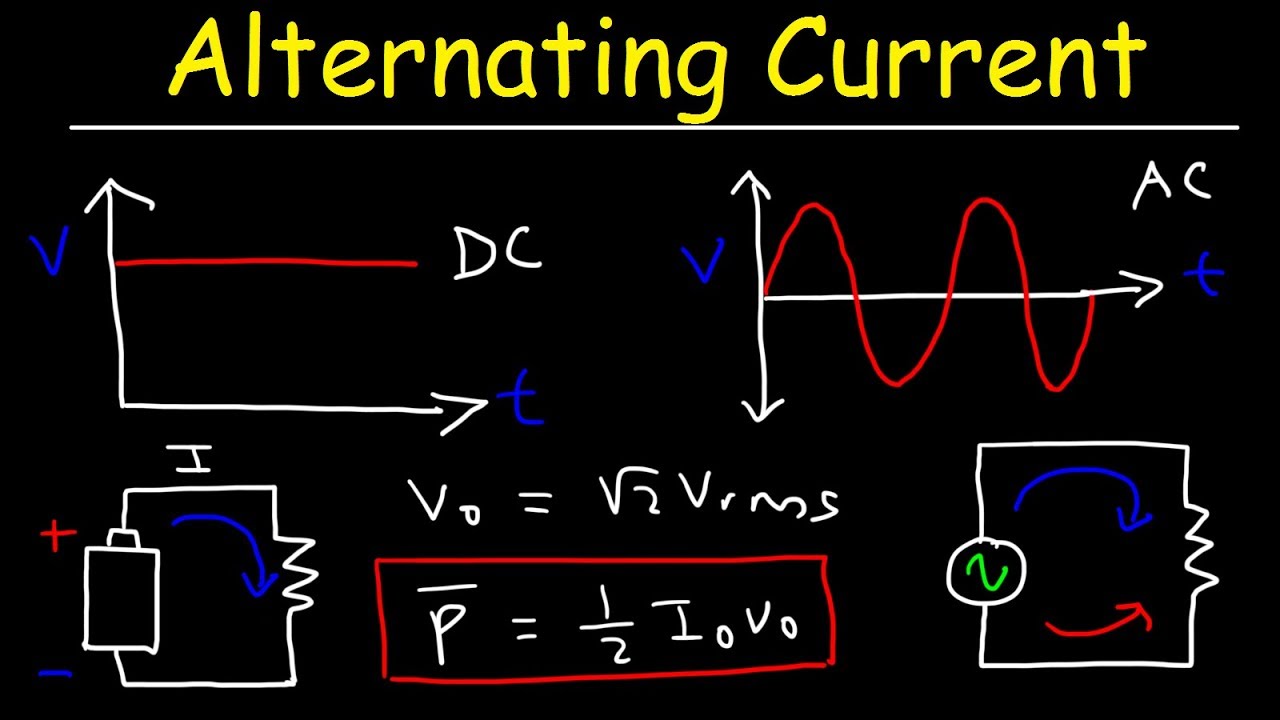
TLDRThis video explains the difference between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). It describes how DC flows in one direction, as seen in batteries, while AC reverses direction periodically, which is measured in frequency (hertz). AC is more practical for use in power grids due to the ease of voltage transformation with transformers. The video also demonstrates how an oscilloscope displays AC and DC, helping viewers understand the characteristics of each type of current through visual traces.
Takeaways
- ⚡ Electrical current is the flow of electrons through a circuit.
- 🔋 Direct current (DC) flows in only one direction, as seen in battery-powered circuits.
- 🔄 Alternating current (AC) changes direction continuously, such as in mains electricity.
- 📏 The frequency of AC, measured in hertz (Hz), is the number of times the current reverses per second.
- 🌍 AC frequency varies in different parts of the world.
- 🔌 AC is preferred for mains supply because its voltage can be easily transformed using transformers.
- 🏗️ Transformers are used to adjust voltage for appliances and to facilitate efficient electricity transmission on the national grid.
- 📊 On an oscilloscope, AC appears as a waveform alternating above and below zero, while DC appears as a flat line.
- 📈 Maximum potential difference (voltage) can be measured from an oscilloscope trace.
- ⏱️ Frequency can be calculated from the time period of one complete cycle on an oscilloscope using the formula f = 1/T.
- 🔍 Understanding oscilloscope traces helps distinguish between AC and DC and analyze electrical circuits effectively.
Q & A
What is electrical current?
-Electrical current is the flow of electrons through a conductor.
What is the main difference between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC)?
-Direct current (DC) flows in only one direction, while alternating current (AC) constantly changes direction.
In a DC circuit, which way do the electrons actually flow compared to the conventional current?
-Electrons, which are negatively charged, flow in the opposite direction to the conventional current, which is considered the flow of positive charges.
Why is mains electricity supplied as AC rather than DC?
-AC is used because it is much easier to change its voltage using transformers, allowing electricity to travel efficiently over long distances.
What is the frequency of an alternating current and how is it measured?
-The frequency of AC is the number of times the current changes direction in one second, measured in hertz (Hz) or cycles per second.
How does an oscilloscope display DC and AC differently?
-On an oscilloscope, DC appears as a constant, unchanging line, while AC appears as a waveform that oscillates between positive and negative voltages.
How can you calculate the frequency of an AC signal using an oscilloscope trace?
-Frequency can be calculated by measuring the time for one complete cycle on the oscilloscope and using the formula: frequency = 1 / time for one cycle.
If an AC waveform takes 0.02 seconds for one complete cycle, what is its frequency?
-The frequency is 50 hertz, calculated as 1 divided by 0.02 seconds per cycle.
What is the maximum potential difference in an AC circuit, as shown in the example?
-The maximum potential difference in the example AC circuit is 200 volts.
Why are transformers important in the national grid?
-Transformers adjust the voltage of AC electricity for efficient transmission over long distances and for use in household appliances.
What does one complete cycle of AC represent on an oscilloscope trace?
-One complete cycle represents the current changing direction and then returning to the starting point.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

AC vs. DC

AC and DC Electricity basics

AC and DC Current Explained | DC and AC current Explained | AC and DC Current |

Electrical Engineering: Basic Concepts (4 of 7) Electric Current: DC vs AC

Memahami Arus Bolak-Balik
Alternating Current vs Direct Current - Rms Voltage, Peak Current & Average Power of AC Circuits
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
