#FLUIDA STATIS pada Pertemuan ke -3
Summary
TLDRThis video explores Archimedes' Law and its implications for static fluids. It explains how an object submerged in a liquid experiences an upward force, which is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the object. The video also covers related concepts such as Pascal’s Law and the relationship between mass, weight, and buoyant force. Through example problems, viewers learn to calculate the upward force and understand the behavior of objects in different liquids. Practical applications, such as ships and submarines, are also discussed to demonstrate Archimedes' principle in action.
Takeaways
- 😀 Archimedes' Law explains that an object submerged in a fluid experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
- 😀 The upward force acting on a submerged object is called the Archimedes' Force, which balances the weight of the displaced fluid.
- 😀 Archimedes' Law is applied to calculate the buoyant force, where the formula is F_a = ρ * V * g, where ρ is the fluid's density, V is the object’s volume, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
- 😀 The buoyant force reduces the effective weight of an object when it is submerged in water, as compared to when it's weighed in air.
- 😀 The weight of an object in water (W_a) is less than its weight in air (W_u) due to the upward force exerted by the displaced liquid.
- 😀 To calculate the buoyant force, the volume of the object needs to be in cubic meters (m³) when using SI units, converting from cm³ if necessary.
- 😀 An example of calculating buoyant force: A rock with a volume of 100 cm³ submerged in water with a density of 1000 kg/m³ and gravity of 10 m/s² results in a buoyant force of 1 N.
- 😀 The weight reduction in water occurs because of the upward buoyant force; this force is equal to the weight of the displaced liquid.
- 😀 To calculate the buoyant force for an object weighing 10 kg in air but 4 kg lighter in water, we subtract the weight in water from the weight in air.
- 😀 When an object floats, the volume submerged in the liquid is related to the density of the object and the fluid, as described by Archimedes' Principle.
Q & A
What is Archimedes' Law and how does it relate to static fluids?
-Archimedes' Law states that when an object is submerged in a fluid, it experiences an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. This force is called the Archimedes force, and it is essential in understanding why objects float or sink in fluids.
How does Archimedes' Law explain why an object feels lighter in water?
-An object feels lighter in water because the upward buoyant force exerted by the water counteracts the object's weight. This upward force is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object, making the object appear lighter in water compared to when it is in air.
What is the formula for calculating the upward buoyant force according to Archimedes' Law?
-The upward buoyant force (Fa) is calculated using the formula: Fa = ρ * V * g, where ρ is the density of the fluid, V is the volume of the displaced fluid, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Why do we need to convert units when calculating the upward force in Archimedes' Law?
-We need to convert units to ensure consistency in the formula, especially when working with gravitational acceleration in meters per second squared (m/s²) and the volume in cubic meters (m³). This ensures the units are compatible for accurate calculations.
In the given example, how is the volume of an object immersed in water calculated?
-In the example, the volume of the object is given as 100 cm³, which must be converted to cubic meters (m³). The conversion factor is 1 cm³ = 10^-6 m³, so 100 cm³ is equal to 0.0001 m³.
What happens to the weight of an object when it is submerged in water?
-When an object is submerged in water, its weight decreases due to the buoyant force. The object appears lighter because the upward force exerted by the water counteracts some of its weight.
How is the weight of an object in air related to its weight in water?
-The weight of an object in water is less than its weight in air because of the upward force exerted by the water. The weight in water can be calculated using the formula: Wa = Wu - Fa, where Wu is the weight of the object in air, and Fa is the buoyant force acting on the object.
How is the buoyant force used in practical applications like ships and submarines?
-The buoyant force is crucial in the design and operation of ships and submarines. Ships rely on the buoyant force to float on water, while submarines can adjust their buoyant force by changing the amount of water in their ballast tanks, allowing them to dive or surface.
What factors affect whether an object sinks, floats, or remains suspended in water?
-An object's ability to float, sink, or remain suspended in water depends on the relationship between its density and the density of the fluid. If the object's density is less than that of the fluid, it will float; if it is greater, it will sink; and if they are equal, the object will remain suspended.
How can you calculate the volume of an object that is partially submerged in a fluid?
-To calculate the volume of an object that is partially submerged, you can use the formula: ρ_liquid * V_submerged = ρ_object * V_total, where ρ_liquid is the density of the liquid, V_submerged is the submerged volume, and ρ_object and V_total refer to the density and total volume of the object. This will give you the volume of the submerged part of the object.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

FISIKA KELAS XI: FLUIDA STATIS (PART 1) Tekanan dan Hukum Pascal
Fluida Statis ( Hukum Pascal - Archimedes ) - Simple Konsep - Fisika Kelas 11

Kelas XI Bab 3 Fluida Statis Part 1 Massa Jenis

TEKANAN ZAT CAIR (Tekanan Hidrostatis, Hukum Archimedes, Hukum Pascal)
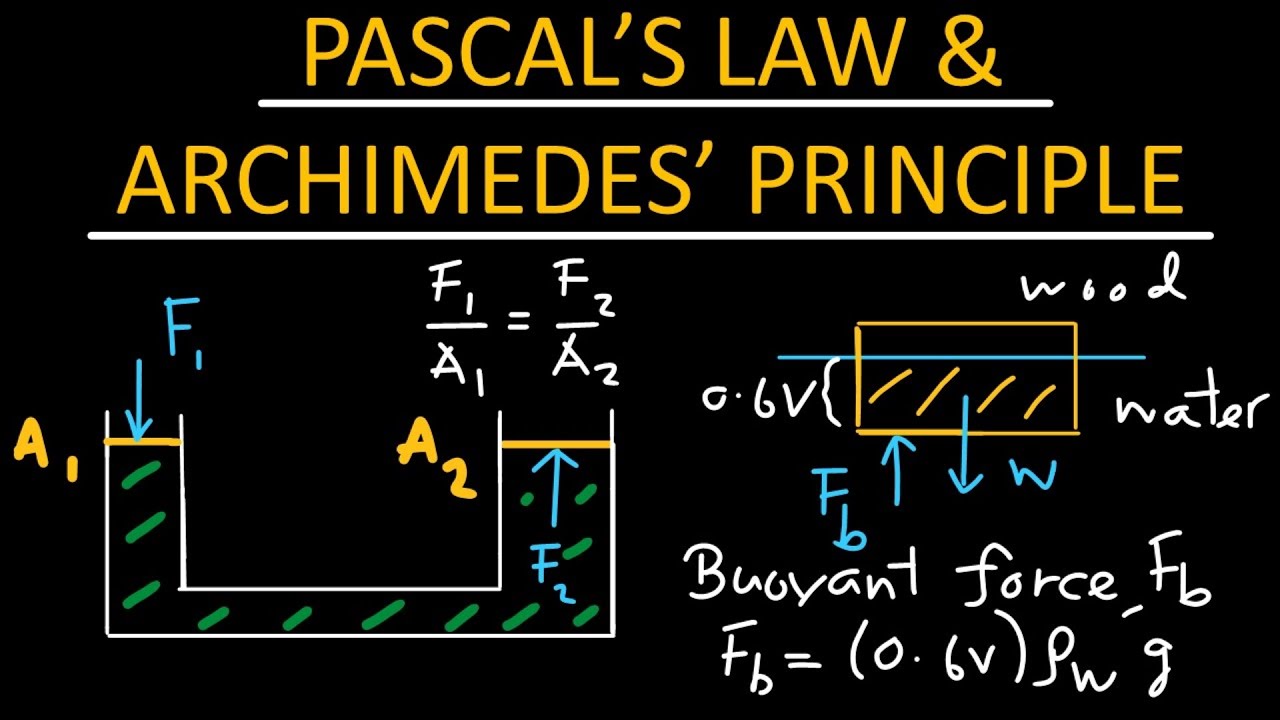
Understanding Pascal's Law and Archimedes' Principle - Physics

FISIKA Kelas 9 - Listrik Statis | GIA Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
