KOMPOSISI PENDUDUK, PIRAMIDA PENDUDUK, PERTUMBUHAN DAN KEPADATAN PENDUDUK
Summary
TLDRThis video covers key demographic concepts such as population composition, pyramid structure, population growth, and population density. It explains how populations are categorized based on biological, social, economic, and geographical factors. The video also highlights concepts like sex ratio and dependency ratio, providing calculations for better understanding. Additionally, it explores the different types of population pyramids (expansive, stationary, and constructive) and how they relate to population growth. Finally, it addresses methods to calculate population growth and density, including arithmetic, physiological, and agrarian density, with practical examples for each concept.
Takeaways
- 😀 Population composition refers to the grouping of the population based on specific criteria such as biological, social, economic, and geographic factors.
- 😀 Biological composition involves categorizing the population based on age and gender.
- 😀 Social composition is based on factors like education level, marital status, and other social indicators.
- 😀 Economic composition groups the population based on employment sectors, income levels, and economic activity.
- 😀 Geographic composition focuses on where people live, such as urban vs. rural areas or specific provinces and cities.
- 😀 Sex ratio is the comparison between the number of males and females in a specific area, expressed as the number of males per 100 females.
- 😀 Dependency ratio measures the proportion of non-productive (young and elderly) to productive (working-age) populations, indicating the economic burden on working individuals.
- 😀 Population pyramids visually represent the distribution of a population by age and gender, providing insights into population structure.
- 😀 Expansive population pyramids indicate high birth and death rates and are typical of developing countries with large young populations.
- 😀 Stationary population pyramids suggest low birth and death rates with balanced age groups, common in developed countries.
- 😀 Constrictive population pyramids represent countries with low birth rates and high elderly populations, often found in more developed nations like the USA or Germany.
Q & A
What is population composition?
-Population composition refers to the grouping of the population based on certain criteria such as biological factors (age and gender), social factors (education and marital status), economic factors (employment and income), and geographical factors (urban vs. rural areas).
What is the sex ratio, and how is it calculated?
-The sex ratio is the comparison of the number of males to the number of females in a given area. It is calculated using the formula: SR = (L / P) * 100, where L is the number of males, and P is the number of females.
What is the dependency ratio, and how do you calculate it?
-The dependency ratio measures the economic burden on the productive population (ages 15-64). It is calculated by dividing the non-productive population (ages 0-14 and 65+) by the productive population (ages 15-64), and then multiplying by 100.
What are the three types of population pyramids?
-The three types of population pyramids are: Expansive (youthful population with high birth and death rates), Stationary (balanced population with low birth and death rates), and Constrictive (aging population with fewer young people).
How does an expansive population pyramid differ from a constrictive pyramid?
-An expansive pyramid represents a country with high birth and death rates, where the population is younger. In contrast, a constrictive pyramid represents a country with low birth and death rates, with a higher proportion of elderly people.
What factors influence the structure of a population pyramid?
-The structure of a population pyramid is influenced by factors such as birth rates, death rates, and migration.
What is the difference between natural population growth and total population growth?
-Natural population growth is the difference between the number of births and deaths, excluding migration. Total population growth includes migration (immigration and emigration) in addition to natural growth.
How do you calculate natural population growth?
-Natural population growth is calculated using the formula: PA = L - M, where L is the number of births, and M is the number of deaths.
What is arithmetic population density?
-Arithmetic population density is the total population of an area divided by the total land area. It gives an indication of how crowded an area is on a basic level.
What is physiological population density, and how is it calculated?
-Physiological population density is the number of people per unit of arable (productive) land. It is calculated by dividing the total population in a region by the total area of arable land.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Population COMPOSITION, Explained [AP Human Geography Review—Unit 2 Topic 3]

Chapter 53: Population Ecology

Penduduk sebagai Sumber Daya Manusia #geography #geografi #kurikulummerdeka #erlanggaofficial

Terminologi ilmu kependudukan
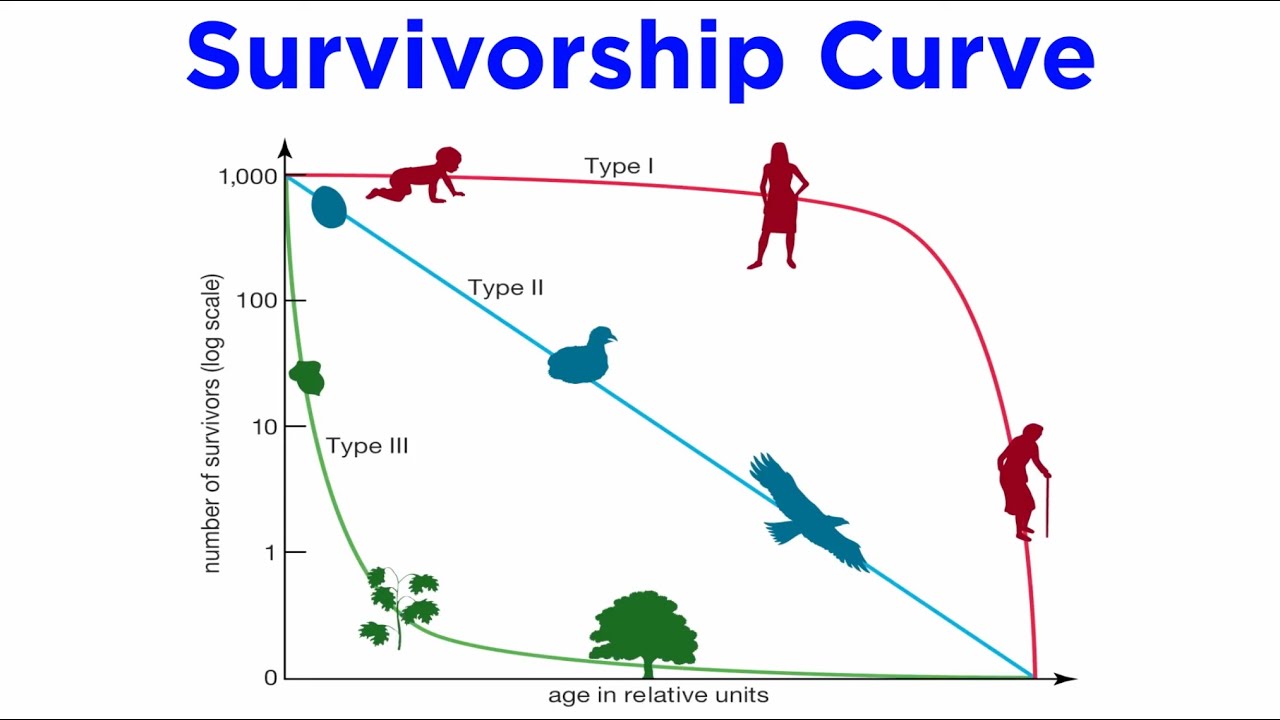
Population Ecology (Life Tables, Age Structure, Population Growth)
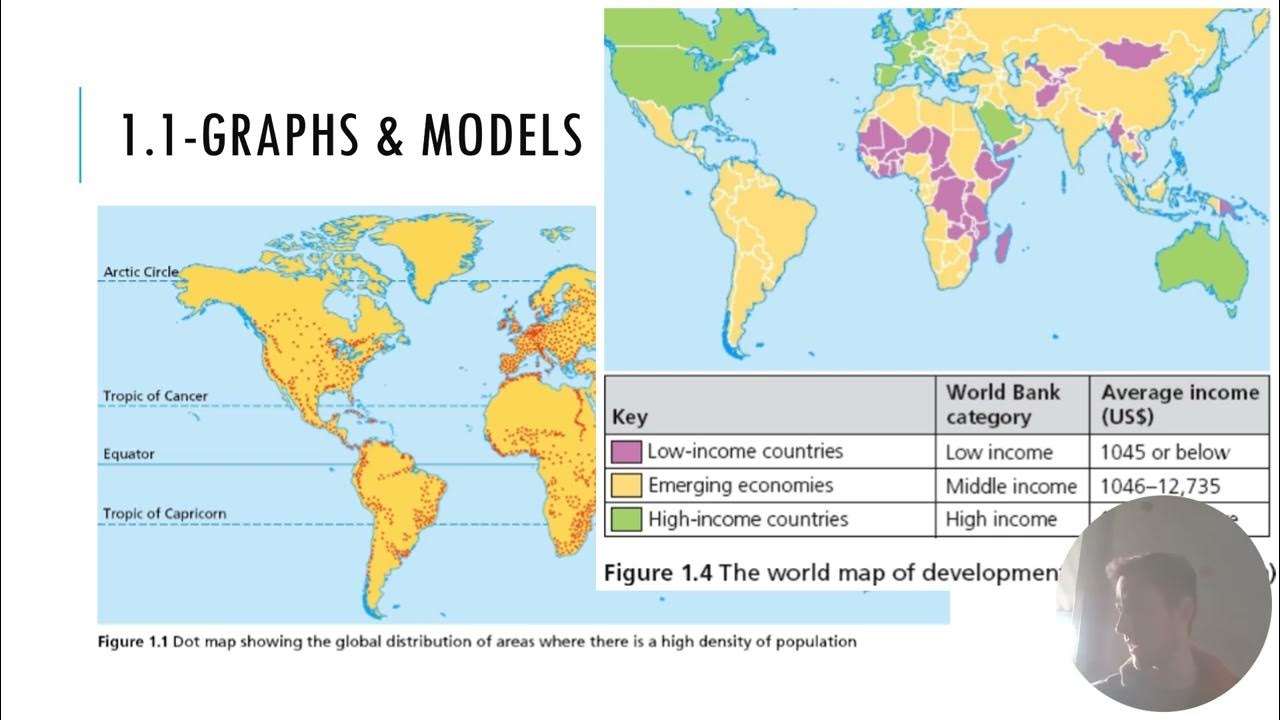
Finnian & Mr. Carley Review IB Geo Unit 1 (Part 1)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
