Earthquake - How Earthquakes Happen || video for kids || earthquake
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the powerful and often destructive force of earthquakes, highlighting their natural occurrence and causes. Earthquakes are the result of shifting tectonic plates, which create faults and cause the earth’s surface to shake. The video covers various types of earthquakes based on plate movements, such as convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries. It also explains the role of seismographs in studying seismic activity. With a focus on safety, the video offers tips for staying safe during and after an earthquake, emphasizing preparedness and awareness to mitigate the dangers of these natural disasters.
Takeaways
- 😀 Earthquakes are natural disasters caused by the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth's surface.
- 😀 The Earth's surface is made up of around 20 tectonic plates that move slowly and can cause earthquakes when they interact.
- 😀 Earthquakes can range from small tremors that go unnoticed to large, destructive quakes that can affect vast areas.
- 😀 The point where tectonic plates slip is called a fault, and the origin of the earthquake is the hypocenter.
- 😀 The epicenter is the location on the Earth's surface directly above the hypocenter where the earthquake is felt most strongly.
- 😀 There are three main types of earthquakes: Convergent boundary, Divergent boundary, and Transform fault, each based on plate movement.
- 😀 Convergent boundaries occur when one plate is forced over another, creating thrust faults.
- 😀 Divergent boundaries occur when plates move apart, usually forming a rift zone.
- 😀 Transform faults occur when plates slip past each other, leading to strike-slip faults.
- 😀 Earthquakes are studied using a seismograph, which measures and records seismic waves.
- 😀 Earthquakes can be extremely destructive, as seen in events like the Tohoku earthquake (2011) and the Chile earthquake (1960), which caused significant loss of life.
Q & A
What are some natural calamities caused by nature's sheer power, as mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions tornadoes, hurricanes, wildfires, flooding, volcanic eruptions, and earthquakes as examples of natural calamities caused by nature's power.
What is an earthquake, and how is it described in the script?
-An earthquake is described as the shaking, rolling, or sudden shock on the Earth's surface, often causing objects to fall and people to be thrown from their seats.
How many earthquakes occur worldwide each year?
-More than a million earthquakes occur around the world every year.
Which areas are most prone to earthquakes according to the script?
-The West Coast is most earthquake-prone, although earthquakes can also occur in the Midwest and along the East Coast.
What is the structure of the Earth's surface, and how does it relate to earthquakes?
-The Earth's surface is made up of around 20 tectonic plates that move slowly. Earthquakes occur when these plates bump, smash, or slide past one another, creating faults.
What are the two key locations associated with an earthquake's origin?
-The two key locations are the hypocenter, where the earthquake originates, and the epicenter, which is the location on the Earth's surface directly above the hypocenter.
What are the three main types of earthquakes based on plate movements?
-The three main types are: 1) Convergent Boundary (plates are forced over one another), 2) Divergent Boundary (plates are forced apart), and 3) Transform Fault (plates slip past each other).
How do scientists study earthquakes, as mentioned in the script?
-Scientists use a seismograph (or seismometer), an instrument that measures and records seismic waves generated by an earthquake.
Can you name some major earthquakes mentioned in the script, along with their magnitude?
-The script mentions the 2011 Tohoku earthquake in Japan with a magnitude of 9.0, the 1960 Valdivia earthquake in Chile with a magnitude of 9.5, and the 2015 Nepal earthquake.
What are some safety tips provided during an earthquake?
-Safety tips include: drop, cover, and hold on; stay indoors until the shaking stops; protect your head with a pillow if you're in bed; and if outdoors, find a clear spot away from buildings and trees.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Earthquakes 101 | National Geographic
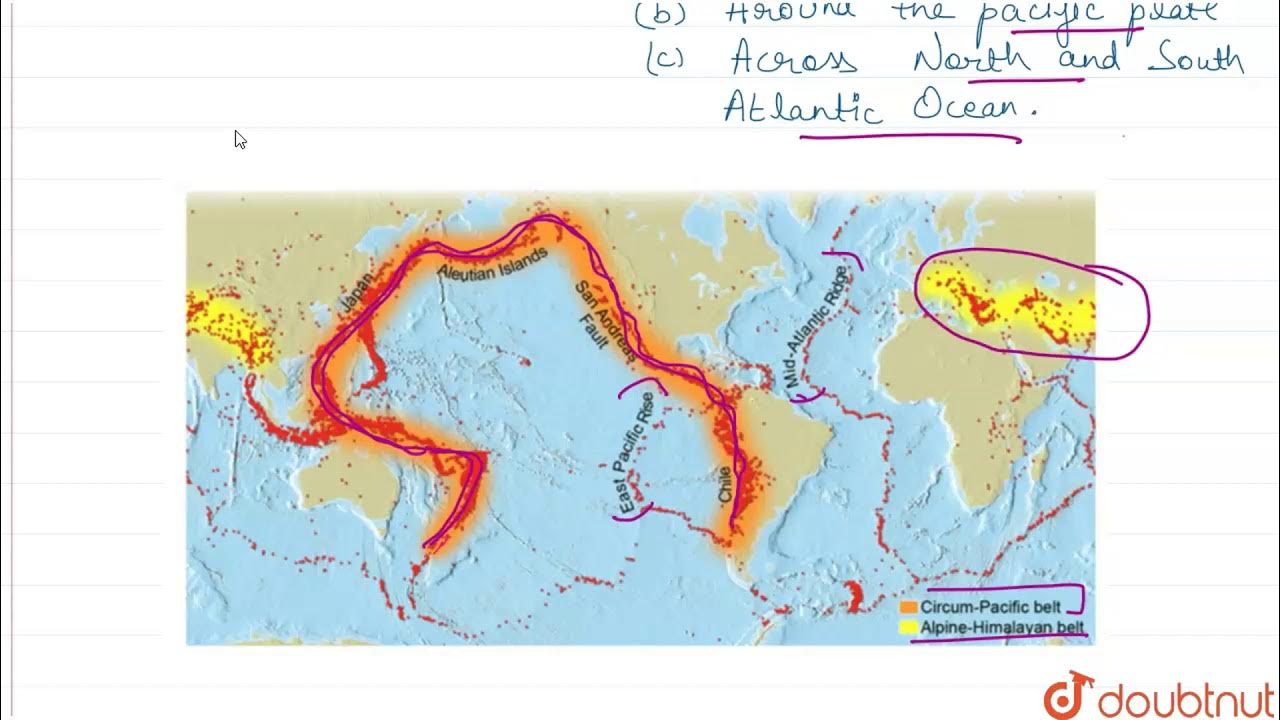
DISTRIBUTION OF EARTHQUAKE AND VOLCANOES

The 4 Tectonic Plate Boundaries and the Hazards they Create

[Why series] Earth Science Episode 2 - Volcanoes, Earthquakes, and Plate Boundaries

Earthquakes 101 | National Geographic

Konsep Dasar | Mengenal Macam-Macam Bencana Alam | Animasi Gempa Bumi | Animasi Banjir Untuk Anak
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
