Why do downloads look like waves?
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we explore the evolution of the internet in the late 1980s, focusing on the crucial issue of network congestion. The video delves into how TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) congestion control saved the internet from collapse by managing data flow, balancing speed and reliability. The process of slow start, congestion avoidance, and fast recovery in TCP is explained through the famous sawtooth pattern of download speed. Additionally, the video touches on the advancements in TCP, including newer versions like TCP Cubic, offering better performance on modern networks.
Takeaways
- 😀 The internet in the 1980s faced significant congestion issues, particularly in 1987, where data throughput dramatically decreased due to congestion collapse.
- 😀 TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) was developed to ensure reliable data delivery across the internet by breaking down data into smaller packets and managing packet loss.
- 😀 The 'sawtooth pattern' in download speeds, where the speed increases and then drops, is a result of TCP's congestion control mechanisms in action.
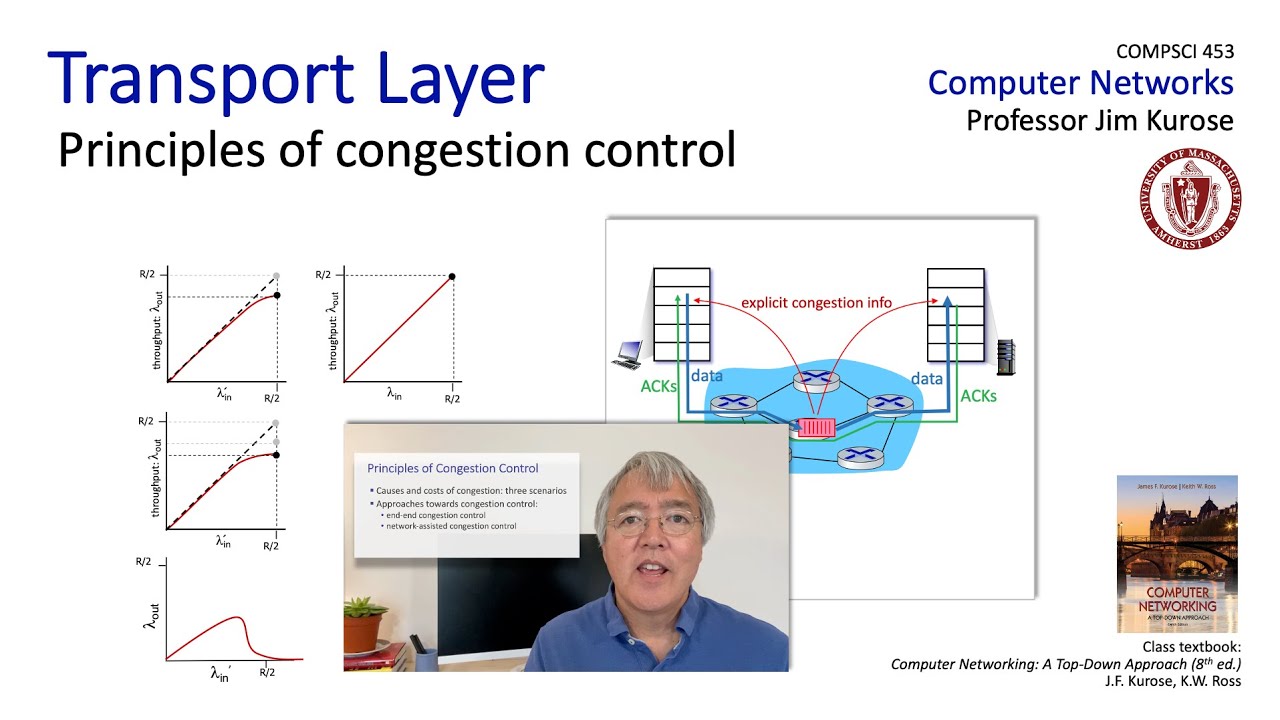
- 😀 TCP congestion control was introduced to prevent overwhelming the network, allowing for more efficient use of available bandwidth while avoiding network collapse.
- 😀 The key approach of TCP congestion control is Additive Increase Multiplicative Decrease (AIMD), which regulates data flow based on network conditions.
- 😀 TCP uses a variable called the 'congestion window' to manage how much data can be sent through the network without causing congestion or errors.
- 😀 Slow Start is the process that allows TCP to begin sending data conservatively, starting with a small congestion window and increasing it rapidly until packet loss or congestion occurs.
- 😀 When packet loss is detected, TCP reacts by reducing the congestion window, often restarting the process with Slow Start, or using 'fast recovery' to reduce congestion more gradually.
- 😀 The sawtooth pattern in download speed graphs is a result of TCP's exponential increase during Slow Start, followed by a dramatic drop during congestion, and a more linear increase during congestion avoidance.
- 😀 Newer versions of TCP, like TCP Cubic, have been developed to improve performance and handle congestion more efficiently, especially on certain networks.
- 😀 Despite the evolution of TCP, many devices still use the congestion control mechanisms developed in the 1980s, which are crucial for maintaining internet stability.
Q & A
What was the main issue with the internet in the 1980s?
-The main issue was a congestion collapse, where increased network traffic overwhelmed routers, causing a significant drop in data throughput and rendering the internet nearly unusable.
What is TCP, and why is it important for the internet?
-TCP, or Transmission Control Protocol, is a core protocol that ensures reliable and in-order delivery of data over the internet. It handles the problem of lost packets, retransmitting them to ensure complete data delivery.
What is the 'sawtooth' pattern in download speed graphs?
-The 'sawtooth' pattern occurs when download speeds fluctuate, starting slow, then increasing, and then sharply dropping. This happens due to TCP's congestion control mechanisms reacting to network congestion.
What does TCP's congestion control aim to solve?
-TCP's congestion control aims to prevent network congestion by adjusting the flow of data, ensuring that data is sent at a rate that the network can handle without overwhelming it.
What is the key concept behind TCP's congestion control?
-The key concept is the congestion window, which regulates how much data TCP can send at a time. This window is adjusted based on network conditions to avoid congestion and ensure efficient data transfer.
How does TCP detect network congestion?
-TCP detects congestion through packet loss, timeouts, or duplicate acknowledgements, which signal that data is being lost or delayed, indicating that the network is congested.
What happens when TCP detects congestion?
-When TCP detects congestion, it dramatically reduces the amount of data it sends by either restarting the slow start process or halving the congestion window in a process called fast recovery.
What is the slow start phase in TCP's congestion control?
-The slow start phase begins with a small congestion window, which increases exponentially with each round trip, allowing TCP to quickly find an optimal data transfer rate without overwhelming the network.
What happens during the fast recovery phase in TCP?
-During fast recovery, TCP reduces its congestion window by half and enters a more cautious congestion avoidance phase, allowing it to gradually increase the window again while avoiding further congestion.
How has TCP evolved since the 1980s?
-TCP has evolved with newer versions like TCP Cubic, which improves performance by adjusting the congestion window more efficiently, and other protocols like TCP VR and DCTCP that aim to reduce the severity of congestion control.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)