CARA MUDAH MEMPELAJARI SEL HEWAN DAN SEL TUMBUHAN
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth exploration of plant and animal cell structures, highlighting key organelles and their functions. It covers essential components such as the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes, as well as unique structures found in plant cells like the cell wall, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. The script delves into the roles of each organelle, such as protein synthesis, energy production, and cell division. The video also contrasts the differences between plant and animal cells, emphasizing the presence of certain organelles in plants that are absent in animals, making the comparison clear and informative.
Takeaways
- 😀 A cell is the smallest functional and structural unit of life, with sizes ranging from 10 to 100 micrometers, and the largest known cell is an ostrich egg.
- 😀 Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus.
- 😀 Plant cells have a cell wall, which animal cells do not have. Plant cells also contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis, which animal cells lack.
- 😀 The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is present in both plant and animal cells, but the cell wall is unique to plant cells.
- 😀 Ribosomes are tiny particles scattered throughout the cytoplasm and are responsible for protein synthesis.
- 😀 The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) exists in two forms: smooth (without ribosomes) and rough (with ribosomes attached). The rough ER helps in protein storage.
- 😀 Mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration and energy production, with their unique shape and inner membrane structures called cristae.
- 😀 Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles containing hydrolytic enzymes like lysozyme, responsible for digestion within the cell.
- 😀 The Golgi apparatus (or body) processes and synthesizes proteins from the rough ER and is involved in the synthesis of polysaccharides.
- 😀 Chloroplasts in plant cells are crucial for photosynthesis, containing the green pigment chlorophyll.
- 😀 Plant cells also have vacuoles and amyloplasts for storage of food and metabolic products, which are not present in animal cells.
- 😀 Centrioles, found near the nucleus in animal cells, play an important role in cell division.
- 😀 The key structural differences between plant and animal cells are the presence of a cell wall and plastids like chloroplasts in plants, while animal cells possess centrioles for division.
Q & A
What is the definition of a cell?
-A cell is the smallest functional and structural unit of life, and it is known to be microscopic, typically ranging from 10 to 100 micrometers in size.
What makes plant and animal cells eukaryotic?
-Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic because they have a nucleus, which is enclosed by a membrane.
What is the role of the cell membrane?
-The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, maintaining the cell's integrity.
What is the function of the cell wall, and which cells possess it?
-The cell wall is present only in plant cells and provides structural support and protection. It is rigid and made of polysaccharides.
How do ribosomes function within the cell?
-Ribosomes are responsible for synthesizing proteins, and they can be found either freely floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum?
-The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is not covered by ribosomes and is involved in the synthesis of lipids and cholesterol, while the rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes attached and is involved in protein storage.
What is the primary function of mitochondria?
-Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for energy production through the process of cellular respiration, which breaks down glucose to generate ATP.
Why do plant cells have chloroplasts and animal cells do not?
-Chloroplasts are found only in plant cells, where they carry out photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell?
-The Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins received from the rough endoplasmic reticulum, and it also synthesizes polysaccharides.
What are vacuoles, and in which type of cells are they most prominent?
-Vacuoles are membrane-bound structures involved in storage, waste disposal, and maintaining cell turgidity. They are more prominent in plant cells, where they are large and used for storing water and nutrients.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Overview of animal and plant cells | Biology | Khan Academy

WCLN - Cell Organelles - Biology

Grade 10 - Cell Theory and Cell Parts and Function

CÉLULA ANIMAL E CÉLULA VEGETAL - DIFERENÇAS | Biologia com Samuel Cunha
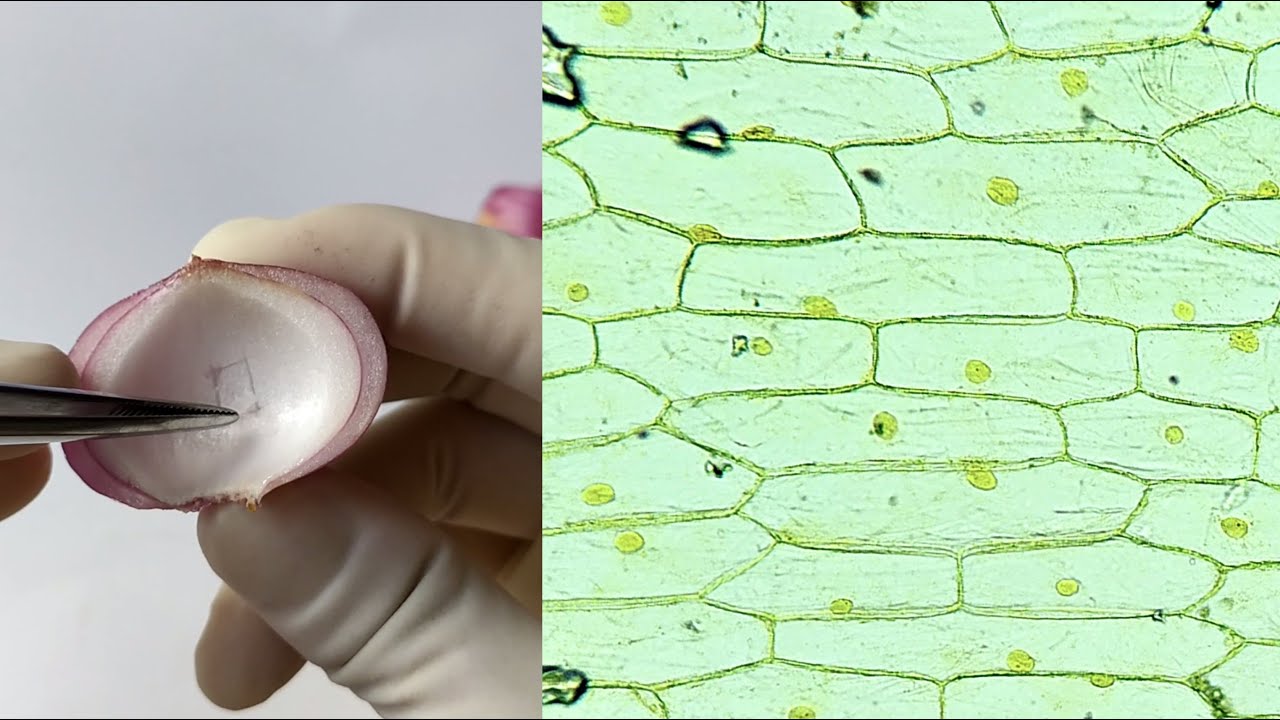
Onion Epidermal Cell Peel Slide Preparation Practical Experiment

Organelas Celulares : Estrutura celular e citoplasma - Animação 3D
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
