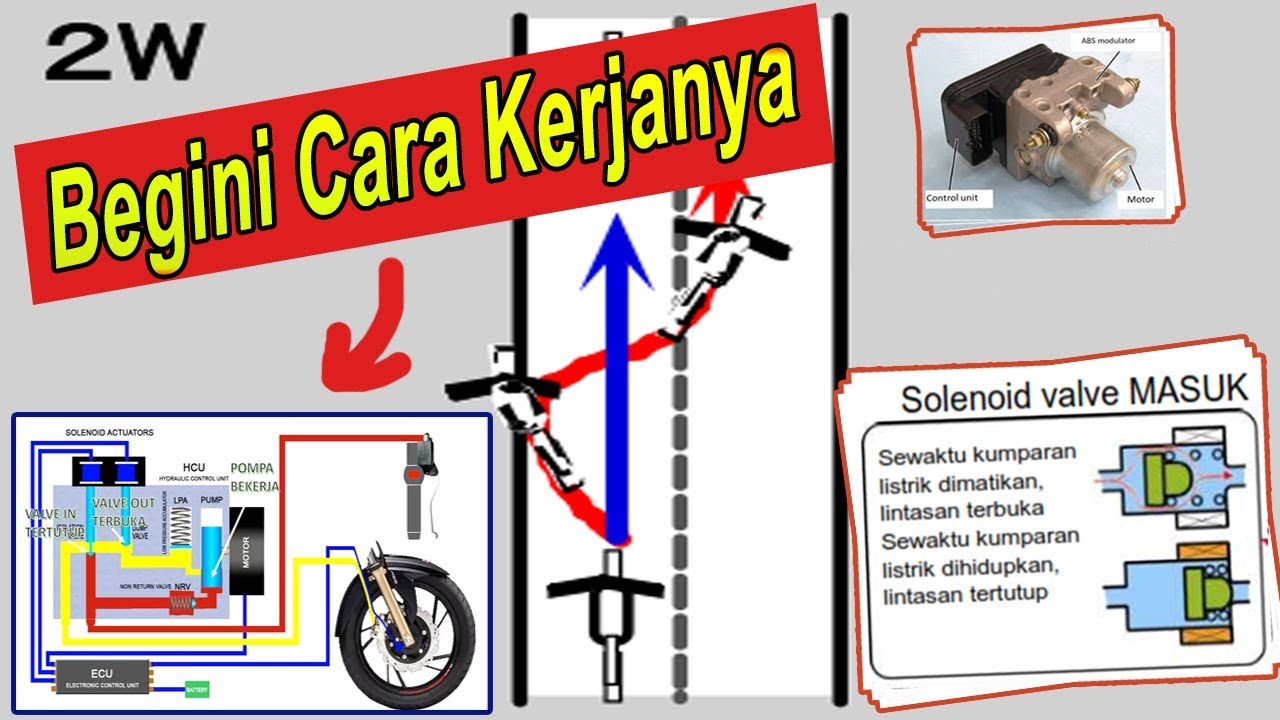
Cara kerja ABS dan Komponennya
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) works to enhance vehicle safety by preventing wheel lock-up during sudden braking. ABS uses several key components including the master cylinder, ABS pump, hydraulic valves, modulator valve, and wheel speed sensors to monitor and adjust braking pressure in real-time, ensuring vehicle stability and control. The video covers how ABS works in wet or slippery conditions, its components, and its operation in detail, highlighting the system's ability to rapidly adjust braking pressure, offering advantages like increased stability and faster stopping times. However, it also discusses some limitations of ABS, such as its reduced effectiveness in wet environments or on rough terrain.
Takeaways
- 😀 ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) prevents wheel lock-up during sudden braking, enhancing safety on slippery roads.
- 😀 The system works by quickly applying and releasing brake pressure to maintain traction and control of the vehicle.
- 😀 Slip occurs when braking force exceeds the traction between the tires and the road, causing the wheels to stop spinning.
- 😀 ABS uses sensors to detect wheel speed and adjusts braking pressure to prevent lock-up, allowing the vehicle to remain controllable.
- 😀 The process of applying and releasing brake pressure happens rapidly—multiple times per second—without the driver noticing.
- 😀 Key components of ABS include the master cylinder, ABS pump, hydraulic valves, modulator valve, wheel speed sensor, and the ABS control unit (ECU).
- 😀 The master cylinder transmits braking force from the brake pedal to the braking system.
- 😀 The wheel speed sensor detects wheel speed and sends data to the ABS control unit, which adjusts the brake pressure as needed.
- 😀 ABS is especially effective on wet, icy, or sandy roads where traction is reduced, improving vehicle stability and braking efficiency.
- 😀 Despite its advantages, ABS has limitations, such as reduced performance in wet conditions or on uneven terrain, and a higher risk of collisions during short-distance braking.
Q & A
What is ABS and why is it important in vehicles?
-ABS, or Anti-lock Braking System, is a technology designed to prevent a vehicle's wheels from locking up during braking, especially on slippery or wet surfaces. It is important because it helps maintain control of the vehicle during hard braking, thereby reducing the risk of accidents.
How does ABS prevent wheel slippage during braking?
-ABS prevents wheel slippage by automatically modulating brake pressure. If the system detects that a wheel is about to lock up (i.e., slip), it momentarily reduces brake pressure to allow the wheel to regain traction, then applies the brakes again. This cycle repeats rapidly, ensuring the vehicle remains under control.
What are the main components of the ABS system?
-The main components of the ABS system include the master cylinder, ABS pump, hydraulic valves (relay valve), modulator valve, wheel speed sensors, and the control unit (ECU). Each of these components plays a specific role in ensuring the ABS operates effectively.
How does the master cylinder function in the ABS system?
-The master cylinder in the ABS system is responsible for receiving pressure from the brake pedal and sending it to the brake system. It works in conjunction with the hydraulic pump and valves to regulate brake pressure and prevent wheel lock-up.
What role do the wheel speed sensors play in ABS?
-The wheel speed sensors measure the speed of each wheel and send this data to the ECU. If a sensor detects that a wheel is decelerating too quickly, the ECU triggers the ABS to modulate brake pressure to prevent the wheel from locking.
How does the modulator valve contribute to ABS operation?
-The modulator valve controls the hydraulic pressure applied to the wheels. It works in conjunction with the wheel speed sensors to adjust the brake pressure, preventing the wheels from locking up while allowing for proper braking force.
What happens when the ABS system detects wheel slippage?
-When the ABS detects wheel slippage, it reduces brake pressure to allow the wheel to regain traction. Once the wheel has traction again, the system re-applies brake pressure. This cycle repeats rapidly to ensure continuous control of the vehicle.
What are the advantages of using ABS in vehicles?
-ABS offers several advantages, including improved vehicle stability during emergency braking, reduced stopping distance on slippery surfaces, and enhanced safety. It also helps prevent the vehicle from skidding, especially on wet, icy, or sandy roads.
What are the disadvantages or limitations of ABS?
-Some disadvantages of ABS include decreased performance on uneven or off-road terrain, as ABS might not function as effectively on rough surfaces. Additionally, ABS may not perform optimally if the wheel speed sensors get wet or dirty, and in some cases, ABS might increase the risk of collisions in very close-range situations due to longer braking distances in certain scenarios.
How fast does the ABS system operate to prevent wheel lock-up?
-The ABS system operates extremely fast, cycling between brake pressure release and re-application 4 to 6 times per second. This ensures that the vehicle maintains optimal control during emergency braking without locking the wheels.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)