Types of Logistics
Summary
TLDRIn this conversation, a professor explains the concept of logistics to Jessica, covering its types and real-world applications. Logistics is the movement of goods from origin to consumption, encompassing activities like warehousing, transportation, inventory management, and order processing. The professor discusses three main types of logistics: inbound logistics (receiving products into a warehouse), outbound logistics (sending products out to customers), and reverse logistics (handling returns, such as empty drink bottles being sent back to the manufacturer). Through examples, Jessica gains a clearer understanding of how logistics operates in practice.
Takeaways
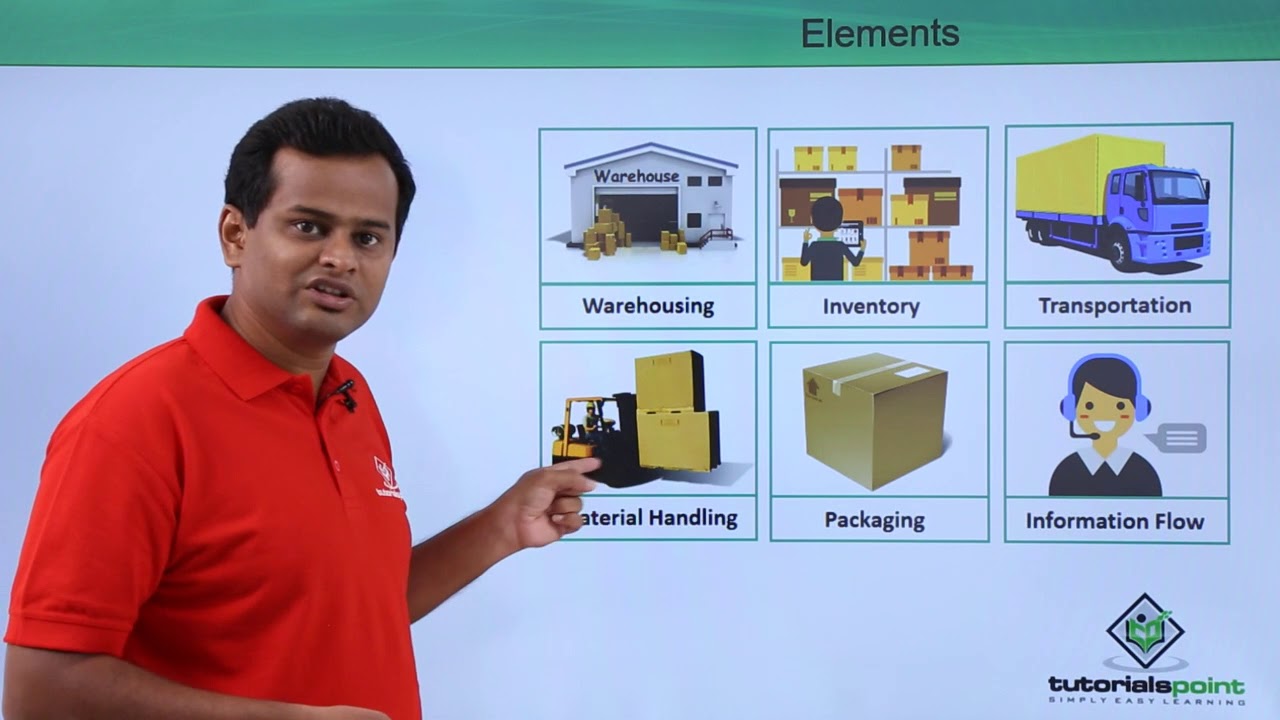
- 😀 Logistics is the movement of goods from point of origin to point of consumption.
- 😀 The process of logistics includes activities like warehousing, transportation, inventory management, and order processing.
- 😀 Inbound logistics refers to receiving products into a warehouse.
- 😀 Outbound logistics refers to sending products from a warehouse to another destination.
- 😀 Reverse logistics, also known as 'return to origin,' involves products being returned to the manufacturer or origin.
- 😀 An example of reverse logistics is when empty glass bottles are returned to the manufacturer after consuming cold drinks.
- 😀 The movement of goods involves multiple stages, such as warehousing, transportation, and inventory management, all of which fall under logistics.
- 😀 Logistics ensures products reach the end consumer from the manufacturer or retailer.
- 😀 The activities involved in logistics help maintain the flow of products through different points in the supply chain.
- 😀 Understanding logistics is essential for managing and optimizing the supply chain, from receiving to shipping products.
Q & A
What is logistics?
-Logistics is the movement of goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption. It includes all activities involved in getting a product to the end consumer.
Can you provide an example of logistics?
-An example of logistics would be a chair that is manufactured, stored in a warehouse, transported to a retailer, and eventually sold to a customer. This process involves warehousing, transportation, inventory management, and order processing.
What are the types of logistics discussed in the conversation?
-The types of logistics discussed are inbound logistics, outbound logistics, and reverse logistics.
What is inbound logistics?
-Inbound logistics refers to the process of receiving products into a warehouse. It involves the activities required to bring goods into a storage facility.
What is outbound logistics?
-Outbound logistics is the process of sending products from a warehouse to different destinations, such as retailers or directly to customers.
What is reverse logistics?
-Reverse logistics refers to the process where products are returned to the company, such as when a customer returns a product or when defective products are sent back to the manufacturer.
Can you provide an example of reverse logistics?
-An example of reverse logistics is when empty glass bottles from a cold drink are returned to the manufacturing unit after the product is consumed. These bottles are reused or recycled, which is a typical reverse logistics process.
Why is reverse logistics important?
-Reverse logistics is important because it helps companies manage returns efficiently, recover reusable materials, and reduce waste. It also ensures customer satisfaction by handling product returns effectively.
What role does inventory management play in logistics?
-Inventory management is a key aspect of logistics, ensuring that the right amount of products is stored in the right place. It helps maintain stock levels, minimize excess inventory, and fulfill customer orders in a timely manner.
How does transportation fit into logistics?
-Transportation in logistics refers to the movement of goods from one location to another, whether it’s from a warehouse to a retailer or from a manufacturer to a customer. It's essential for ensuring products reach their destination.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)