GARIS DAN SUDUT
Summary
TLDRThis lesson, presented by Vivi Nur Afida, covers essential concepts about lines and angles. It starts with an introduction to points, lines, rays, and line segments, explaining their definitions and notations. The lesson proceeds to explore the relationships between lines, such as parallel, intersecting, and coincident lines, with practical examples. It also delves into angles, their formation, and measurement, highlighting different types like acute, right, obtuse, and reflex angles. The session concludes with guidance on converting angle units and using a protractor for accurate angle measurement, making the concepts accessible for students learning geometry.
Takeaways
- 😀 A point is represented by a dot and denoted with a capital letter, like A, B, or C.
- 😀 A line is a set of points extending infinitely in both directions, represented with lowercase letters like k, l, or m.
- 😀 A ray has a starting point but extends infinitely in one direction, denoted with an arrow at the end, like OA.
- 😀 A line segment has two endpoints and is written without arrows, such as AB.
- 😀 A point can lie on a line, be outside a line, or on a specific position relative to it.
- 😀 Lines can be parallel, meaning they never meet, or intersect at a single point if not parallel.
- 😀 Perpendicular lines meet at a 90° angle and are denoted with a right angle symbol.
- 😀 Types of angles include acute (less than 90°), right (90°), obtuse (greater than 90° but less than 180°), straight (180°), reflex (greater than 180° but less than 360°), and a full circle (360°).
- 😀 Angle measurement can be expressed in degrees or radians, with conversions between minutes and seconds in degrees.
- 😀 Bushels are used to measure angles, where the center point aligns with the angle's vertex, and the horizontal and vertical lines assist in identifying the angle.
Q & A
What is the difference between a line, ray, and line segment?
-A line is infinite in both directions, represented by two points and extending forever. A ray has a fixed starting point and extends infinitely in one direction, while a line segment has two fixed endpoints and is a finite part of a line.
How do you represent a point in geometry?
-A point is represented by a dot and is denoted using an uppercase letter, such as A, B, or C.
What does it mean for two lines to be parallel?
-Parallel lines are lines that are equidistant from each other and never meet, regardless of how far they are extended.
What is the characteristic of perpendicular lines?
-Perpendicular lines intersect at a right angle (90°). This means they form a 90° angle at the point of intersection.
What is an acute angle and how is it measured?
-An acute angle is an angle that is less than 90°. It is measured in degrees, with any angle between 0° and 90° being considered acute.
How do you name an angle geometrically?
-An angle is named by its vertex and the two rays forming the angle. For example, the angle formed by rays AB and BC can be named as ∠ABC or ∠B.
What are the types of angles in geometry?
-The types of angles include acute angles (less than 90°), right angles (90°), obtuse angles (greater than 90° but less than 180°), straight angles (180°), and reflex angles (greater than 180° but less than 360°).
What is the full rotation of an angle in degrees?
-A full rotation of an angle is 360°. This represents a complete turn around a point.
What are the units used to measure angles?
-Angles are commonly measured in degrees (°), with further subdivisions into minutes (′) and seconds (″). Additionally, angles can be measured in radians, where 2π radians equal 360°.
How do you convert between degrees, minutes, and seconds?
-To convert between degrees, minutes, and seconds, 1° is equal to 60 minutes (′), and 1 minute is equal to 60 seconds (″). For example, 30 minutes equals 0.5° and can be expressed as a fraction of a degree.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Garis dan Sudut Kelas 7 SMP Semester 2

Pembahasan Mari Kita Periksa Garis Sejajar dan Segi Banyak Hal 115 Bab 4 Kelas 8 Kurikulum Merdeka

Garis dan Sudut (5) | Hubungan Antar Sudut pada Dua Garis Sejajar | Matematika Kelas 7
GARIS DAN SUDUT (PART 2)

Garis dan Sudut (1) | Pengenalan Garis dan Sudut | Matematika Kelas 7
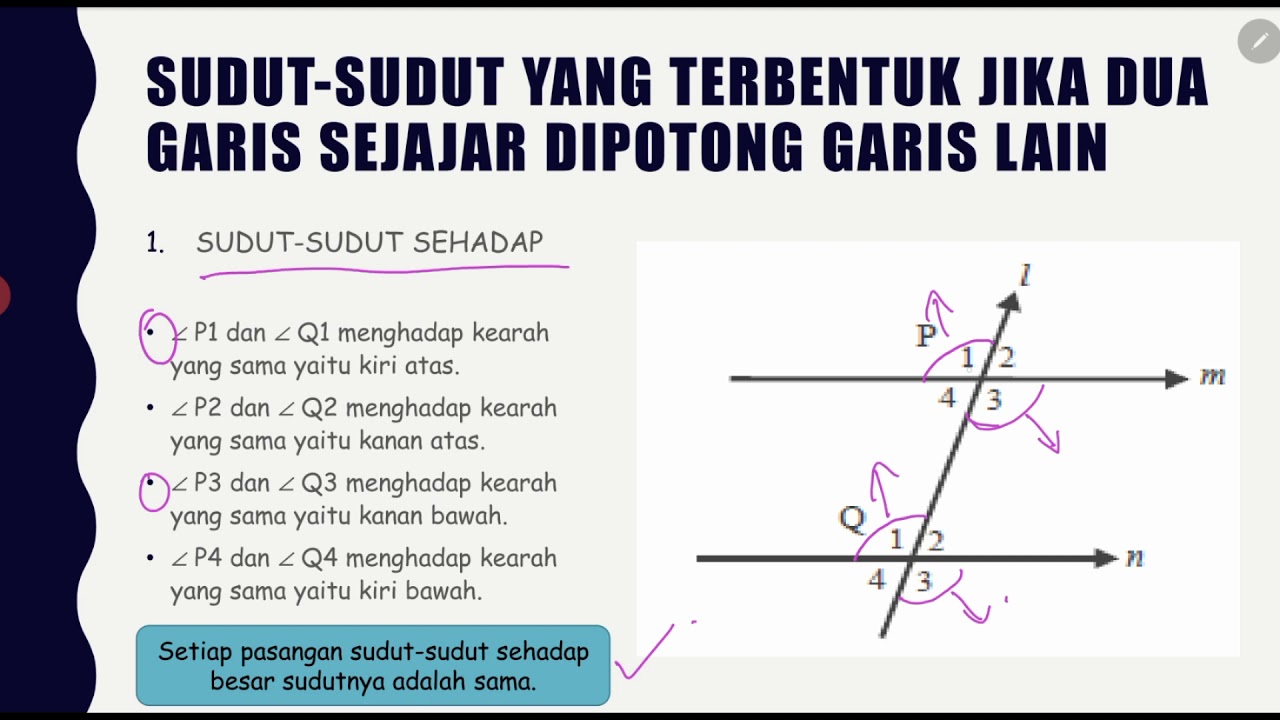
Kedudukan Dua Garis & Hubungan Antara Sudut dan Garis Kelas 7 SMP
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
