[BAKTERIOLOGI] Part 1 Metabolisme Bakteri
Summary
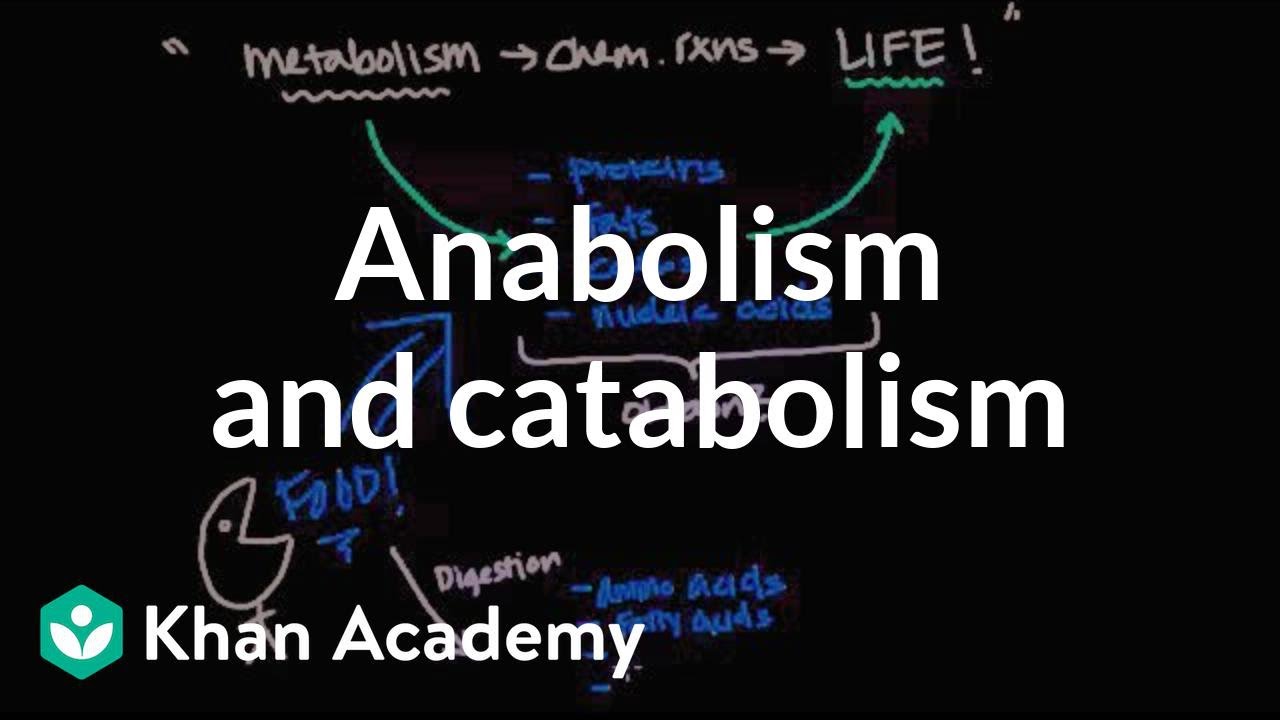
TLDRThis script provides an in-depth explanation of bacterial metabolism, breaking down the two key processes: anabolism and catabolism. Anabolism involves building complex molecules using energy, while catabolism breaks down molecules to release energy, which powers the cell's functions. The script also covers the roles of enzymes, such as dehydrogenase, in these reactions and explains the importance of oxidation and reduction in bacterial energy production. Environmental factors like temperature, pH, nutrients, and other organisms influence bacterial metabolism, affecting their survival and function in diverse habitats.
Takeaways
- 😀 Metabolism refers to all the chemical reactions that occur in cells to generate and utilize energy, essential for various functions like breathing, thinking, growing, and movement.
- 😀 Bacterial metabolism involves complex biochemical processes, including both anabolism (synthesis of molecules) and catabolism (breakdown of nutrients to release energy).
- 😀 Anabolism uses energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones, while catabolism breaks down molecules, releasing energy that can be stored in ATP.
- 😀 Energy required for anabolic reactions can come from light (photosynthesis) or chemical energy.
- 😀 Catabolic reactions release energy, which is used by cells for various activities, including growth, reproduction, and transport.
- 😀 Oxidation-reduction reactions are crucial in bacterial metabolism, where electrons are transferred from one molecule to another to generate energy.
- 😀 The energy produced in oxidation reactions is transferred to electron acceptors, such as NAD+ and NADPH, to facilitate further metabolic processes.
- 😀 ATP is the primary energy carrier used by cells to perform various chemical reactions, such as growth, reproduction, and movement.
- 😀 Environmental factors, such as temperature, nutrient availability, and pH, greatly affect bacterial metabolism and survival.
- 😀 Examples of metabolic processes in bacteria include respiration, where food sources like carbohydrates, fatty acids, and amino acids are broken down to release energy.
- 😀 The proper functioning of bacterial metabolism depends on the balance between anabolism and catabolism, with each supporting the overall energy needs of the cell.
Q & A
What is bacterial metabolism?
-Bacterial metabolism refers to all the biochemical reactions occurring within a bacterial cell that generate energy for various cellular functions such as growth, movement, and respiration.
What are the two primary processes involved in bacterial metabolism?
-The two primary processes in bacterial metabolism are catabolism and anabolism. Catabolism involves the breakdown of complex molecules to release energy, while anabolism involves synthesizing complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy input.
What is catabolism, and how does it benefit the bacteria?
-Catabolism is the process of breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy in the form of ATP. This energy is crucial for the bacteria to perform essential functions such as reproduction and maintaining cellular processes.
What is anabolism, and how does it function in bacteria?
-Anabolism is the process in which bacteria use energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones, such as proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. This process is essential for bacterial growth and reproduction.
How do bacteria obtain energy through oxidation-reduction reactions?
-Bacteria obtain energy through oxidation-reduction reactions, where oxidation (electron loss) is coupled with reduction (electron gain). This results in the formation of energy-rich molecules like NADH and ATP, which are used in cellular activities.
What is the role of ATP in bacterial metabolism?
-ATP acts as the primary energy currency in bacterial metabolism. It stores and transports energy within the cell, driving essential processes like growth, transport, and reproduction.
What is the process of bacterial respiration?
-Bacterial respiration is a catabolic process where bacteria break down nutrients such as carbohydrates, fatty acids, and amino acids to produce energy, water, and carbon dioxide.
What are the sources of energy for bacteria in anabolism?
-In anabolism, bacteria use energy from light (in photosynthetic bacteria) or from chemical reactions to synthesize complex molecules from simpler ones.
How do environmental factors affect bacterial metabolism?
-Environmental factors such as temperature, pH, nutrient availability, and the presence of other organisms can significantly influence bacterial metabolism, growth, and survival.
What is the difference between oxidation and reduction in bacterial metabolism?
-Oxidation is the process where bacteria lose electrons, while reduction involves the gain of electrons. These processes are linked in bacterial metabolism and are essential for generating energy through oxidation-reduction reactions.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)