What is corrosion?
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the science of corrosion, a costly and widespread problem that leads to metal loss when it interacts with moisture. Environmental factors like salt water, humidity, and soil resistivity can accelerate corrosion. The process begins in an electrochemical cell, where oxidation occurs at the anode, while reduction happens at the cathode. Corrosion can be identified visually, through testing, or microscopy and can take different forms such as general corrosion, localized corrosion, and microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC). Understanding and identifying corrosion is key to preventing significant damage and costly repairs.
Takeaways
- 😀 Corrosion is caused by an electrochemical reaction between metal and moisture, leading to rust and metal loss.
- 😀 Rust and corrosion can result in significant health, safety, and financial issues, with an estimated cost of $2.5 trillion globally.
- 😀 Effective corrosion control practices can save between $375 billion and $875 billion annually.
- 😀 Corrosion is influenced by environmental factors such as exposure to salt water, humidity, and soil resistivity.
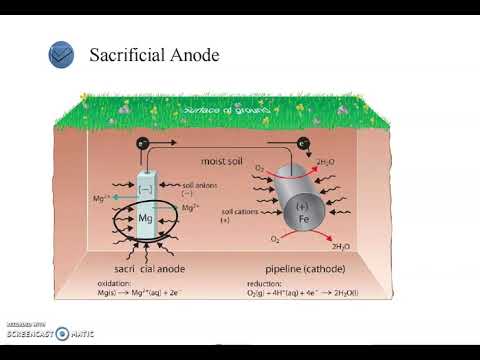
- 😀 Corrosion forms when an electrochemical cell is created, causing metal to lose electrons at the anode while the cathode remains unaffected.
- 😀 The essential components of corrosion cells are an anode, cathode, metallic and electrolytic paths, and a potential difference that drives the process.
- 😀 Corrosion can be identified through visual examination, supplementary methods, or testing verification via microscopy.
- 😀 There are two main types of corrosion: general corrosion (uniform surface damage) and localized corrosion (focused on discrete sites).
- 😀 Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC) is a form of corrosion caused by fungi, bacteria, microalgae, and other microorganisms, often found in environments like sewage.
- 😀 Identifying corrosion is the first step in mitigating and preventing further damage through effective control measures.
- 😀 The next step in corrosion prevention involves understanding different forms of corrosion and applying suitable control methods.
Q & A
What is the main cause of rust formation on metals?
-Rust formation occurs when metal is exposed to moisture, leading to an electrochemical reaction that causes metal loss.
How much does corrosion cost globally?
-Corrosion costs approximately 2.5 trillion dollars, which is more than three percent of the global gross domestic product.
What are the potential benefits of corrosion control practices?
-Corrosion control practices can limit damage, saving between 375 to 875 billion dollars annually.
What factors can cause corrosion to form more quickly?
-Exposure to saltwater, humidity, and soil resistivity are three common environmental factors that increase the likelihood of corrosion.
What is the process that leads to corrosion?
-Corrosion begins in the electrochemical cell, where the anode corrodes while the cathode remains unaffected, creating a potential difference that drives corrosion.
What are the key elements in all corrosion cells?
-The key elements are the anode (where oxidation and metal loss occur), the cathode (where reduction and protective effects occur), metallic and electrolytic paths for electronic and ionic current flow, and a potential difference that drives the process.
How can corrosion be identified?
-Corrosion can be identified through visual examination, supplementary examination, or testing verification by microscopy.
What are the two main types of corrosion?
-The two main types of corrosion are general corrosion, which is uniform over an exposed surface, and localized corrosion, which occurs at discrete sites.
What is microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC)?
-Microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) occurs in the presence of microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria, microalgae, and other microbiologically active materials like sewage.
Why is identifying corrosion important?
-Identifying corrosion is crucial because it is the first step in preventing and mitigating further damage to materials.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)