Muscles and Movement | Antagonist Pairs of Muscles
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we explore 15 out of over 600 muscles in the human body, focusing on their functions and how they work in antagonist pairs to control joint movements. Key concepts such as flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and muscle contractions (isometric and isotonic) are explained. The video details the origins and insertions of these muscles, and covers muscles in the arms, shoulders, torso, and legs, including the biceps, triceps, deltoids, pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, and more. Practical examples and diagrams are used to illustrate these concepts.
Takeaways
- 💪 The human body has over 600 muscles, and the video focuses on 15 common superficial muscles that control movement of joints like the elbow and shoulder.
- 🤔 The video introduces movement terms such as flexion (decreasing joint angle), extension (increasing joint angle), abduction (moving away from the midline), adduction (moving towards the midline), and rotation (turning a joint).
- 🤸♂️ Antagonist pairs of muscles are highlighted, where one muscle (e.g., biceps for flexion) works against another (e.g., triceps for extension) to control joint movement.
- 🦴 The concepts of origins and insertions are explained, with origins being the stationary attachment point of a muscle and insertions being the moving point.
- 🏋️♂️ Two types of muscle contractions are discussed: isometric (same length, no movement) and isotonic (same force, with movement).
- 📐 The script explains the muscles' actions, such as the biceps brachii flexing the elbow and the triceps brachii extending it.
- 🤲 The deltoids are responsible for abducting the arm, while the pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi work together as antagonists to adduct the arm.
- 🧘♂️ The rectus abdominis bends the spine, and the external abdominal obliques assist in lateral bending and rotation.
- 🏃♂️ The gluteus maximus extends the hip joint, while its antagonist, the iliopsoas, flexes the hip joint.
- 🧗♂️ The biceps femoris (hamstrings) flex the knee, and the quadriceps muscle group extends the knee.
- 🚶 The gastrocnemius plantar flexes the ankle, and the tibialis anterior dorsiflexes the ankle.
Q & A
How many muscles does the human body have, and what is the focus of the video?
-The human body has over 600 muscles, but the video focuses on 15 common superficial muscles that control the movement of different joints.
What are antagonist pairs in the context of muscles?
-Antagonist pairs refer to pairs of muscles that work against each other to control the movement of joints, such as the biceps and triceps working in opposition to flex and extend the elbow joint.
What are the main movement terms covered in the video?
-The main movement terms covered in the video are flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation.
What is the difference between flexion and extension of a joint?
-Flexion is the movement that decreases the angle of a joint, such as bending the elbow. Extension is the opposite movement that increases the angle of a joint, such as straightening the elbow.
What are the origins and insertions of a muscle?
-The origin of a muscle is the bone to which the muscle attaches and does not move, while the insertion is the bone that moves when the muscle contracts.
What are isometric and isotonic contractions?
-Isometric contractions occur when a muscle contracts but there is no movement, such as trying to lift a heavy object that doesn't move. Isotonic contractions involve movement with consistent force, like lifting a book with your bicep.
Which muscle is responsible for flexing the elbow joint, and what is its antagonist?
-The biceps brachii is responsible for flexing the elbow joint, and its antagonist is the triceps brachii, which extends the elbow joint.
What is the primary function of the deltoids and their antagonist muscles?
-The primary function of the deltoids is to abduct the arm or move it away from the body. The antagonist muscles are the pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi, which work together to adduct the arm and bring it back to the midline.
What is the action of the rectus abdominis muscle and its location?
-The rectus abdominis muscle is responsible for bending the spine, such as during a sit-up, and is located in the abdominal area, commonly known as the 'six-pack' or 'abs'.
What muscles are primarily responsible for the extension and flexion of the hip joint?
-The gluteus maximus is responsible for extending the hip joint, while the iliopsoas muscle is the antagonist that flexes or bends the hip joint.
What are the functions of the gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior muscles in relation to the ankle joint?
-The gastrocnemius is responsible for plantar flexion of the ankle joint, pulling the heel up, while the tibialis anterior is responsible for dorsiflexion, pulling the foot upward.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
The Muscular System Explained In Less Than 4 Minutes!

"How the Human Musculoskeletal System Works | Bones, Muscles & Movement Explained"

Movement in humans skeleton, muscle, joints

Muscle Tissue | Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth

Rangkuman IPAS KELAS 6 BAB 1: Bagaimana Tubuh Kita Bergerak?. Topik A: Rangka, sendi, dan otot
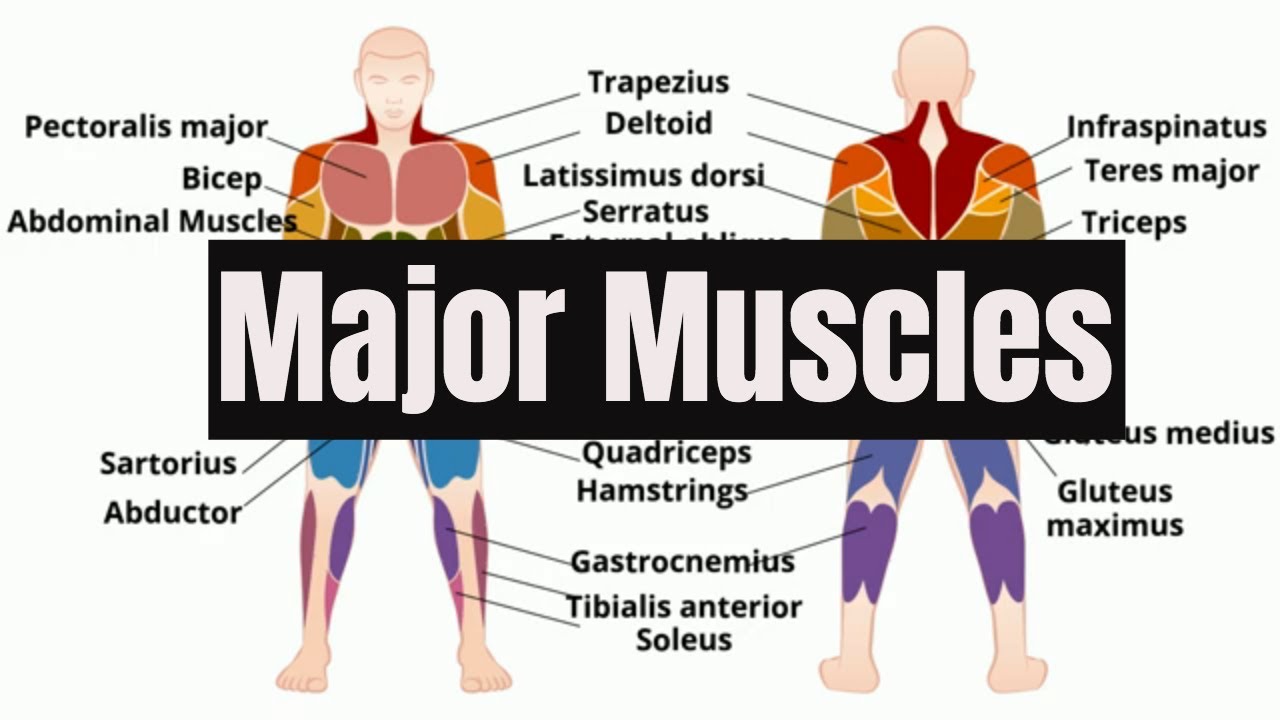
Major Muscles of the Human Body
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
