MMC - MÍNIMO MÚLTIPLO COMUM
Summary
TLDRIn this tutorial, Gis explains how to calculate the Least Common Multiple (LCM) using two methods: the conventional and the practical approach. She begins by illustrating the conventional method, where students calculate multiples of the numbers involved and identify the smallest common one. Gis then introduces the faster, practical process, using prime factorization to find the LCM more efficiently. With examples of LCM calculation for both two and three numbers, she emphasizes the importance of multiplication tables and understanding prime numbers. Gis encourages viewers to learn the concepts thoroughly for a smoother experience with LCM calculations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Learning about Least Common Multiple (LMC) or MMC: It is the smallest common multiple between at least two numbers.
- 😀 The script introduces two methods to calculate MMC: the conventional method and the practical method.
- 😀 The conventional method involves listing the multiples of both numbers until a common multiple is found, then selecting the smallest one.
- 😀 The practical method involves using prime numbers to decompose the numbers and find the MMC quickly.
- 😀 To use the conventional method effectively, it’s important to be familiar with multiplication tables and multiples.
- 😀 The MMC of 8 and 12 was calculated through both methods, with the result being 24.
- 😀 In the conventional method, multiples of 8 and 12 were listed, and the first repeated multiple (24) was identified as the MMC.
- 😀 The practical method requires knowledge of prime numbers and decomposing numbers step by step using division.
- 😀 Prime number decomposition is key to the practical method, and you can choose which prime number to start with, though the order doesn’t affect the result.
- 😀 The video also demonstrated the MMC calculation for 9, 15, and 18 using both methods, with the result being 90 in the practical method.
- 😀 The practical method allows for faster MMC calculation compared to listing multiples, making it a more efficient approach once prime number decomposition is understood.
Q & A
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM)?
-The Least Common Multiple (LCM) is the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. It is also known as the Mínimo Múltiplo Comum (MMC) in Portuguese.
What are the two methods for calculating the LCM explained in the video?
-The two methods explained in the video are the conventional method (listing multiples) and the practical method (using prime factorization).
How does the conventional method work for finding the LCM?
-In the conventional method, you list the multiples of each number and find the smallest number that appears in both lists. This smallest common multiple (other than 0) is the LCM.
What is the LCM of 8 and 12 using the conventional method?
-The LCM of 8 and 12 is 24, which is the smallest common multiple found in both sets of multiples.
Why is 0 excluded when calculating the LCM?
-Zero is excluded from the calculation because it would be a common multiple for any number, making it an invalid result for LCM. The LCM must be the smallest positive multiple.
What is the advantage of the practical method for calculating the LCM?
-The practical method is faster and more efficient as it uses prime factorization to find the LCM without having to list out all multiples.
What is the first step in the practical method for calculating the LCM?
-The first step is to write the numbers you want to find the LCM for and then divide them by the smallest prime number (usually 2) that divides at least one of the numbers.
What do you do after dividing the numbers by the prime number in the practical method?
-After dividing, you continue to divide by the next smallest prime number that divides at least one of the results until all numbers are reduced to 1.
How do you find the LCM once you have completed the prime factorization?
-To find the LCM, multiply all the prime factors together, taking each factor the greatest number of times it occurs in any of the numbers' factorizations.
Can the order of prime factorization affect the LCM result?
-No, the order of prime factorization does not affect the result. The LCM will be the same regardless of the order in which you divide the numbers by prime numbers.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

C programming Bangla Tutorial 5.106 : GCD(গসাগু) ও LCM(লসাগু) নির্ণয়ের জন্য Algorithm, Flowchart, C
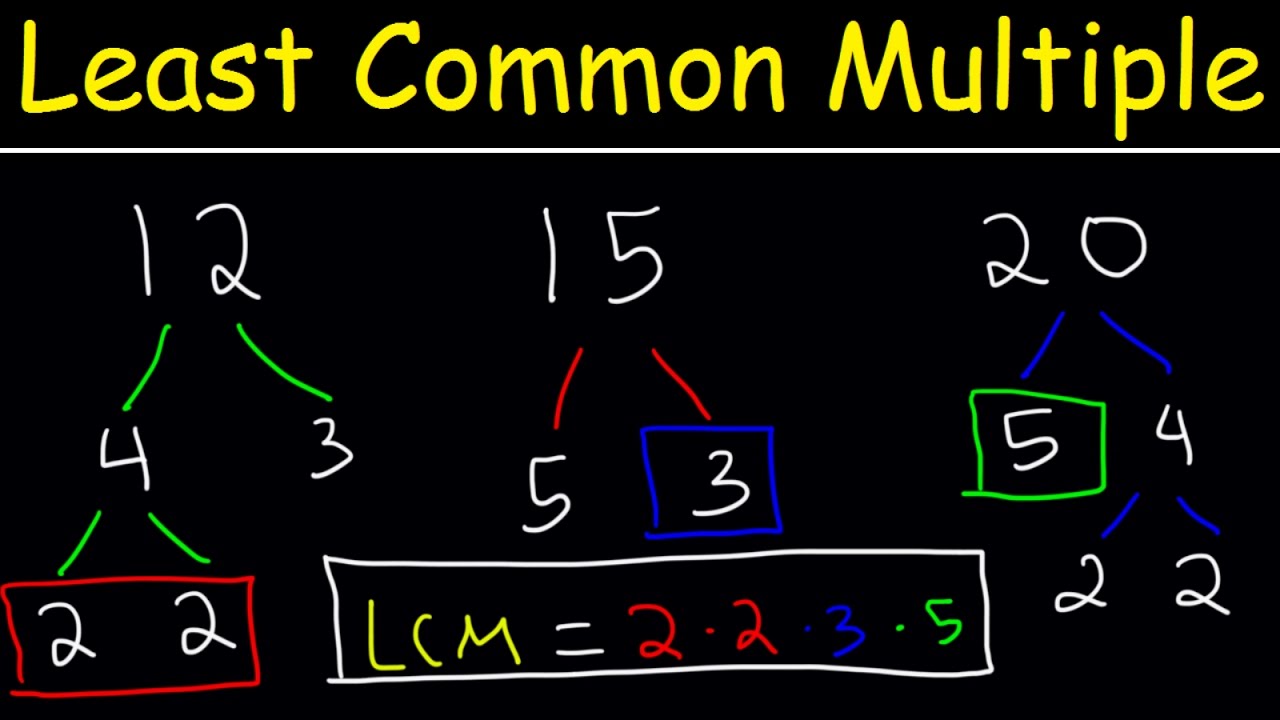
How To Find The LCM of 3 Numbers - Plenty of Examples!

NÃO ERRE MAIS MATEMÁTICA! TODO CONCURSEIRO DEVE SABER. PARTE 1 DE 2. PASSO A PASSO.
How to Find the LCM (2 Different Ways) | Least Common Multiple | Math with Mr. J

minimo comune multiplo (mcm) e Massimo Comun Divisore (MCD): come calcolarli senza confonderli

VIDEO TATA CARA PENGGUNAAN CONGKLAK KPK & FPB
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
