Urinary System | Structure, Function, Plastinated Kidney and Bladder, 3D Model
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the anatomy and physiology of the urinary system, highlighting the kidneys' vital role in filtering blood and regulating key functions like blood pressure, volume, and pH. The script explains the journey of blood entering and leaving the kidneys, the formation of urine, and its passage through the ureters to the bladder. It also covers the role of nephrons in blood filtration and the bladder's function as a storage site for urine. The video provides a detailed look at these processes, breaking them down in an easy-to-understand way for viewers.
Takeaways
- 😀 The urinary system plays a crucial role in regulating fluid balance, blood pressure, blood volume, blood pH, and eliminating waste.
- 😀 The kidneys are the main organs responsible for filtering blood and producing urine to help maintain healthy homeostasis in the body.
- 😀 Adrenal glands sit on top of the kidneys, and although they are not part of the urinary system, they regulate hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
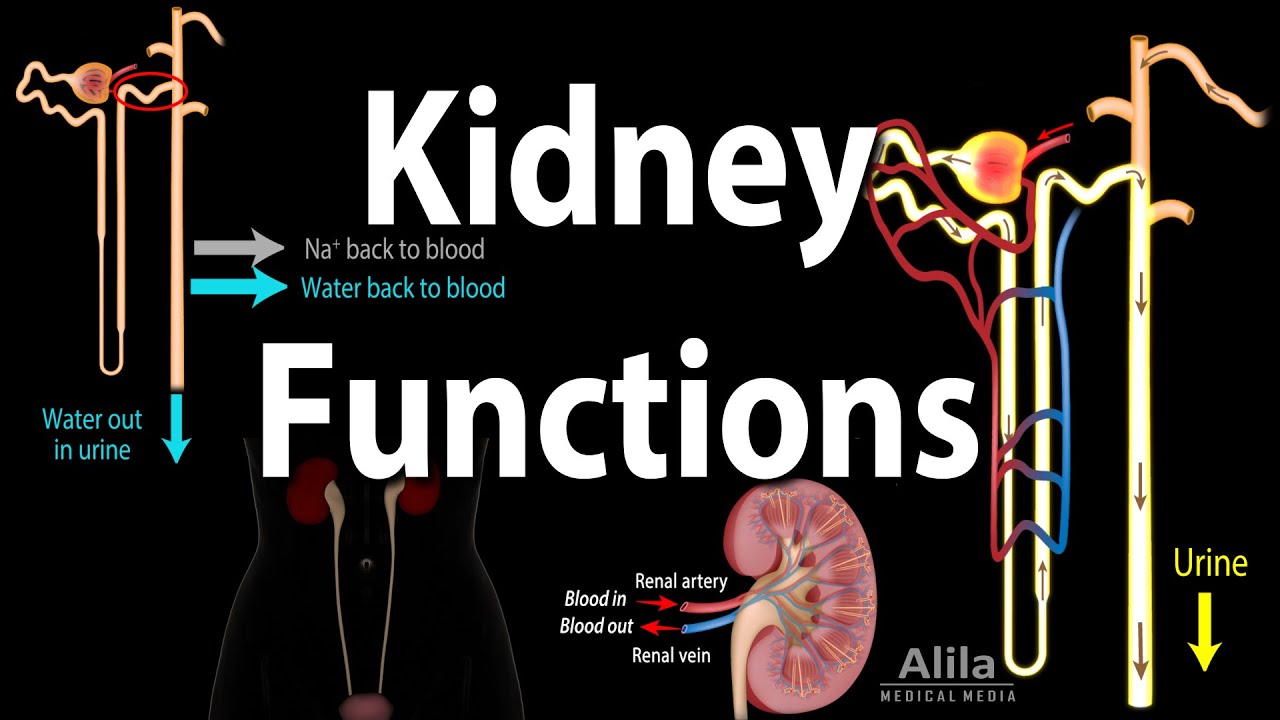
- 😀 Blood enters the kidneys through the renal arteries, which branch from the descending aorta, and leaves through the renal veins back to the heart.
- 😀 The kidneys are composed of the renal cortex (outer part) and renal medulla (inner part), with the nephrons inside the medulla being responsible for filtration.
- 😀 The filtration process happens in the renal pyramids within the renal medulla, where blood is filtered by nephrons and waste becomes urine.
- 😀 The filtered urine travels from the kidneys to the bladder through the ureters, which are tubes that connect each kidney to the bladder.
- 😀 The bladder stores urine until it's ready to be expelled from the body, with a stretchy structure that allows it to expand.
- 😀 The urethra is the tube that transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. In males, it passes through the prostate gland before exiting.
- 😀 Urination is controlled by two sphincters: the internal urethral sphincter (involuntary) and the external urethral sphincter (voluntary).
- 😀 The renal system involves a continuous cycle of blood flow into and out of the kidneys, where filtration occurs, and waste is expelled through urine.
Q & A
What is the main role of the urinary system?
-The urinary system plays a crucial role in regulating fluid balance in the body, maintaining blood pressure and blood volume, regulating the pH of the blood, and eliminating waste from the body.
What are the main functions of the kidneys?
-The kidneys filter the blood to regulate blood pressure, blood volume, pH, and ion balance, while also removing waste products from the bloodstream. The kidneys produce urine, which is essential for these processes.
What is the role of the adrenal glands in relation to the kidneys?
-The adrenal glands are located above the kidneys and are part of the endocrine system. They are not part of the urinary system but play a role in regulating the body's stress response through the production of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
What is the meaning of the term 'renal'?
-'Renal' is derived from Latin and means 'kidney.' It is used in terms like renal artery, renal veins, and renal cortex to refer to anything related to the kidneys.
How does blood flow through the kidneys for filtration?
-Blood flows from the heart through the descending aorta and enters the kidneys via the renal arteries. Once in the kidneys, it travels through smaller branches and reaches the renal cortex and medulla, where it is filtered by nephrons.
What is the role of the renal veins in the circulatory process?
-The renal veins carry filtered blood, which has been cleaned of waste, away from the kidneys and back to the inferior vena cava, which then transports it back to the heart.
What are ureters and what is their function?
-Ureters are tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Each kidney has its own ureter that carries the filtered urine.
What is the structure of the kidney and how is it organized?
-The kidney consists of two main regions: the renal cortex (outer layer) and the renal medulla (inner region). The medulla contains renal pyramids and nephrons, which are responsible for filtering the blood. The urine then passes through the calyxes and ureters to be excreted.
How does urine exit the bladder?
-Urine exits the bladder through the urethra. In females, the urethra exits through the vulva, and in males, it passes through the penis.
What are the internal and external urethral sphincters, and how do they function?
-The internal urethral sphincter is an involuntary muscle that is always closed to control urine retention, while the external urethral sphincter is voluntarily controlled, allowing individuals to hold in urine until they are ready to release it.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)