Biologi Bab sistem ekskresi - sistem ekskresi pada ginjal dan pembentukan urine kelas 11 ipa
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the excretory system in humans, focusing on the kidneys' role in urine formation. It covers the structure of the kidneys, including their layers and the nephrons responsible for filtering blood. The process of urine formation is divided into three stages: filtration, reabsorption, and augmentation. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus, followed by the reabsorption of essential substances like glucose and amino acids in the proximal tubules. Augmentation ensures that necessary ions are reabsorbed in the distal tubules. The final urine flows into the pelvis, then the bladder, and is expelled from the body through the urethra. The video concludes with a reminder to subscribe for more educational content.
Takeaways
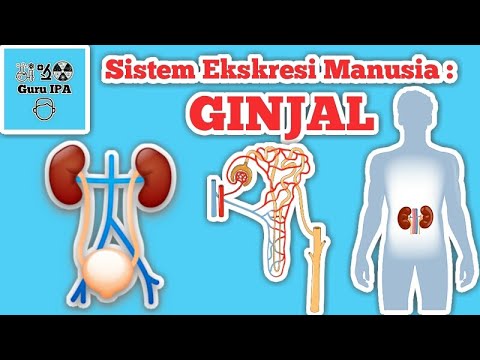
- 😀 The kidneys are located in the lower back region of the body and are responsible for filtering blood and forming urine.
- 😀 The kidneys consist of three main layers: the outer cortex, the inner medulla, and the renal pelvis, which stores urine before it is excreted.
- 😀 Each kidney contains about one million nephrons, the functional units responsible for blood filtration.
- 😀 The glomerulus, a group of capillaries within the Bowman's capsule, is where blood filtration begins.
- 😀 Filtration, the first step in urine formation, occurs when blood pressure forces water and small molecules out of the blood into the nephrons.
- 😀 The filtrate produced during filtration consists of substances like urea, glucose, amino acids, and ions such as sodium and potassium.
- 😀 Reabsorption is the second step where useful substances such as glucose, amino acids, and essential ions are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream from the filtrate.
- 😀 Urine formed after reabsorption is called secondary urine, which contains urea, water, salts, and urobilin.
- 😀 The next step, augmentation, involves further reabsorption of water, sodium, chloride, and urea in the distal tubules of the nephron.
- 😀 Finally, the urine, now concentrated and ready for excretion, flows into the renal pelvis, then through the ureter to the bladder, where it is stored until expelled through the urethra.
Q & A
What are the main layers of the kidney?
-The main layers of the kidney are the cortex (outer layer), medulla (middle layer), and pelvis (inner part that collects urine).
Where are the kidneys located in the body?
-The kidneys are located in the abdominal cavity on both sides of the body, near the lower back, with the left kidney positioned higher than the right.
What is the function of the nephron in the kidney?
-The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering blood, reabsorbing useful substances, and forming urine.
What is the role of the glomerulus in the filtration process?
-The glomerulus is a cluster of capillaries that filters the blood, allowing small molecules such as water, urea, and glucose to pass into the nephron.
What substances are found in the primary urine after filtration?
-Primary urine consists of water, urea, glucose, amino acids, and ions such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride.
What happens during the reabsorption process in the kidney?
-During reabsorption, useful substances such as glucose, amino acids, and certain ions are reabsorbed back into the blood from the filtrate, while waste products remain in the tubules.
How does the structure of the kidney aid in urine formation?
-The structure of the kidney, including the nephron, glomerulus, and renal tubules, allows for effective filtration of blood, reabsorption of essential substances, and formation of concentrated urine.
What is the role of the Henle loop in urine formation?
-The Henle loop is responsible for further reabsorbing water from the urine, concentrating the urine before it moves to the distal tubule.
How is urine stored and expelled from the body?
-Urine is stored in the bladder, which has an elastic wall that can expand. Once the bladder is full, signals trigger muscle contractions that push urine out of the body through the urethra.
What are the three main stages of urine formation?
-The three main stages of urine formation are filtration, reabsorption, and augmentation.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)